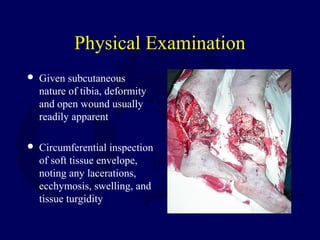
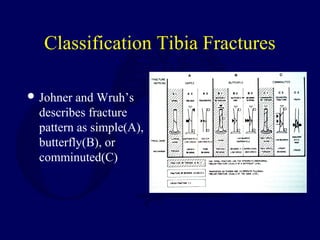
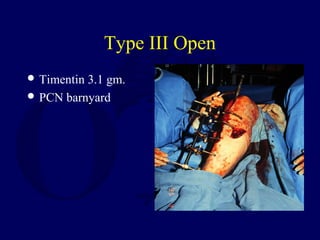
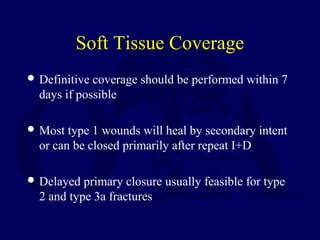
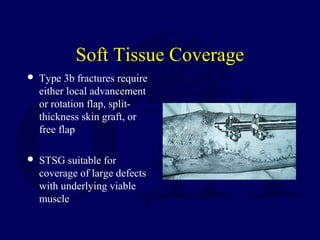
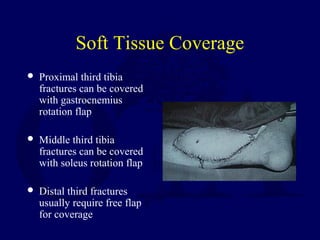
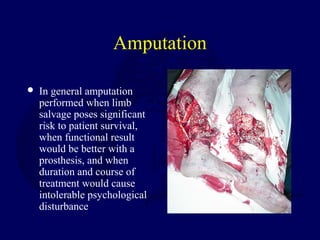
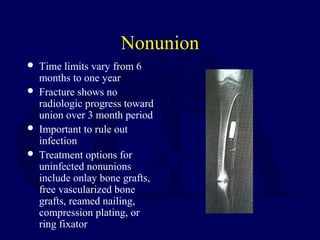
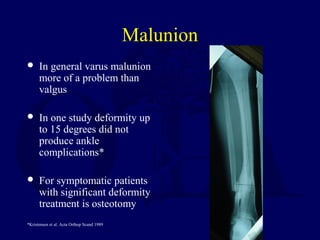
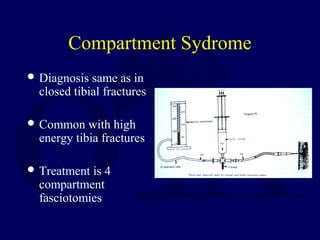
This document discusses open fractures of the tibial diaphysis (shaft). It notes that open tibia fractures account for about 1/4 of all tibial fractures and occur more commonly in the tibia than any other long bone. Treatment involves thorough debridement and irrigation of the soft tissue wound, antibiotics, and stabilization of the bone fracture, which may be via internal or external fixation depending on the fracture pattern and soft tissue injury severity. Complications include infection, nonunion, malunion, and compartment syndrome. Outcomes depend highly on the severity of soft tissue and neurovascular damage based on the Gustilo-Anderson classification.































![Outcomes
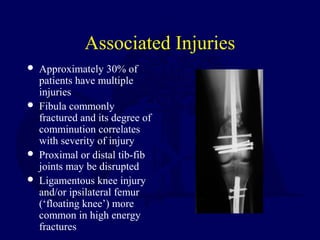
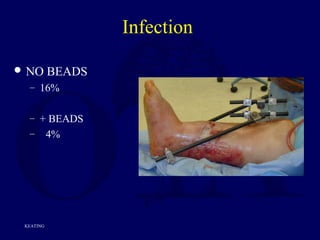
For type 3b and 3c fractures early soft tissue
coverage gives best results
In one study of 84 type 3b and 3c fractures, results
with single stage procedure involving fixation
with immediate flap coverage better than when
coverage delayed more than 72 hours (deep
infection 3% vs. 19%)*
*Gopal et al. JBJS[Br] 2000
Return to
Lower Extremity
Index](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l09-opentibia-161225232459/85/L09-open-tibia-49-320.jpg)