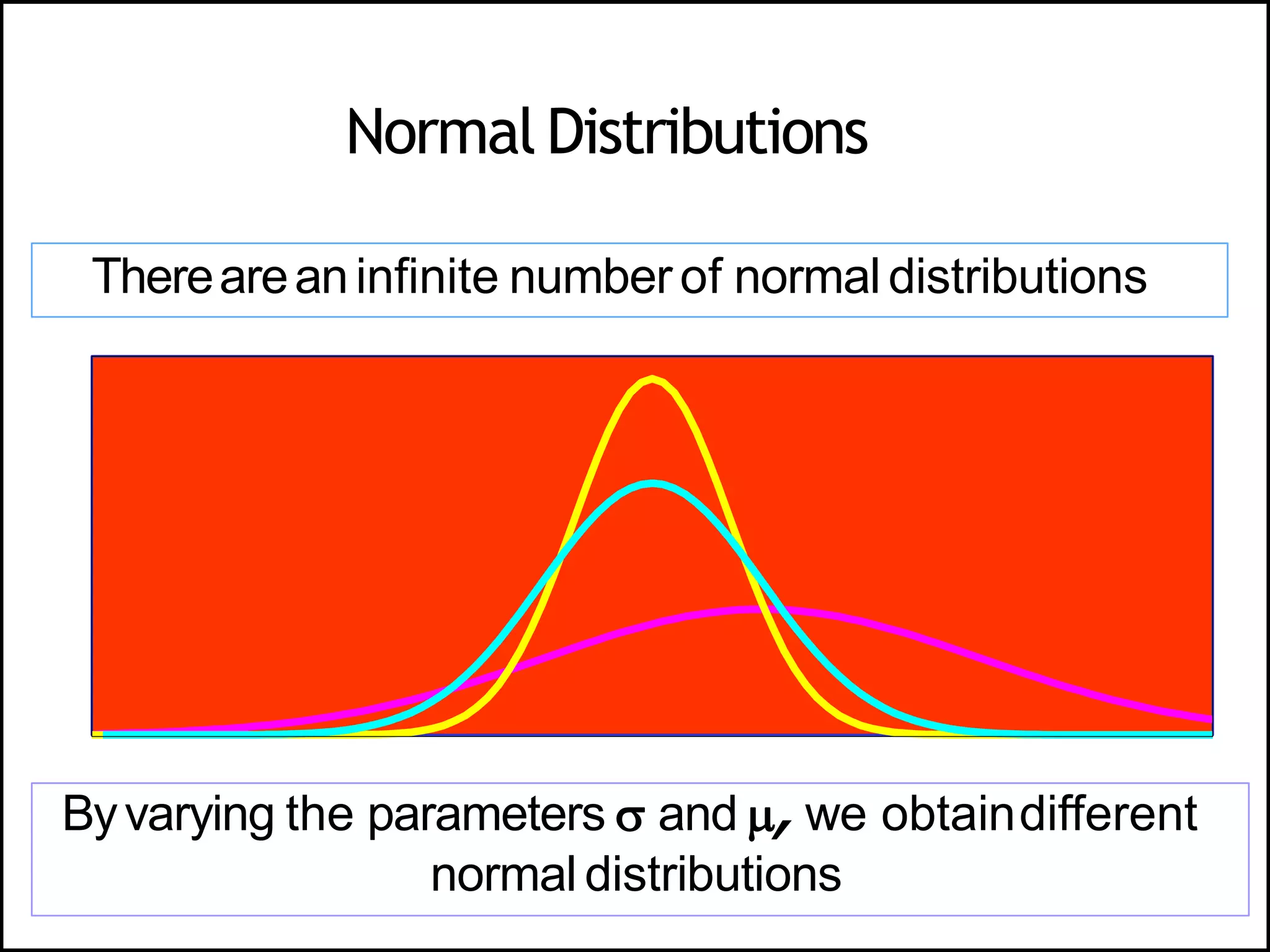
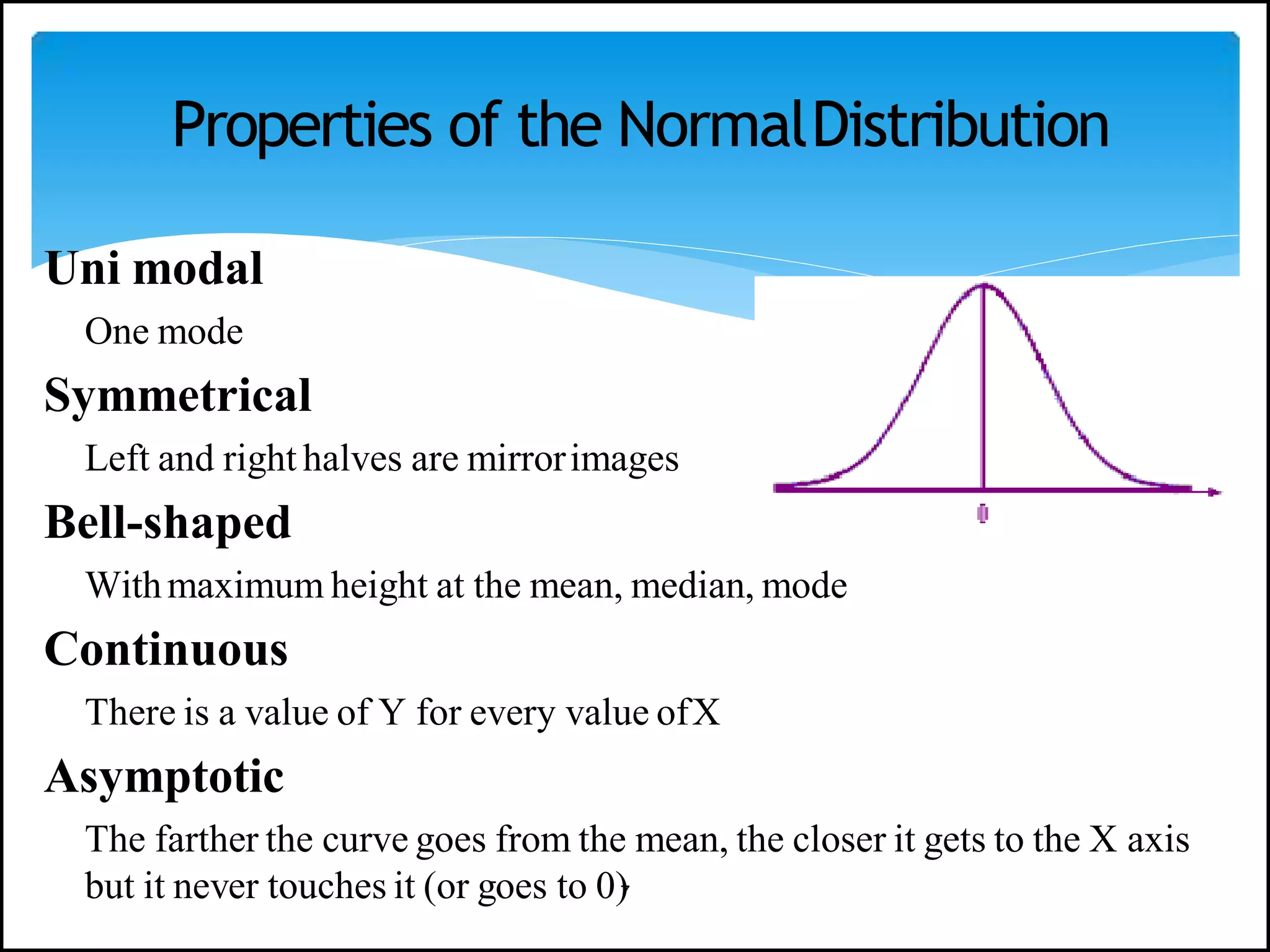
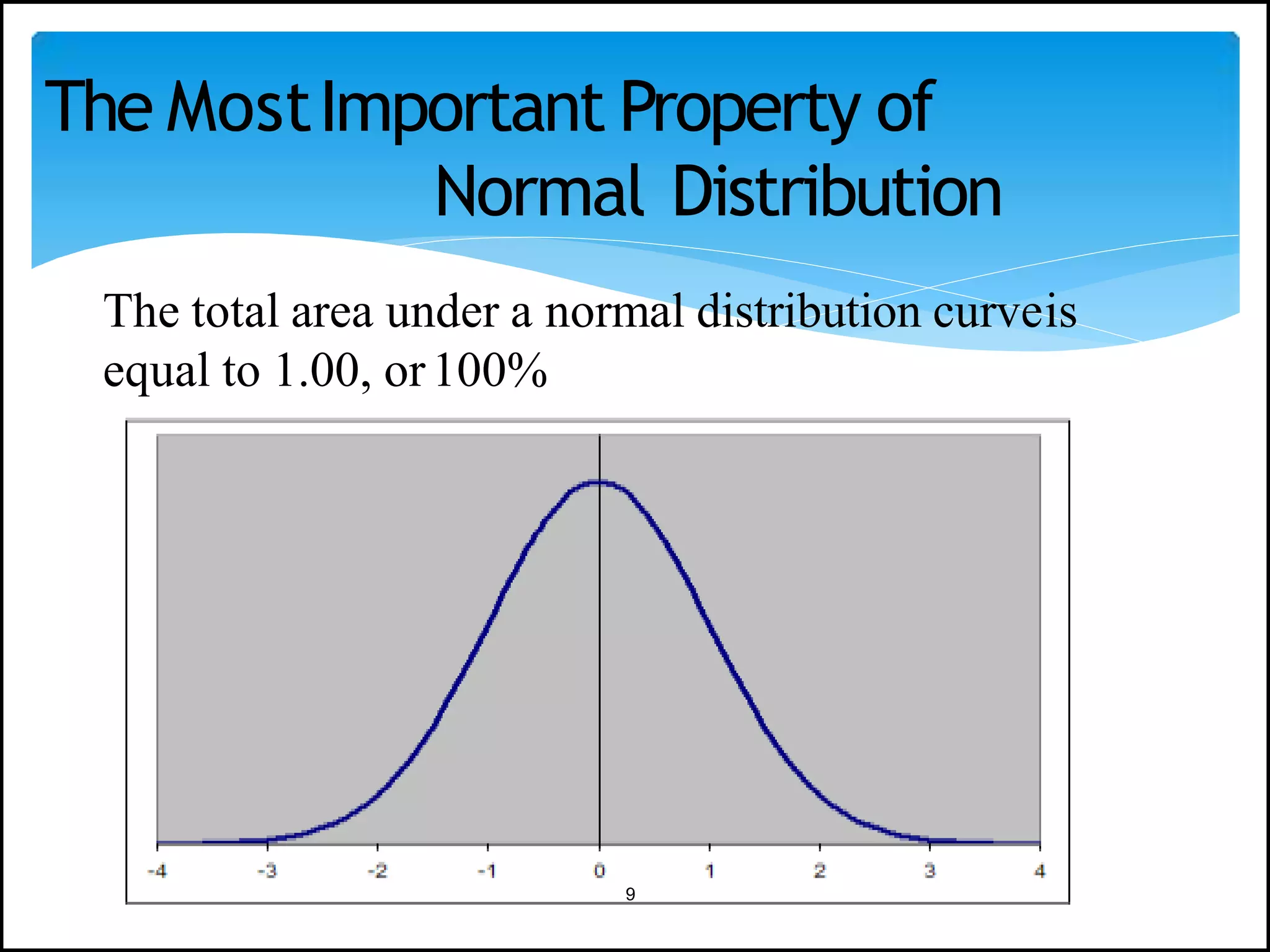
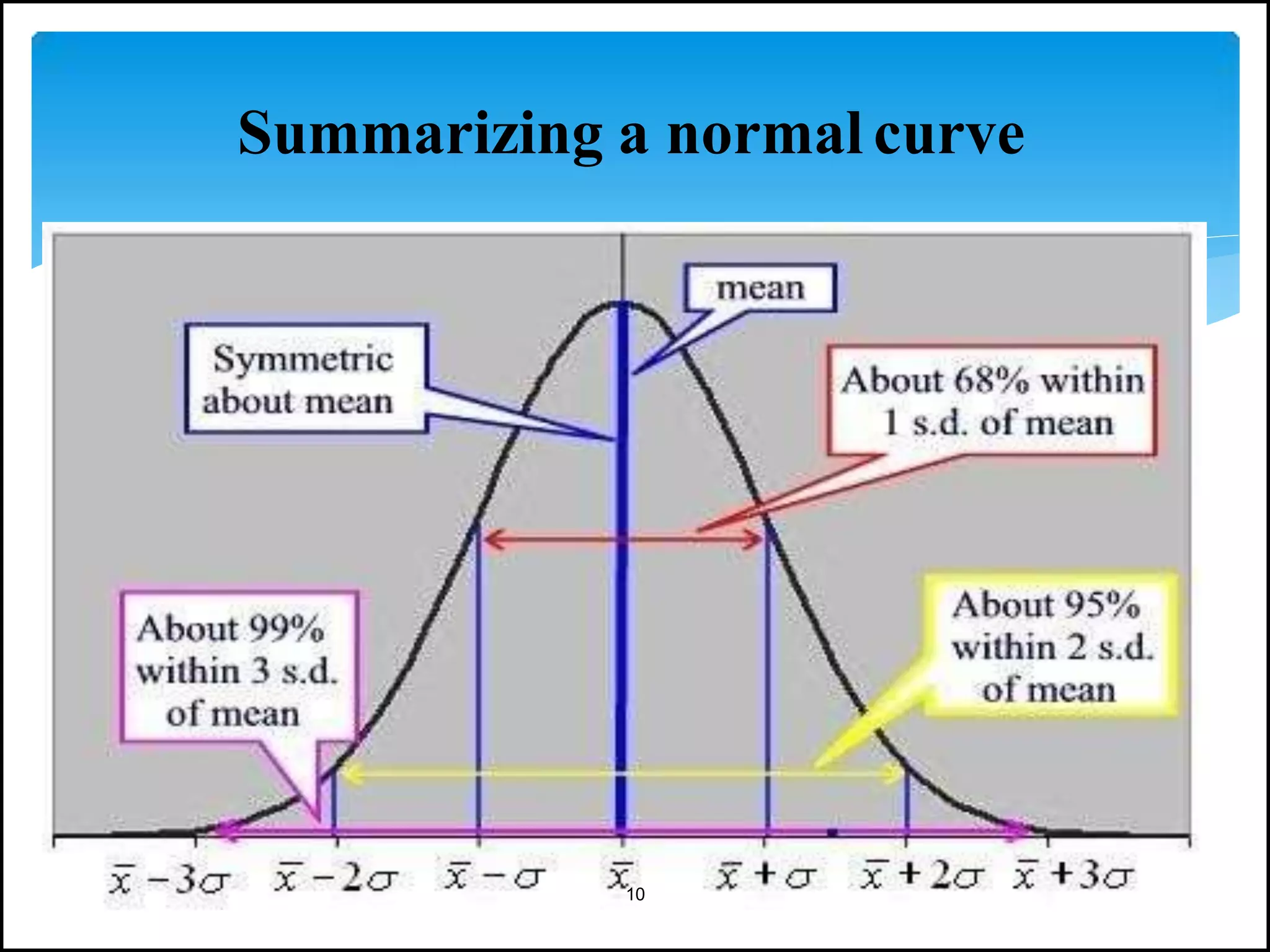
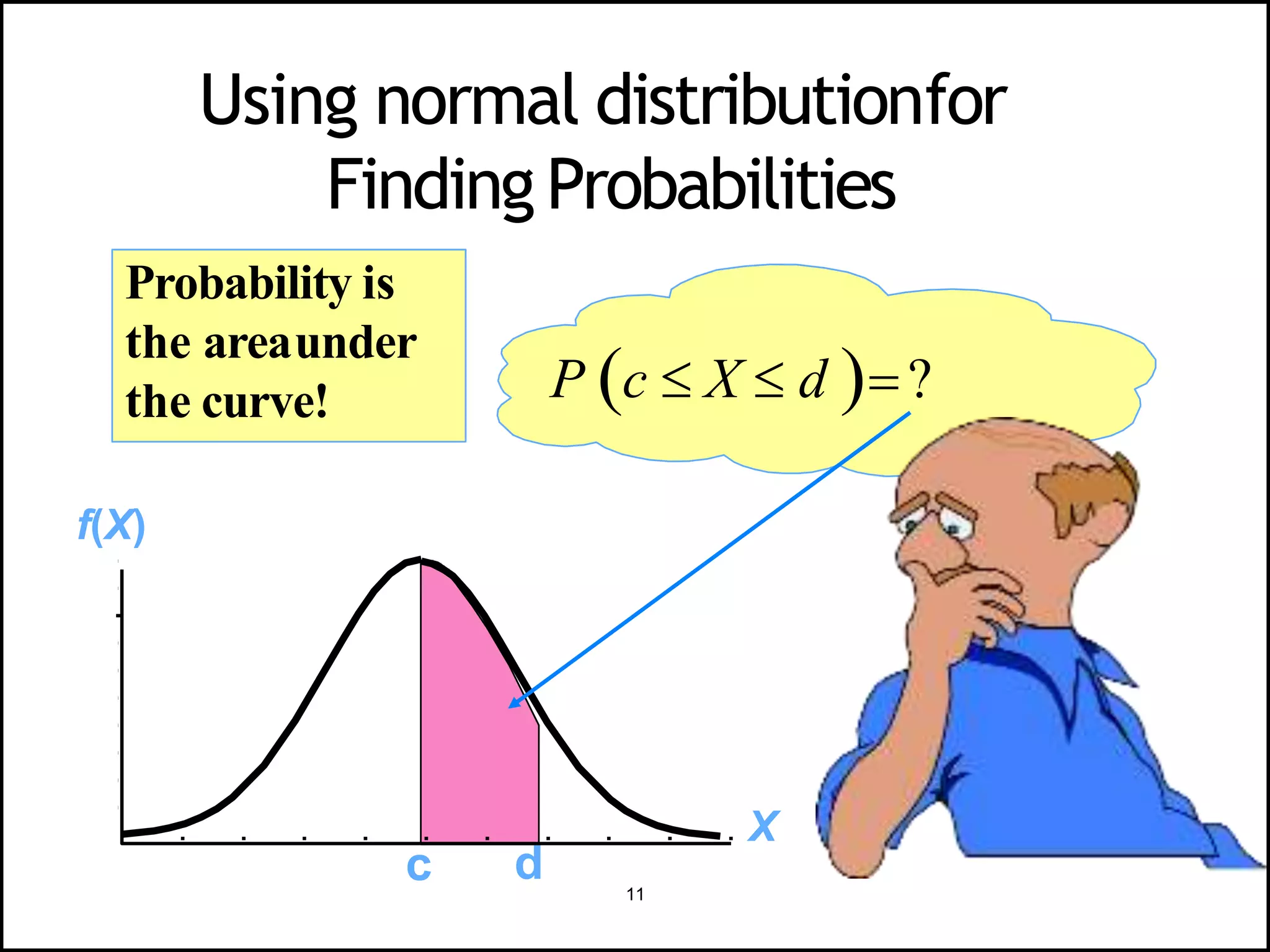
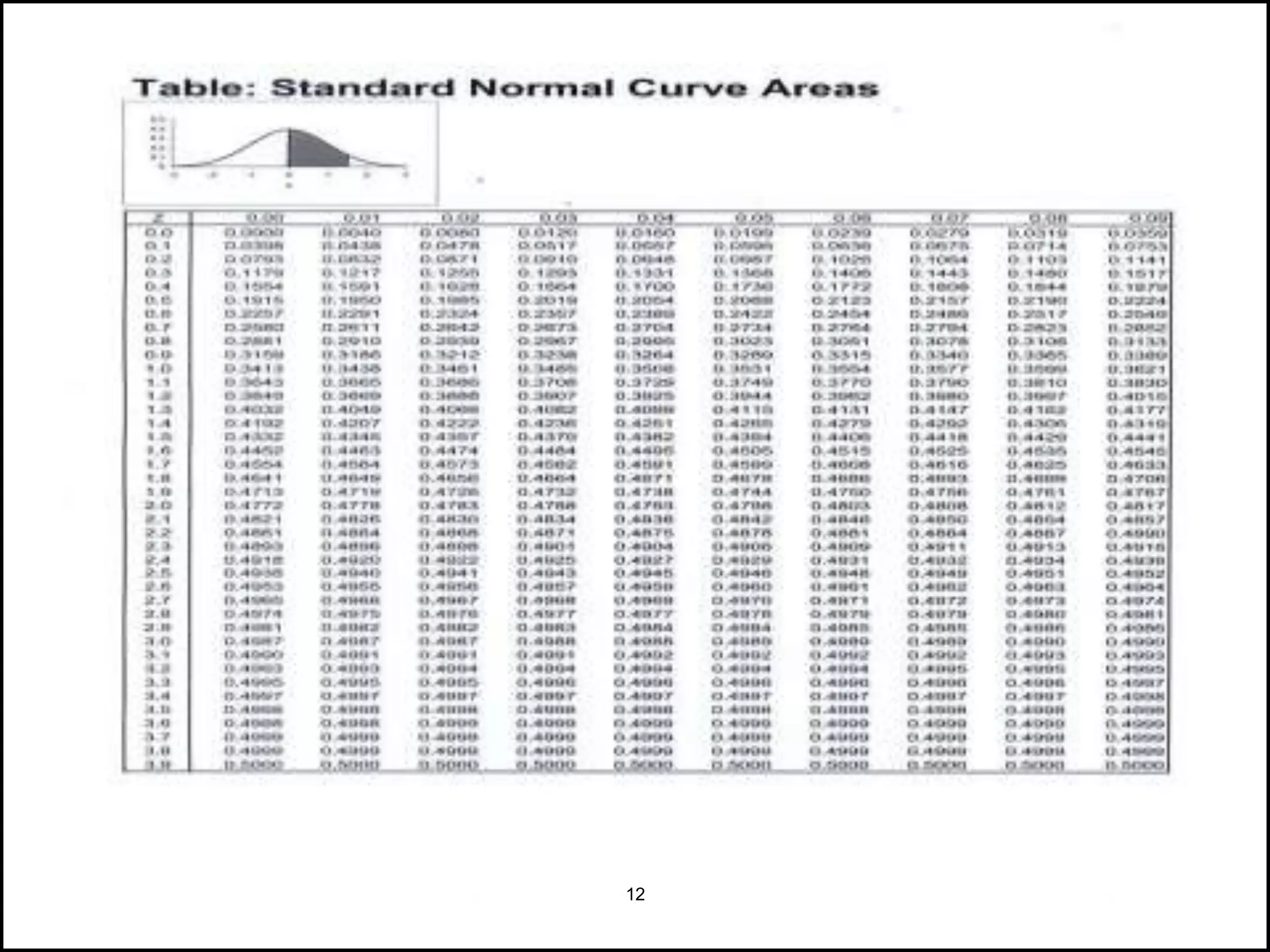
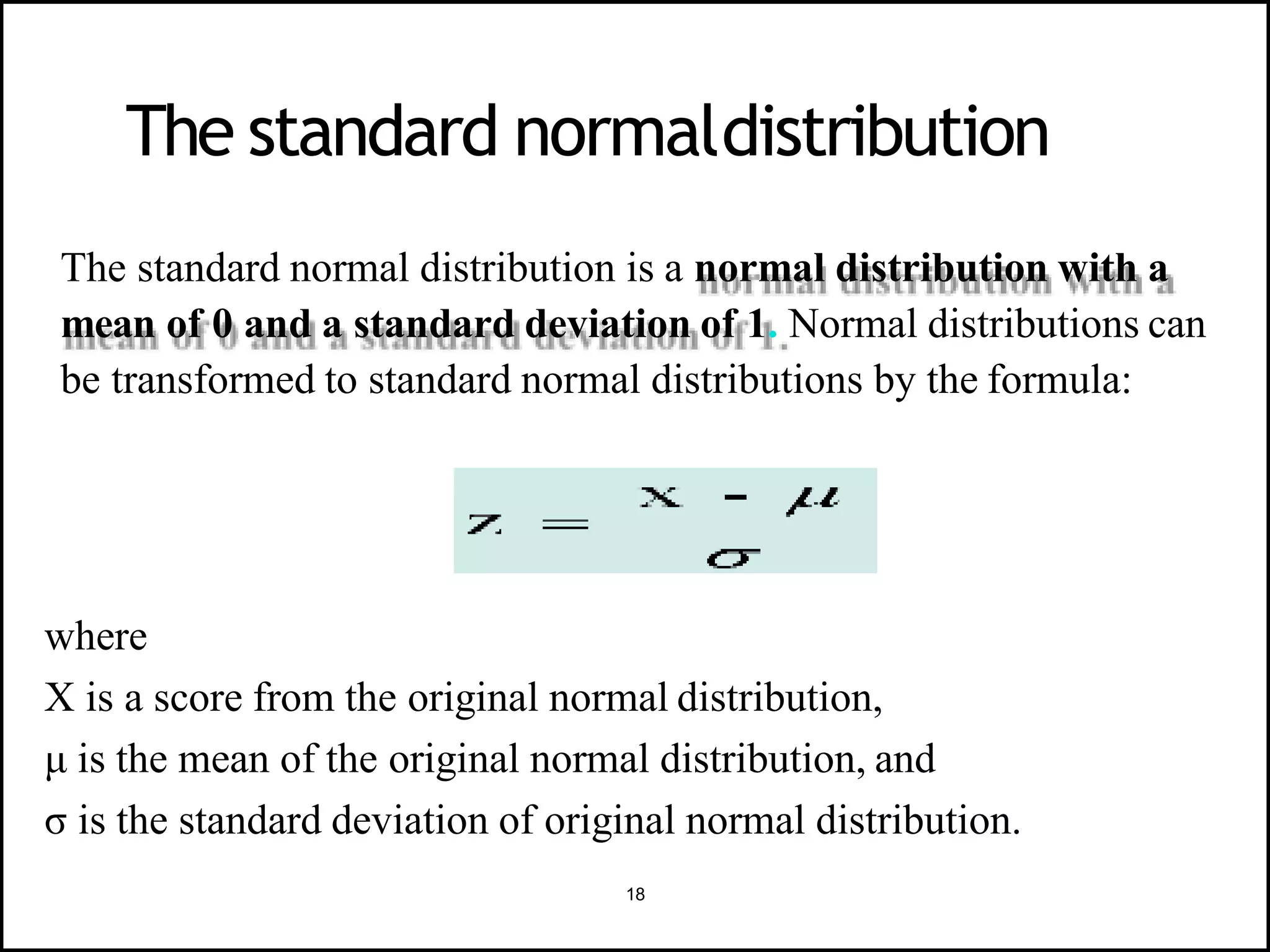
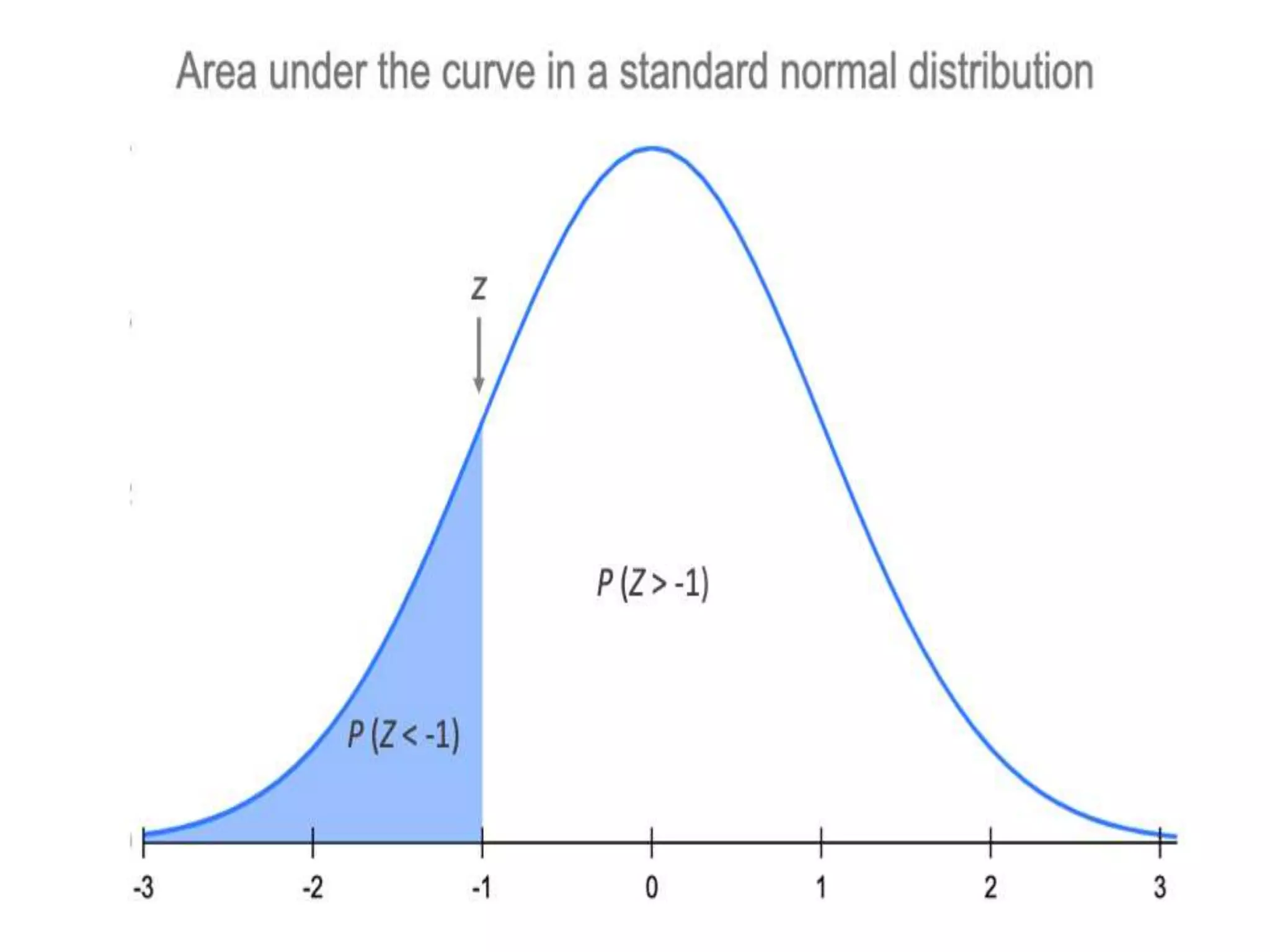
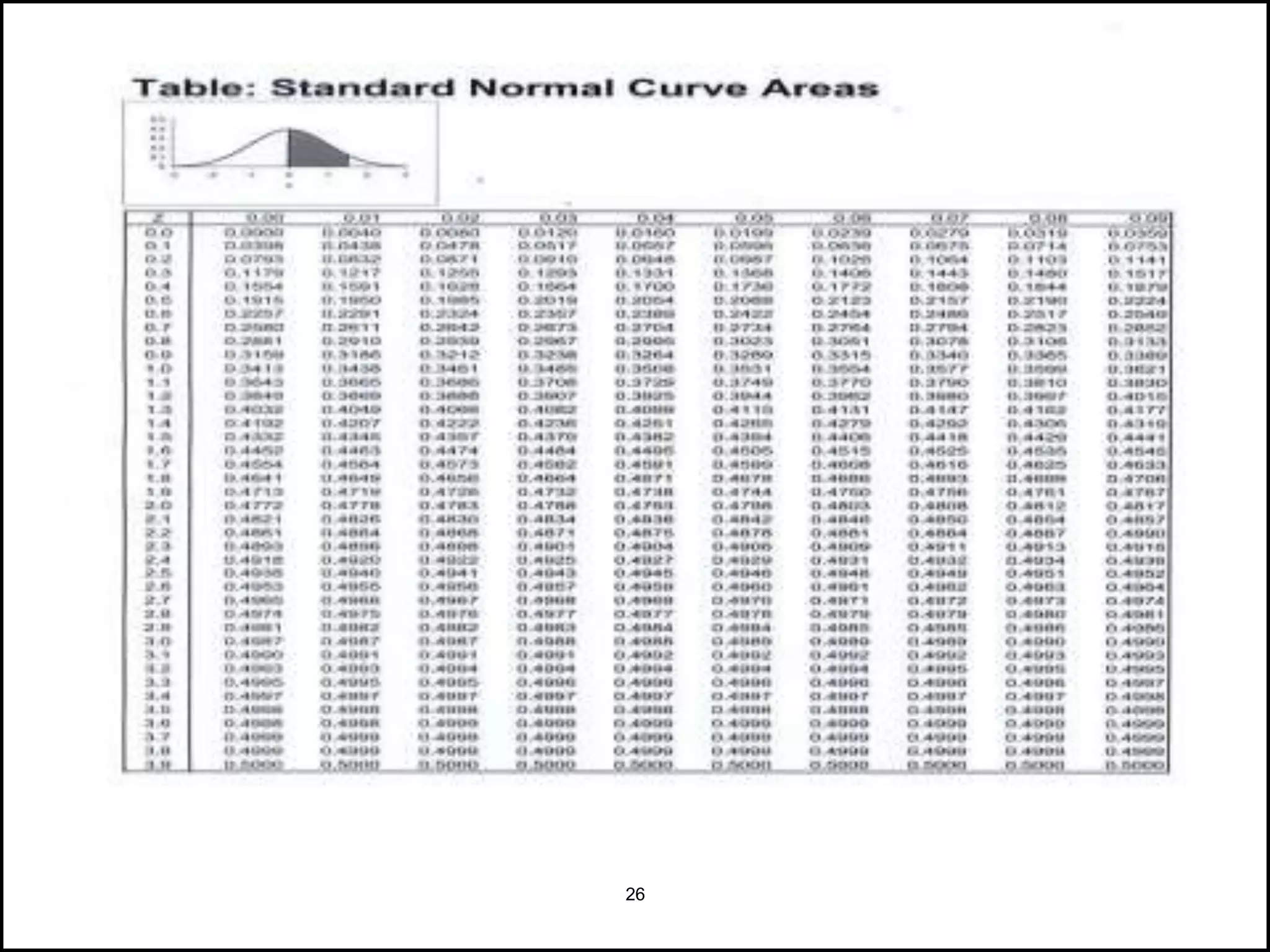
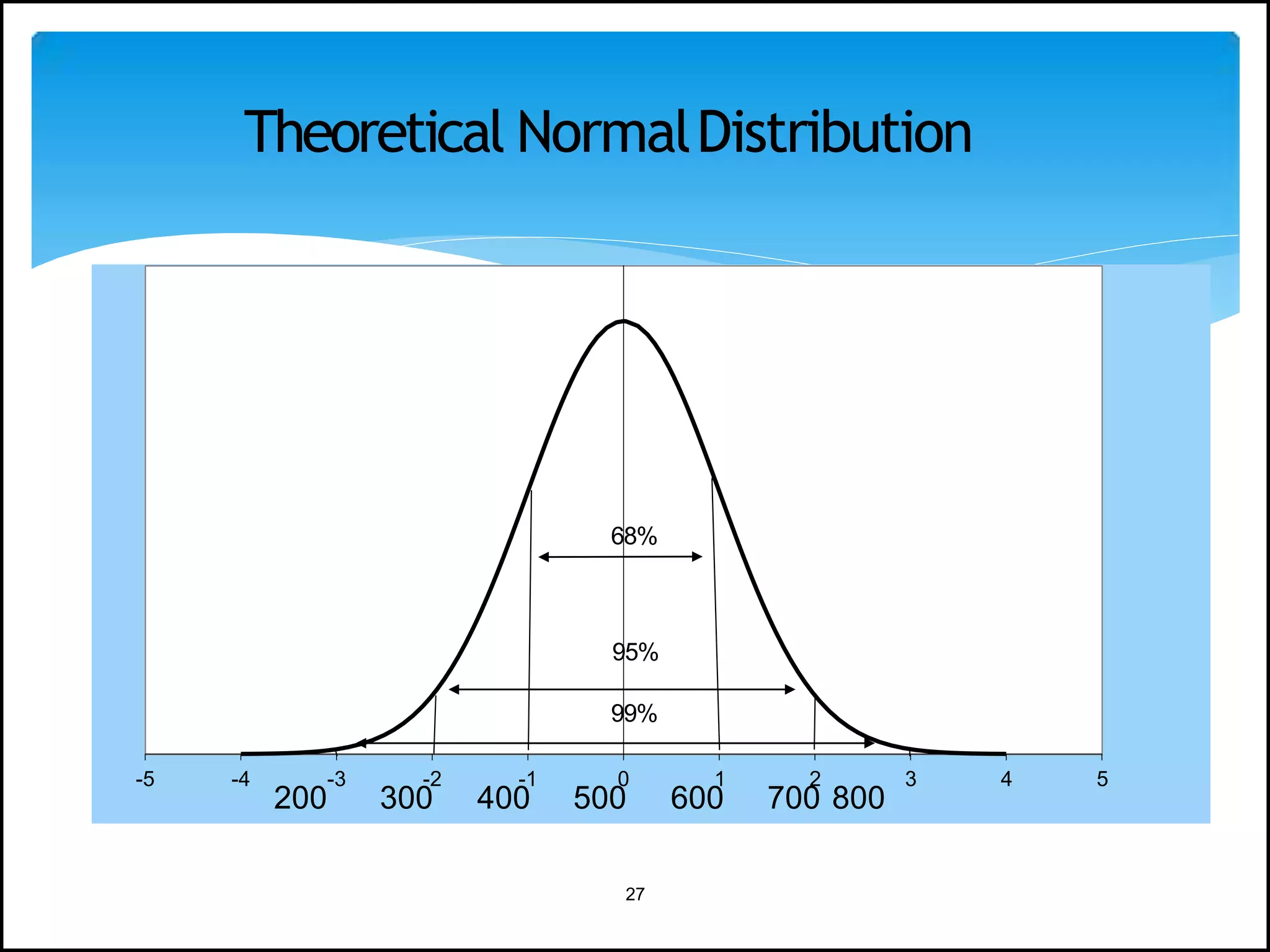
The document discusses the normal distribution in statistics, highlighting its properties, uses in biostatistics, and the transformation to standard normal distribution via z-scores. It explains the symmetrical, bell-shaped nature of normal distributions, where mean, median, and mode are equal, and how probabilities are calculated using the area under the curve. Examples illustrate how to derive z-scores and interpret probabilities related to specific scores within a normal distribution.