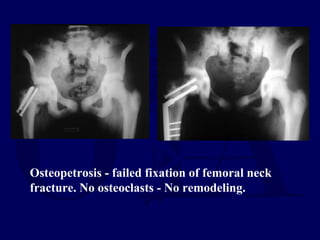
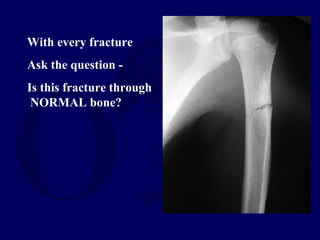
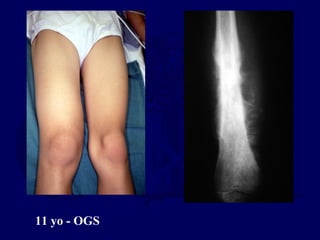
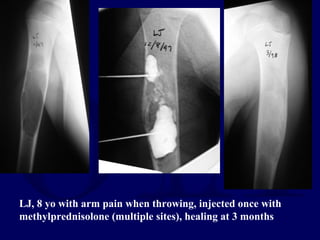
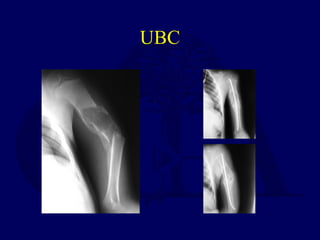
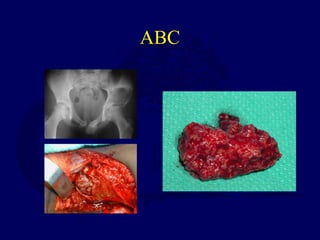
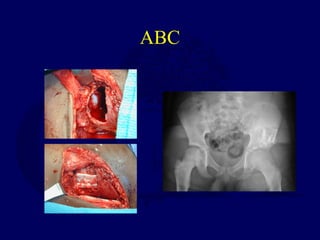
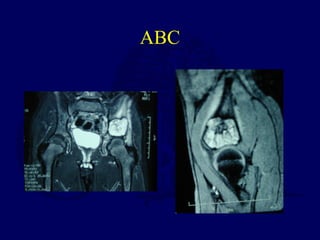
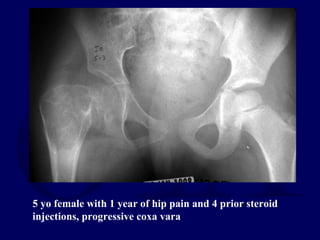
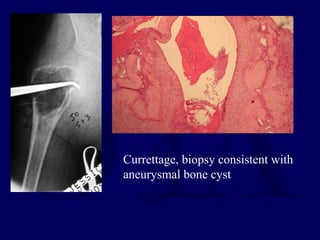
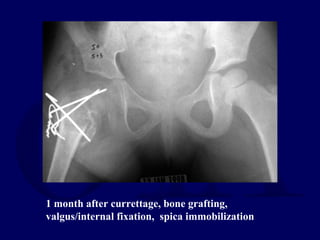
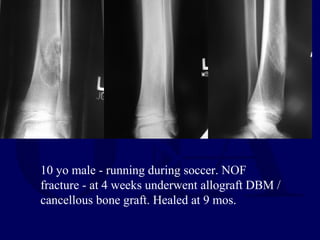
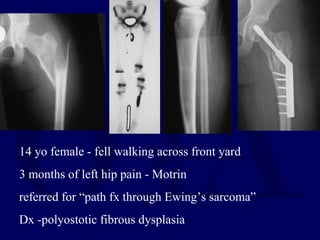
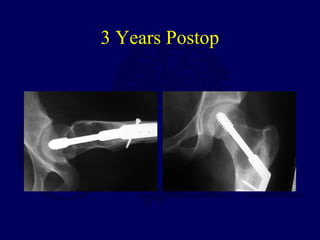
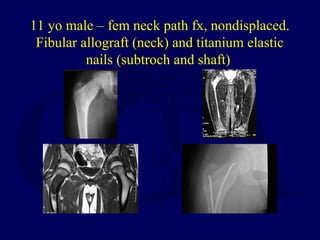
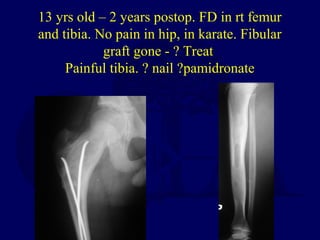
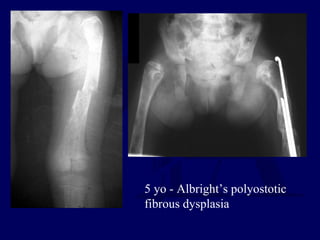
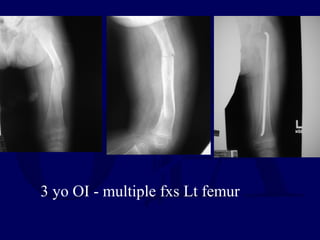
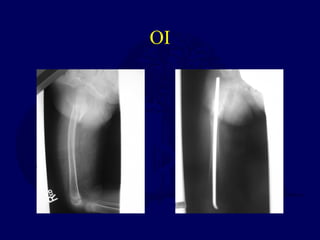
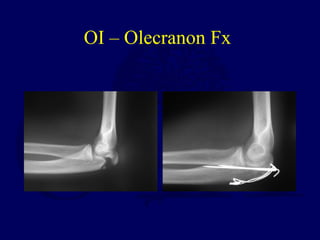
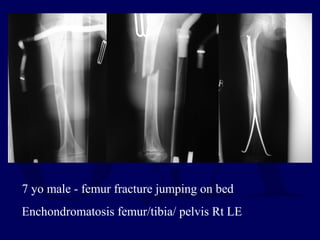
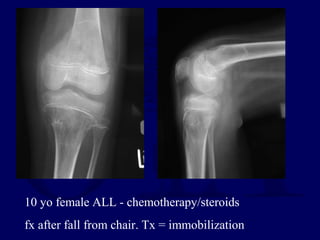
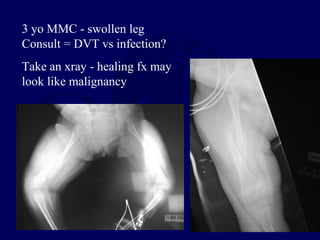
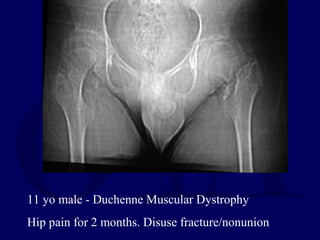
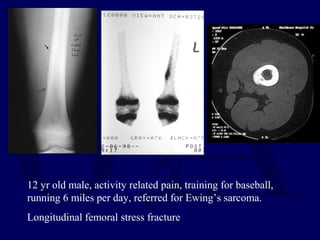
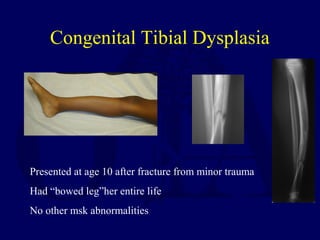
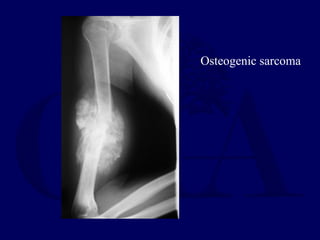
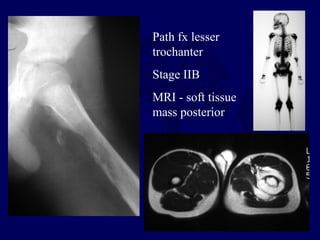
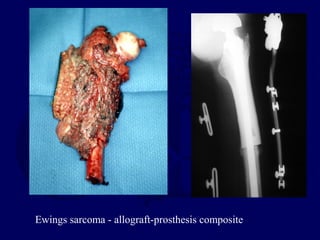
This document discusses pathologic fractures in children. It summarizes that a pathologic fracture occurs through abnormal bone and outlines several potential causes including benign bone lesions like unicameral bone cysts and aneurysmal bone cysts, metabolic bone diseases, skeletal dysplasias, and malignant bone lesions. It emphasizes the importance of being suspicious of every fracture in children and thoroughly investigating to make an accurate diagnosis and guide appropriate treatment.