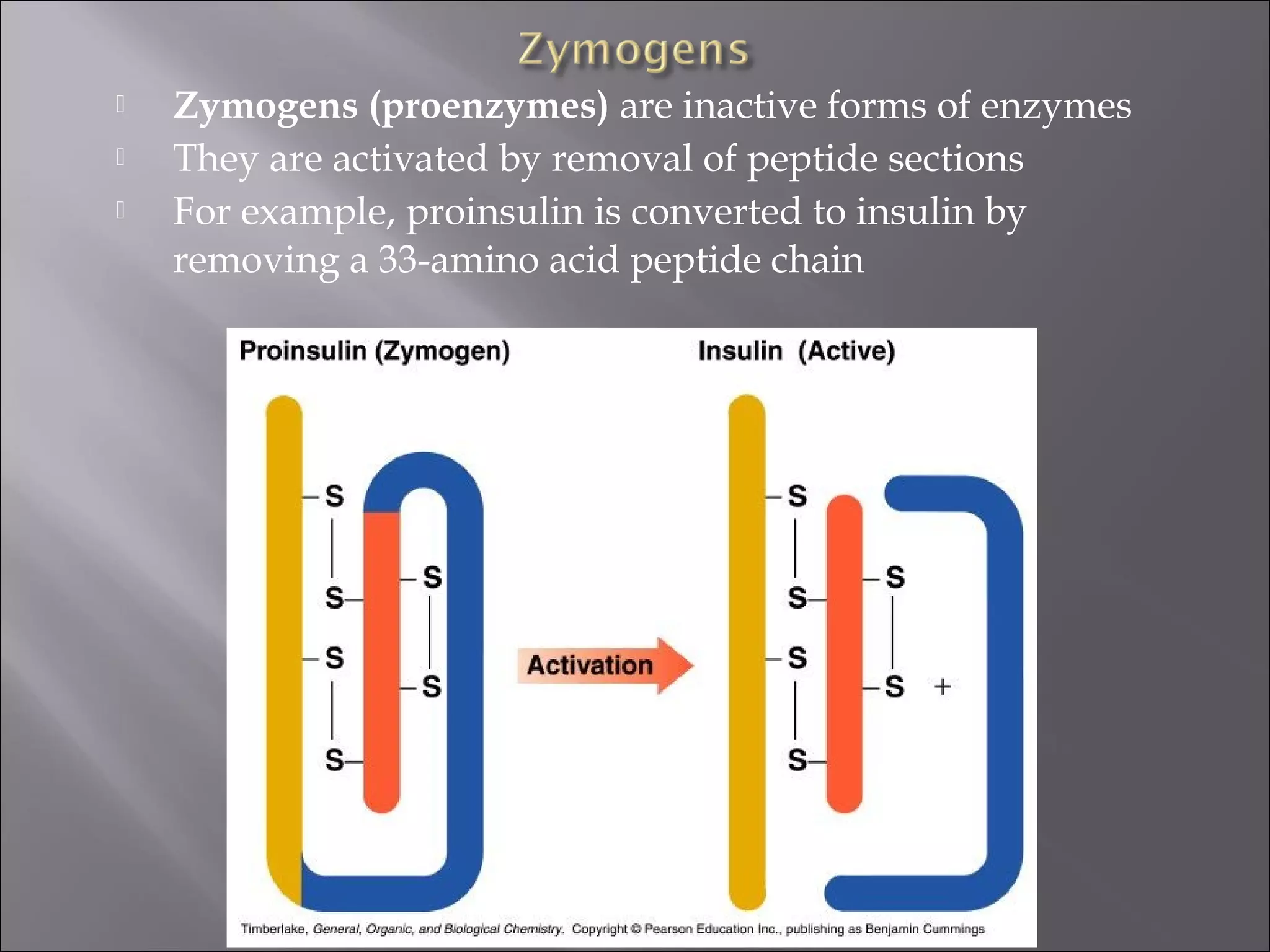
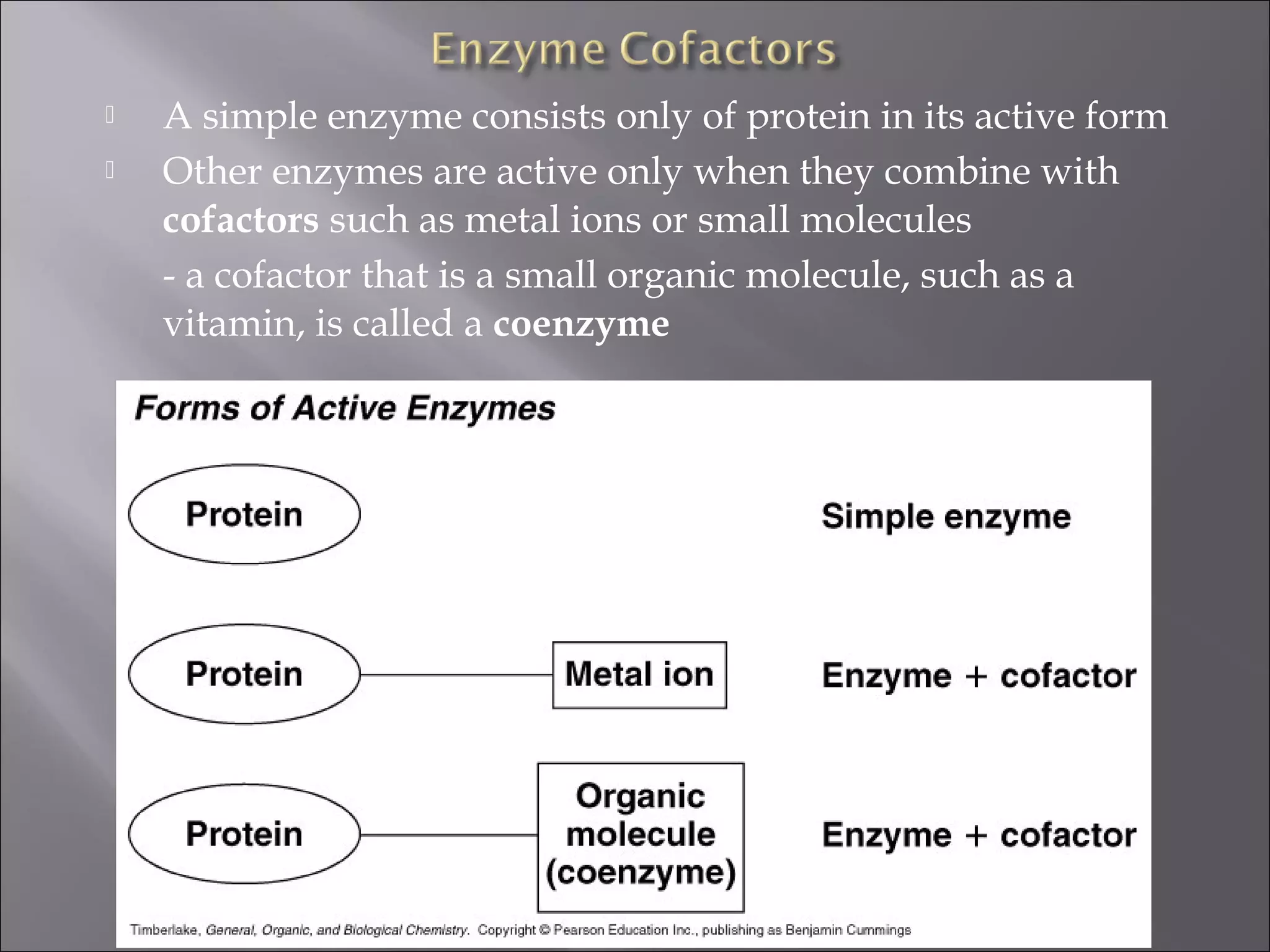
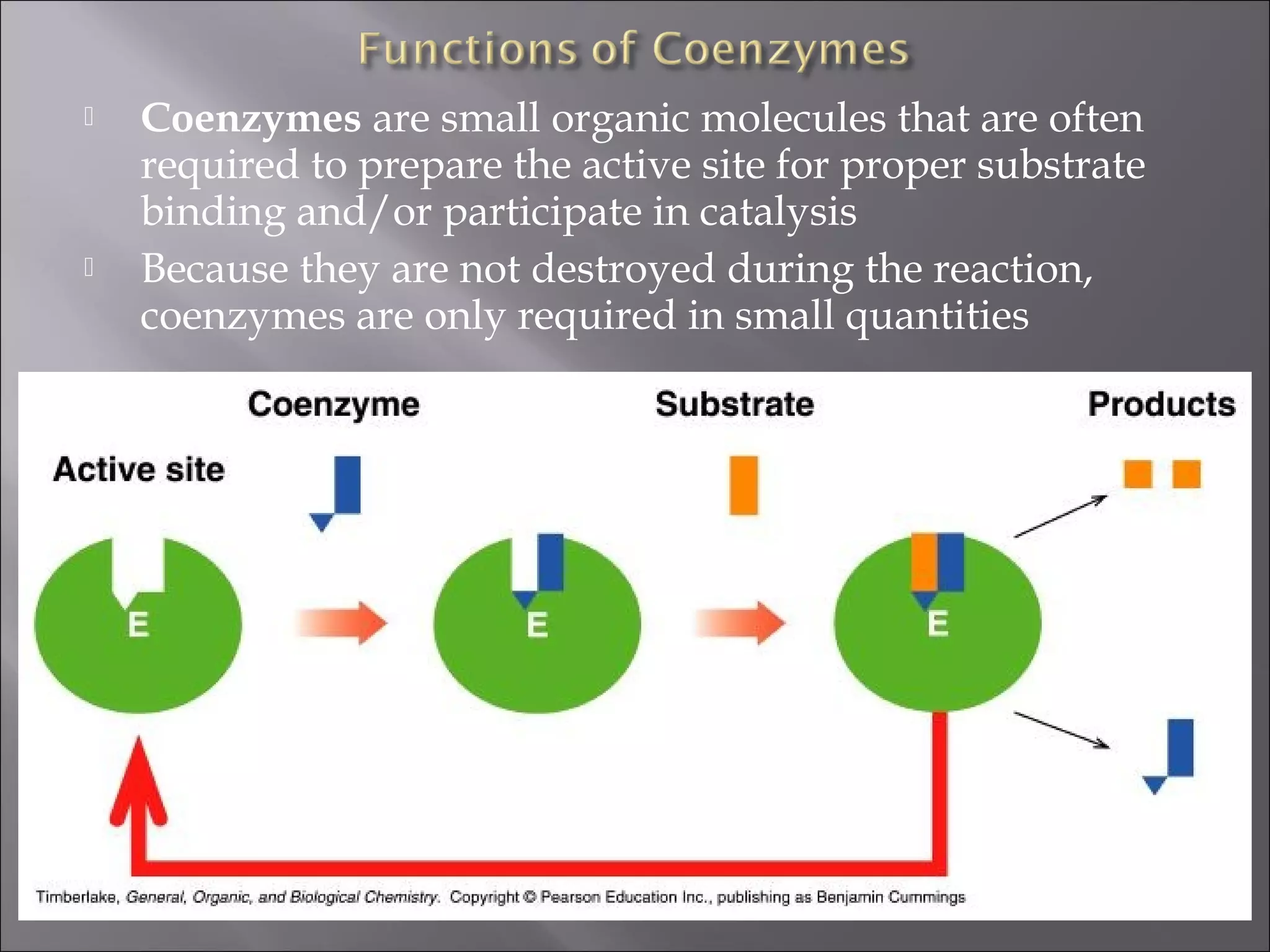
This document discusses enzyme regulation and the roles of cofactors and vitamins in enzyme function. It explains that enzymes are regulated through genetic control, covalent modification, and feedback inhibition. Coenzymes, which include vitamins and metal ions, are required for many enzyme reactions. Deficiencies in water-soluble vitamins can result since they are not stored, while fat-soluble vitamin excesses can be toxic. The roles of specific vitamins as coenzymes are outlined.