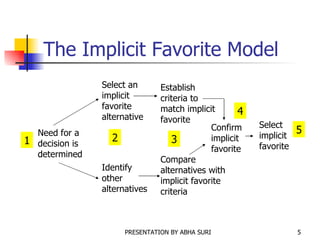
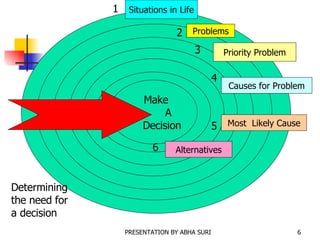
There are three main models for decision making: the satisficing model which selects the first alternative that meets the minimum criteria, the implicit favorite model which selects a pre-determined implicit favorite, and the maximizing model which identifies alternatives, weighs criteria, evaluates options, and selects the optimal choice. Group decision making techniques include brainstorming, nominal groups, Delphi method, and electronic meetings. The chapter discusses understanding problems, analyzing facts, and determining a course of action such as corrective, interim, preventive, contingency, or adaptive actions.