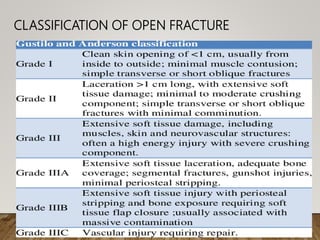
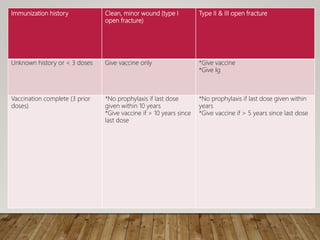
Open fractures occur when a bone fracture communicates with the external environment through a break in the skin. They were classified and early management was discussed, including irrigation, debridement, antibiotics, tetanus prophylaxis, and splinting. Options for fracture stabilization include external fixation, plating, and intramedullary nails. Wound closure considerations involve primary versus delayed closure, skin grafting, and flaps. The goal is thorough debridement and stable fixation to prevent infection while obtaining soft tissue coverage.