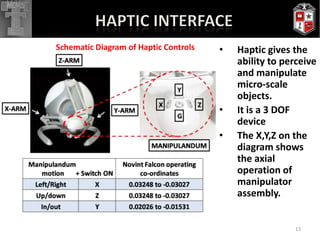
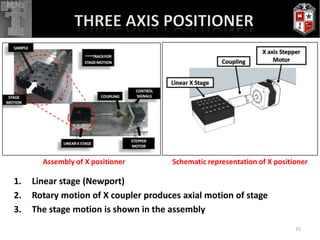
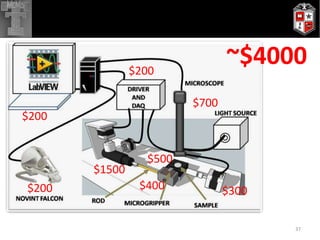
The thesis presents a haptic-controlled MEMS gripper system capable of manipulating micro-scale objects (0-100μm) with sub-micron resolution and meso-scale travel capabilities. It highlights the integration of a high-fidelity three-dimensional force feedback device for precision handling and micro-assembly applications, showcasing experimental results and evidence of successful manipulation of biological cells and microbeads. The developed system achieves travel ranges and high precision that can significantly enhance various micro-manipulation tasks in biological and industrial applications.


![“…You know, in the atomic energy plants they have materials and machines that they can’t handle directly because they have become radioactive. To unscrew nuts and put on bolts and so on, they have a set of master and slave hands, so that by operating a set of levers here, you control the “hands” there, and can turn them this way and that so you can handle things quite nicely.” - Richard Feynmen[1]3motivation[1] There's plenty of room at the bottom, Feynman, R.P.; IEEE JMEMS, vol 1, issue 1, 1992 , pp 60 - 66](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mastersthesispresentation-12877224729247-phpapp01/85/Three-axis-positioning-system-3-320.jpg)
![4objectiveAbility to handle micro-scale objects in the range 0-100µm.Ability to manipulate the micro-objects at sub-micron resolution (~0.5µm) with meso-scale (~25mm) travel.Provide tactile interaction with micro-scale objects (Haptic interface).50 µmZygote [2]Novint Falcon[3][2] Pronuclear Injection – Transgenic mice production, Eppendorf®[3] Image reproduced from Novint® Falcon™, Novint Technologies Inc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mastersthesispresentation-12877224729247-phpapp01/85/Three-axis-positioning-system-4-320.jpg)



![7LITERATURE REVIEWMicromanipulation of micro-objects using electrostatic microgripper and its bio-compatibility was reported by Felix et al.[3].Handling of microbeads aligned in a ultrasonic field [6][3] B. Felix, N. Adrian, O. Stefano, J. B. Dominik, S. Yu, D. Jurg, J. N. Bradley, “Monolithically fabricated microgripper with integrated force sensor for manipulating microobjects and biological cells aligned in an ultrasonic field”, in JMEMS, vol. 16, Iss. 1, 2007, pp. 7-15.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mastersthesispresentation-12877224729247-phpapp01/85/Three-axis-positioning-system-8-320.jpg)
![8LITERATURE REVIEWOur method differs from the work discussed by Trinh Chu et al.[4]. They do not have haptic based control of axial motion and gripper actuation.Handling of glassbeads [4][4] D. Trinh Chu, L. Gih-Keong, J.F. Creemer, P.M. Sarro, “Electrothermal microgripper with large jaw displacement and integrated force sensors”, in JMEMS, vol. 17, Iss. 6, 2008, pp. 1546-1555.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mastersthesispresentation-12877224729247-phpapp01/85/Three-axis-positioning-system-9-320.jpg)
![LITERATURE REVIEWOur method differs from the work discussed by Kim et al.[5] in the electrostatic gripper design by improving compatibility to various biological samples.Handling of He-la cells [5][5] K. Kim, X. Liu, Y. Zhang, Y. Sun, “Micronewton force-controlled manipulation of biomaterials using a monolithic MEMS microgripper with two-axis force feedback” in IEEE Int. conf. on robotics and automation, 2008, pp. 3100-3105.9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mastersthesispresentation-12877224729247-phpapp01/85/Three-axis-positioning-system-10-320.jpg)