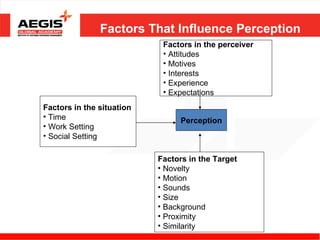
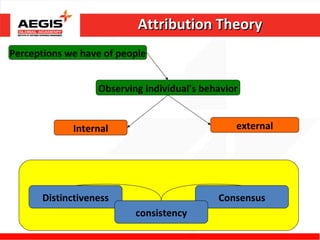
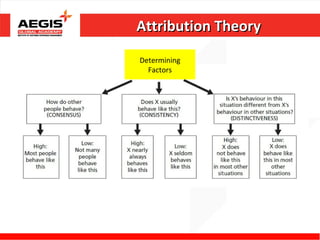
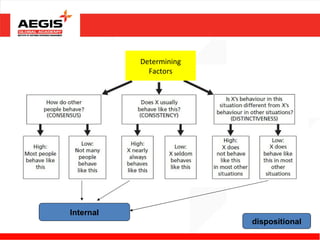
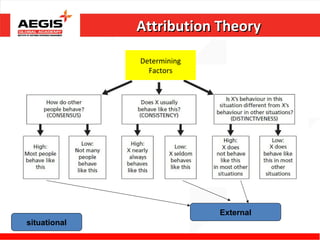
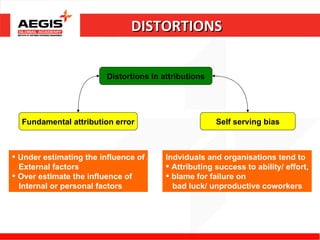
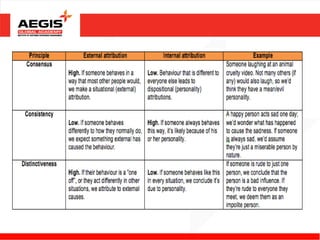
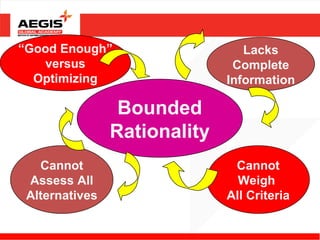
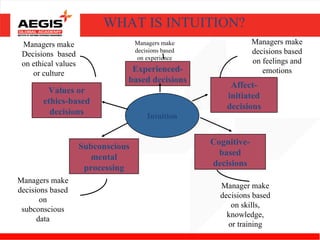
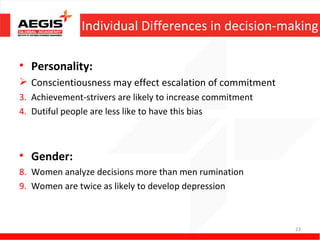
This document discusses various topics related to individual perception and decision making. It covers how perception is influenced by factors in the perceiver, situation, and target. Attribution theory is explained, specifically how people make internal or external attributions about others' behavior. Common biases and shortcuts in judgement like the fundamental attribution error are also reviewed. The rational model of decision making is outlined along with common biases. Individual differences and organizational constraints that can impact decisions are described. Three ethical decision making criteria and the importance of creativity to decision making are also summarized.