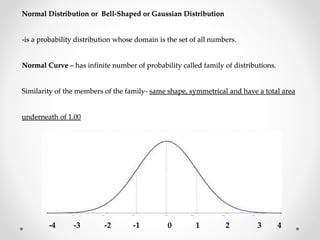
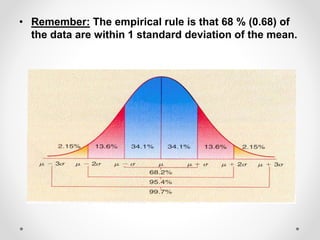
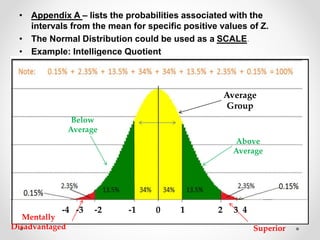
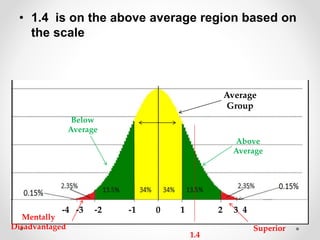
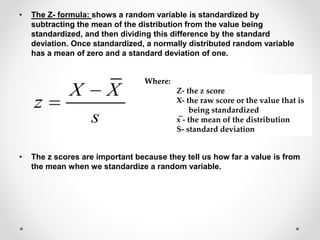
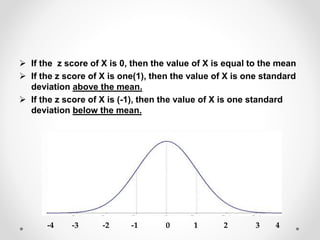
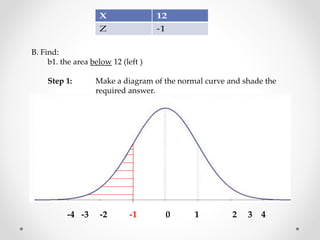
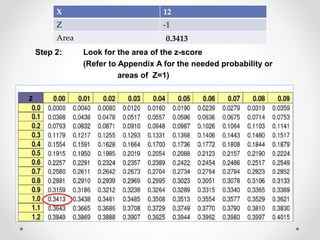
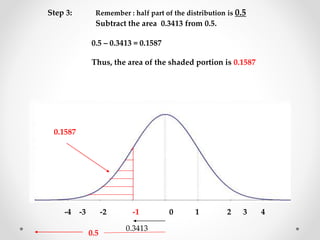
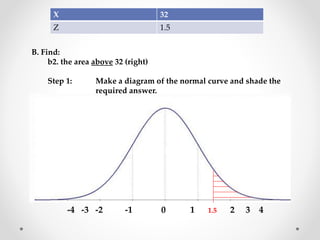
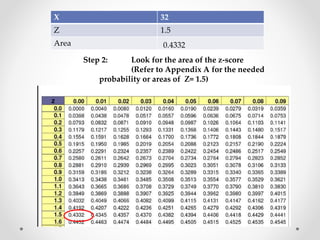
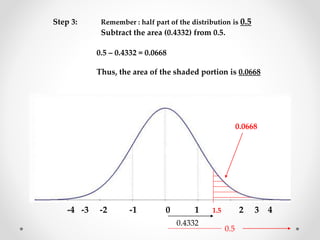
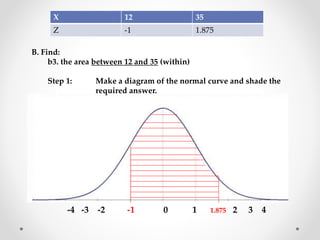
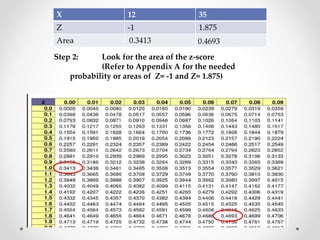
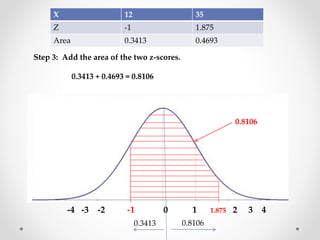
The document discusses standard scores and the normal distribution curve. It defines key terms like the normal curve, z-scores, mean, and standard deviation. It also provides examples of how to convert raw scores to z-scores and find the probability of scores relative to the mean using the normal curve. Areas under the normal curve can be calculated using z-score values from standard normal distribution tables in an appendix.