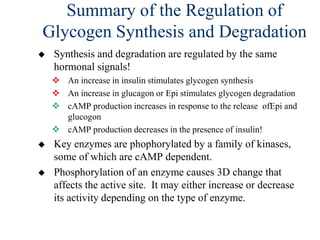
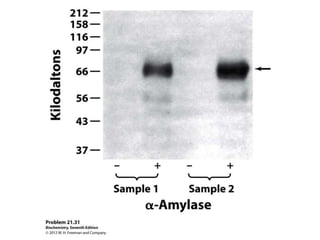
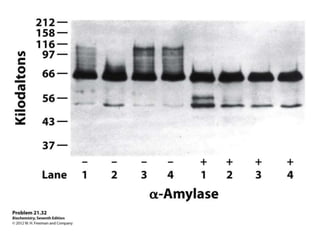
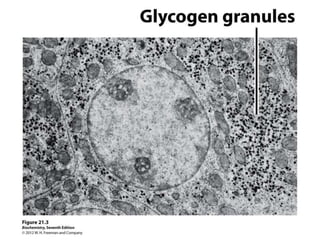
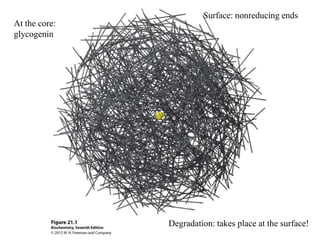
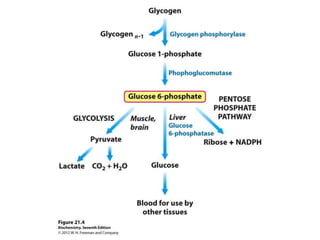
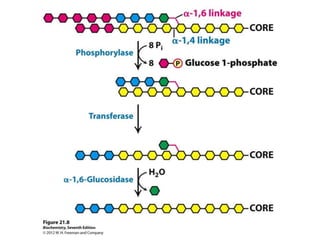
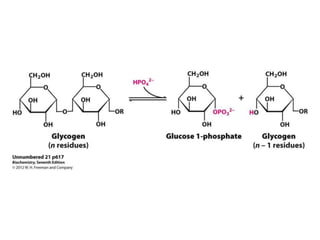
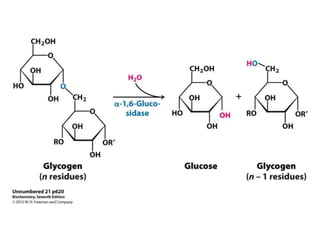
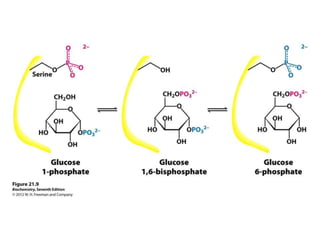
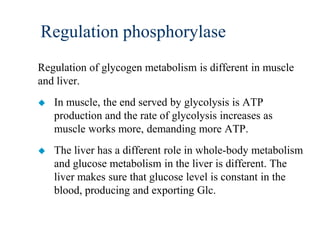
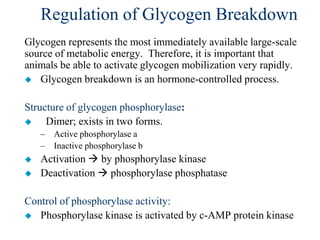
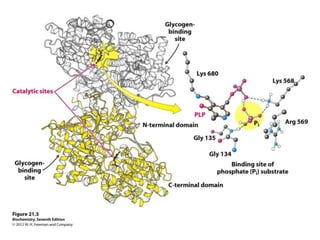
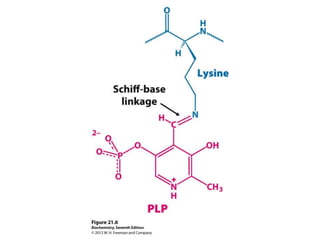
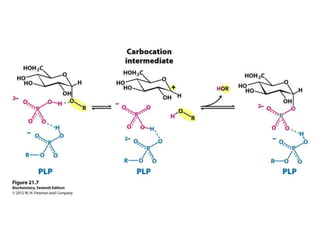
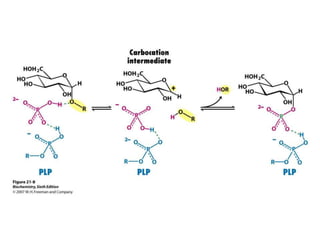
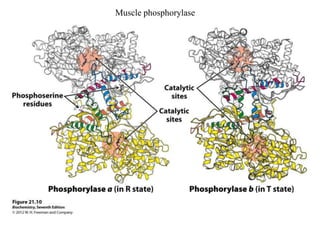
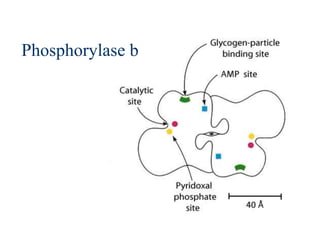
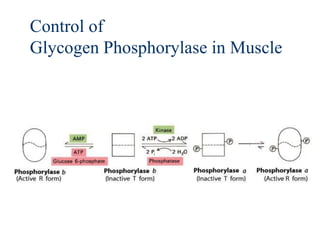
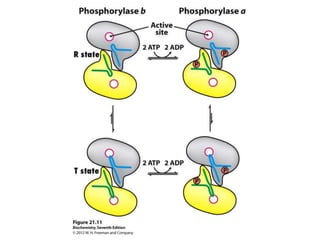
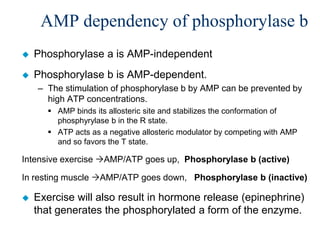
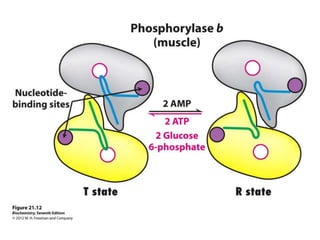
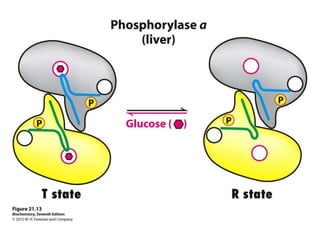
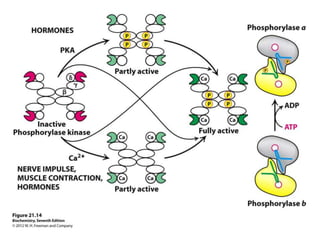
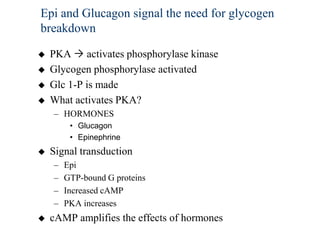
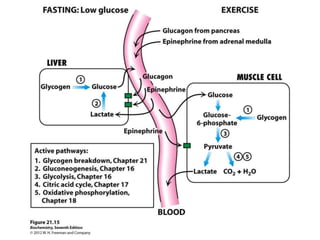
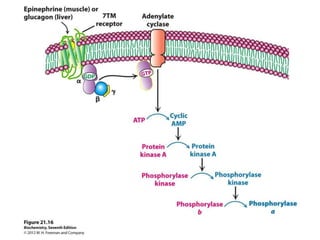
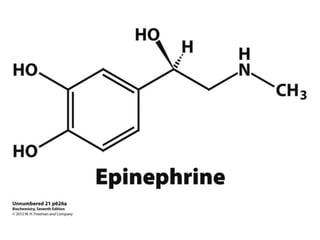
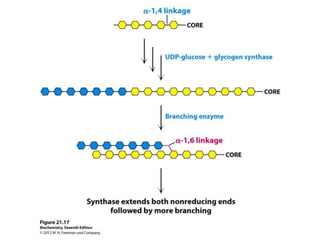
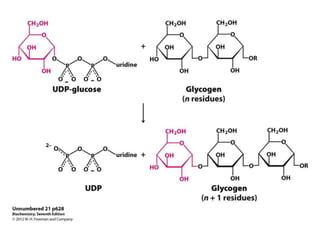
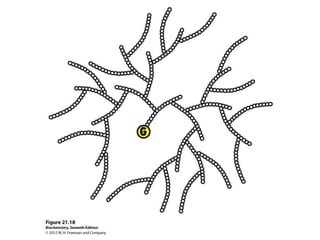
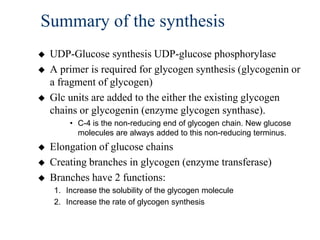
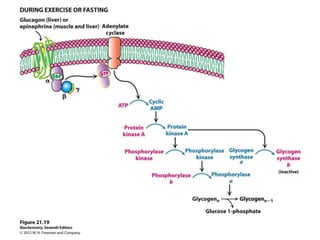
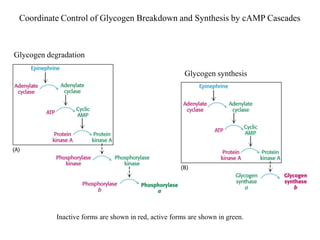
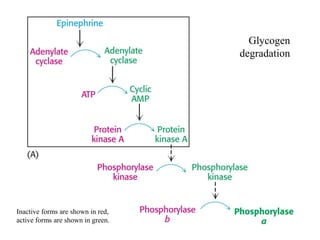
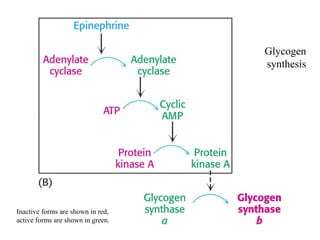
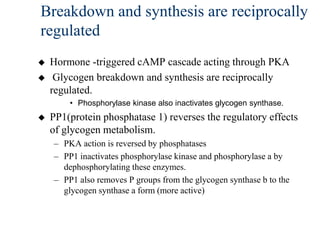
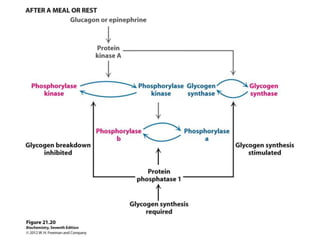
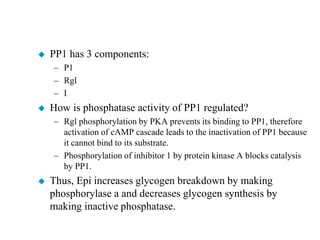
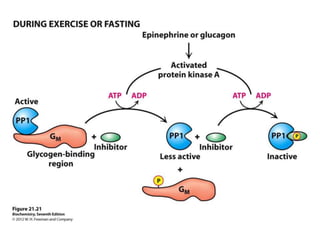
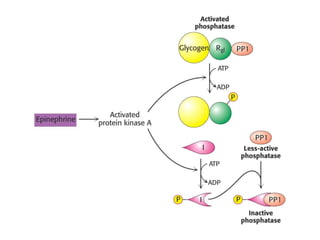
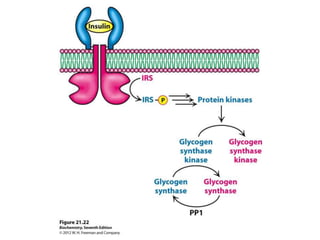
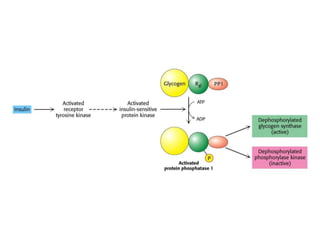
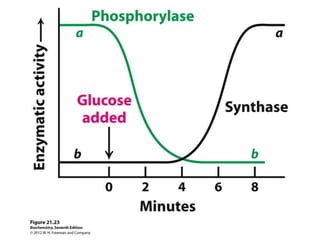
Glycogen metabolism is regulated by hormones through reciprocal control of glycogen breakdown and synthesis. The key enzymes involved are glycogen phosphorylase, which degrades glycogen, and glycogen synthase, which synthesizes glycogen. Epinephrine and glucagon activate phosphorylase through cAMP signaling, while insulin activates protein phosphatase 1, inactivating phosphorylase and activating synthase to stimulate glycogen synthesis. Liver glycogen phosphorylase is directly regulated by glucose levels, sensing glucose to control glycogen breakdown and maintain blood glucose homeostasis.






















![Glucose regulation of glycogen metabolism
[Glycogen breakdown inhibited]
[Glycogen synthesis favored]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec09glycogenmet-130314233411-phpapp02/85/Lec09-glycogen-met-69-320.jpg)