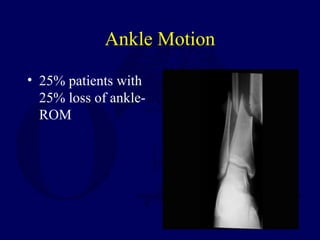
1) Closed tibial shaft fractures are a common injury, with over 492,000 occurring per year in the US. They can be treated nonoperatively with casting or surgically with intramedullary nailing, plating, or external fixation.
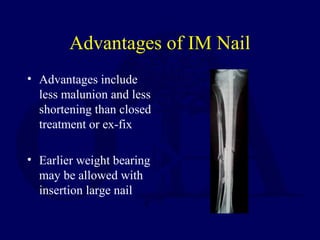
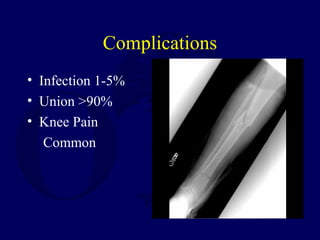
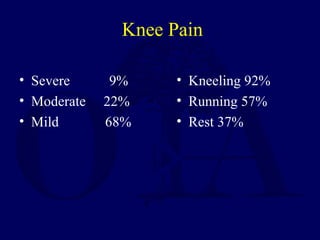
2) Intramedullary nailing is now the preferred surgical treatment, as studies have shown it results in higher union rates and fewer complications compared to other options. However, anterior knee pain remains a common complication after nailing.
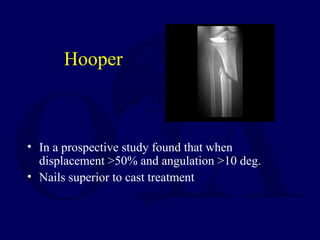
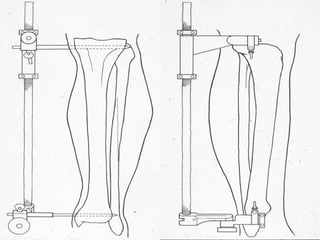
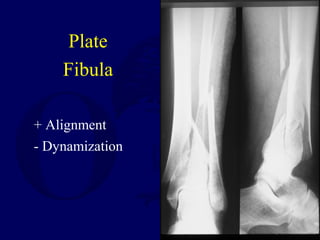
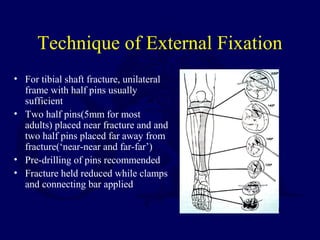
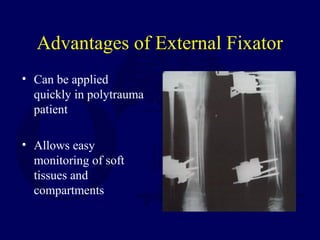
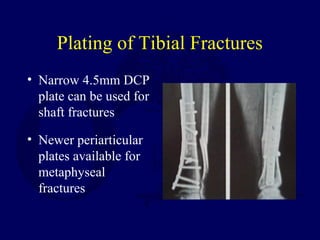
3) External fixation is generally reserved for open or periarticular fractures, as it is associated with higher malunion rates compared to nailing. Plating risks higher infection and soft tissue complications.































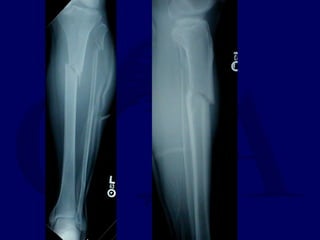

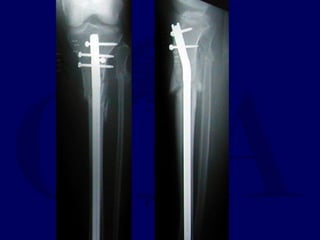
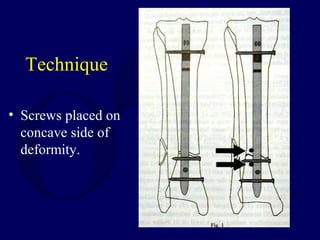


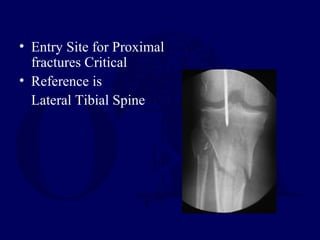
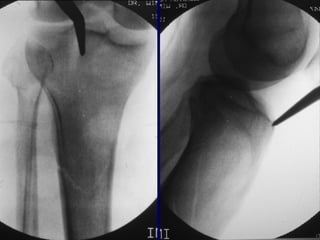
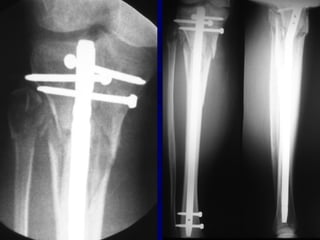

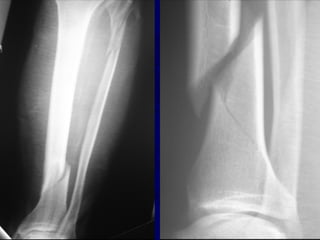

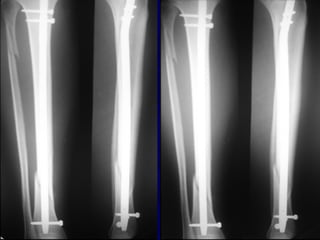
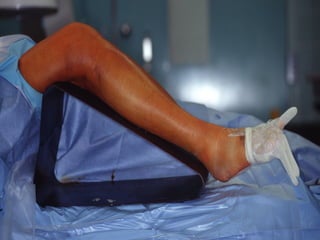
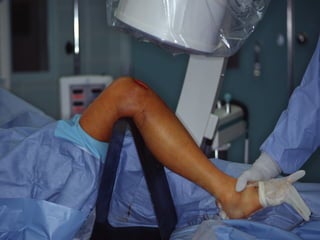
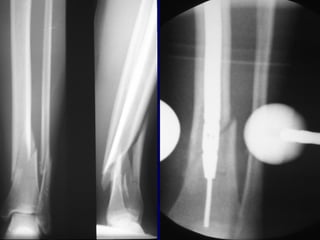
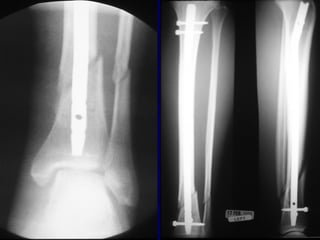
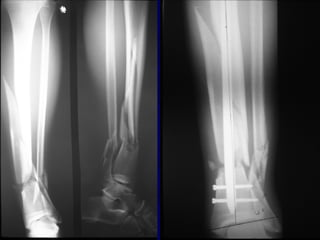
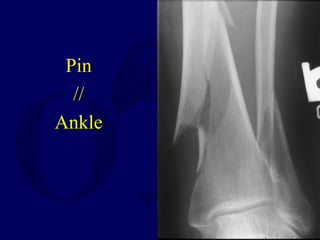
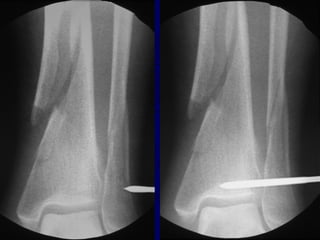
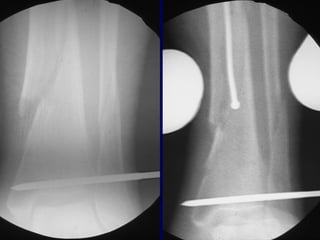
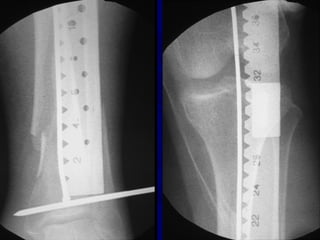
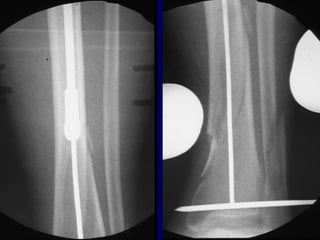
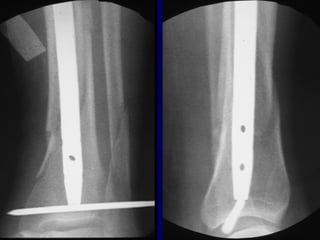
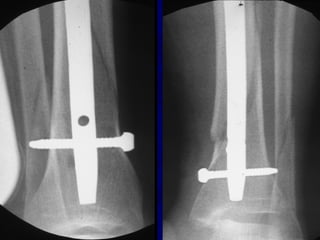
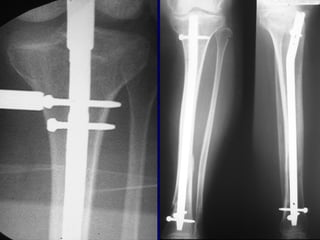
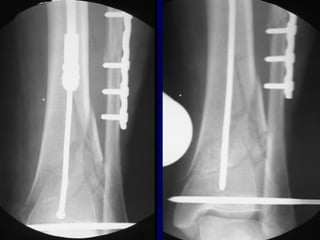
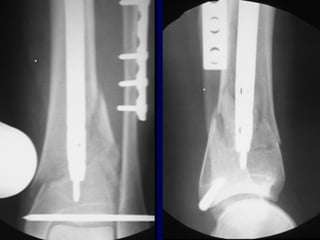
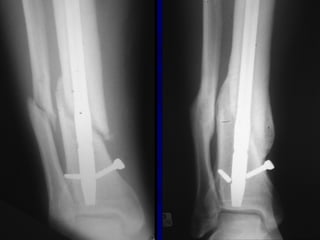
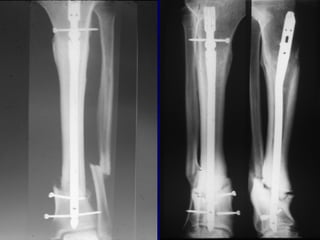


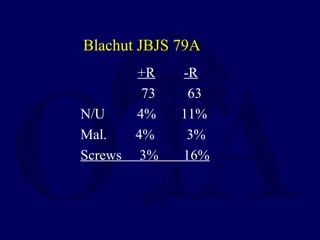












![Outcomes of External Fixation
• 95% union rate has been reported for group of closed and
open tibia fractures, but 20% malunion rate*
• Most common complications are pin track infections and
malunion**
• Loss of reduction associated with removing frame prior to
union
*Anderson et al. Clin Orthop 1974
**Edge and Denham JBJS[Br] 1981](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l10-closedtibia-161225232557/85/L10-closed-tibia-105-320.jpg)

