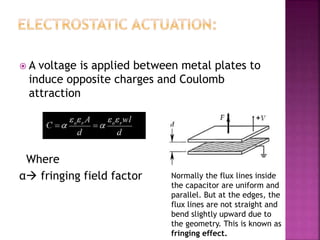
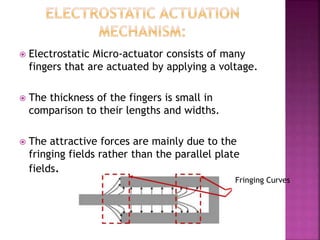
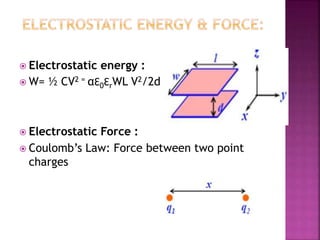
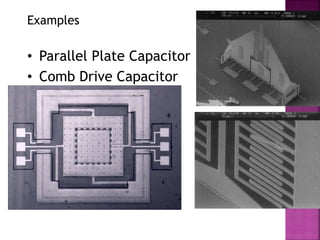
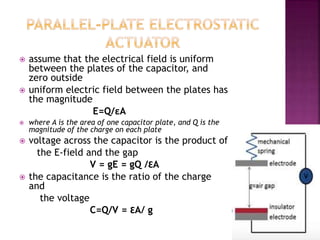
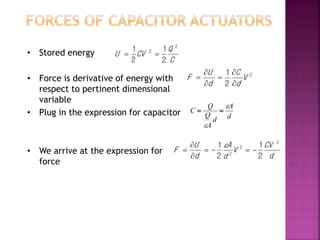
This document discusses microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and electrostatic micro-actuators. It explains that MEMS integrate sensors, actuators and electronics on a silicon substrate using microfabrication technology. Electrostatic micro-actuators consist of thin fingers that are actuated by applying a voltage, generating an attractive electrostatic force due to fringing fields. The document derives equations for the electrostatic energy and force in a parallel plate capacitor model, showing that the force is independent of gap size. It describes the pull-in effect, where the gap decreases until reaching 2/3 of the original spacing, at which point the plates suddenly contact.