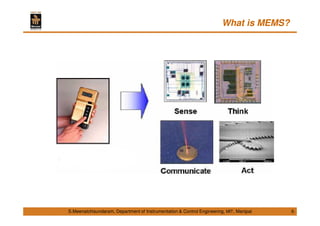
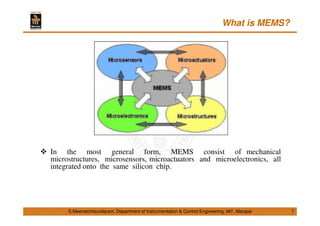
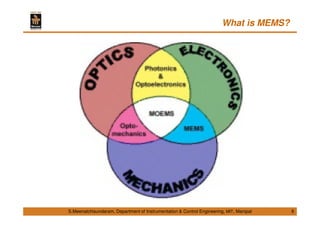
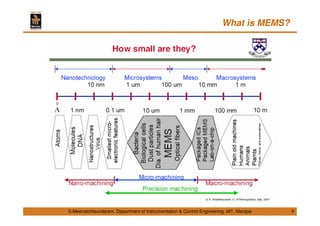
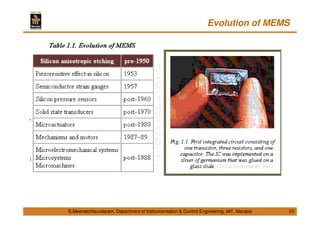
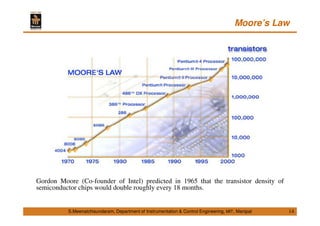
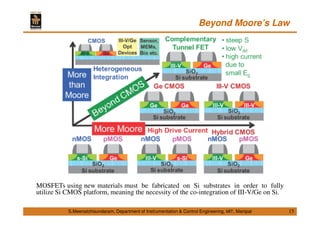
This document discusses Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS). It defines MEMS as the integration of mechanical elements, sensors, actuators and electronics on a common silicon substrate through microfabrication technology. It provides a brief history of MEMS development from the 1950s to present day. It also discusses Moore's Law and the need to go beyond Moore's Law to continue advancing semiconductor chip technology.