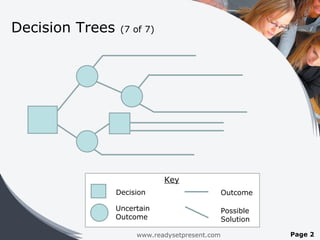
The document outlines various decision-making models with the aims of enhancing creativity, logic, and awareness of common traps in the process. It distinguishes between programmed and nonprogrammed decisions, discusses the importance of risk evaluation, and provides insights on cost/benefit analysis along with methods and factors influencing decisions. Additionally, it mentions the availability of a comprehensive PowerPoint presentation that covers multiple aspects of decision making.