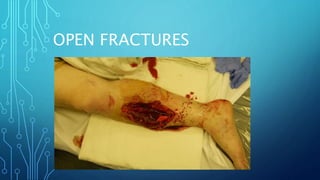
Open fractures are common injuries, especially of the tibia and fingers, often resulting from high-energy trauma. They require urgent treatment including intravenous antibiotics, tetanus prophylaxis, wound stabilization, and irrigation and debridement within 24 hours to minimize infection risk. Temporary stabilization is followed by soft tissue coverage within 5-7 days to further reduce infection rates. Definitive reconstruction and fracture fixation can then be performed once the wound is clean. Complications include surgical site infection, osteomyelitis, and neurovascular injury, with risk varying based on the Gustilo classification and degree of soft tissue damage.