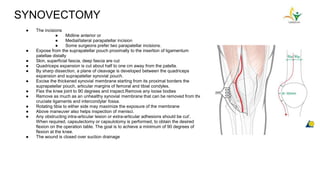
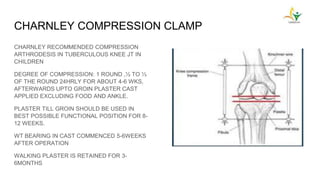
The document discusses tuberculosis of the knee joint. Some key points:
- Skeletal TB accounts for 10-35% of extra-pulmonary TB cases, with the knee being the 3rd most common site after the spine and hip.
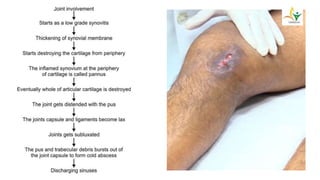
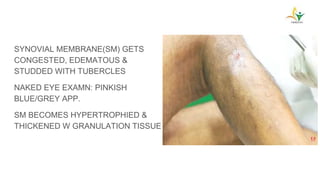
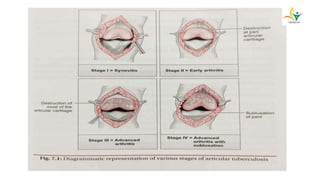
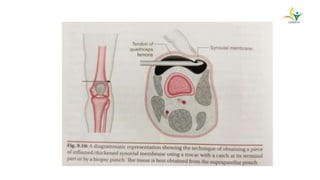
- TB typically spreads to the knee hematogenously from a primary focus. Synovial involvement can initially cause only effusion before advancing to osteoarticular destruction.
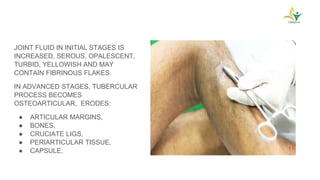
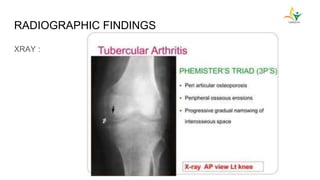
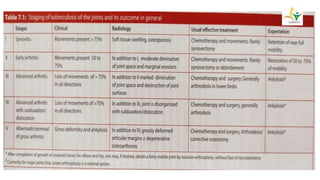
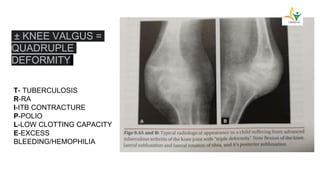
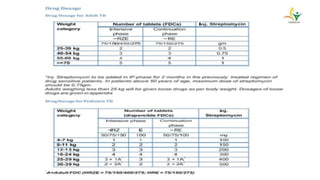
- Advanced cases are characterized by bone erosion, subluxation, fibrosis and ankylosis on x-ray. Synovectomy and antitubercular drugs can cure early cases while arthrodesis is used for advanced cases.
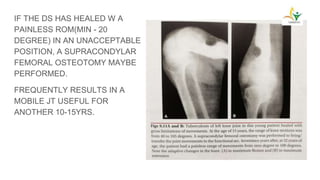
- Prognosis is generally good with antituberc