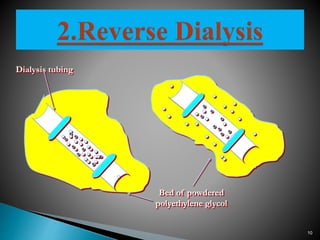
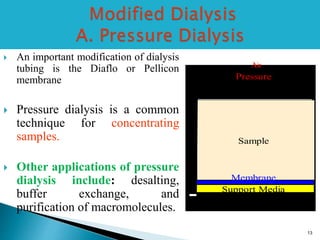
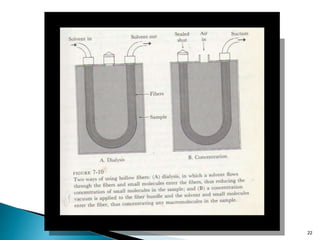
Dialysis is a technique used to separate molecules in solution based on their molecular weight. It involves placing a sample inside a semi-permeable membrane bag and submerging it in a larger volume of buffer solution. Only small molecules can diffuse through the membrane, leaving larger macromolecules concentrated inside the bag. Dialysis is useful for desalting samples, buffer exchange, and purification of biomolecules, though it is a slow process. Variations like pressure dialysis and ultrafiltration allow for faster concentration of samples.