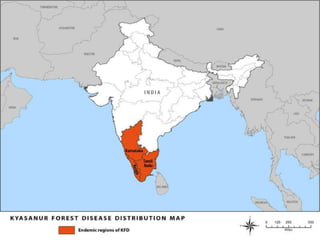
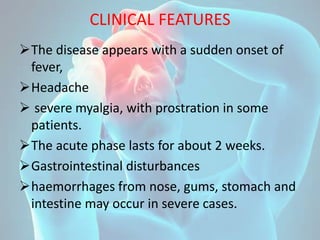
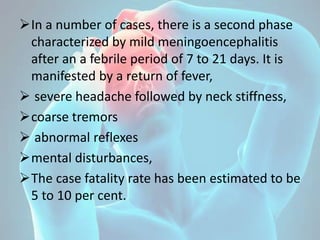
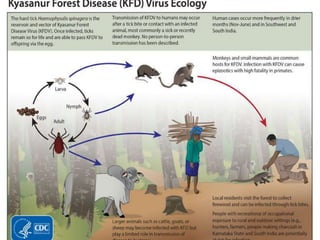
Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD) is a febrile disease caused by the Kyasanur Forest Disease virus, transmitted to humans through tick bites, with a notable incidence in Karnataka, India. Primarily affecting males aged 20 to 40 who engage in forest activities, it presents with fever, headache, severe myalgia, and potential hemorrhagic complications, with a case fatality rate of 5 to 10 percent. Control measures include tick management in forests, use of insect repellents, and educational initiatives to avoid tick exposure.