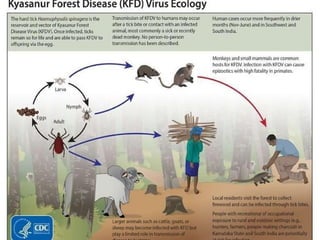
Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD) is a febrile, hemorrhagic disease caused by the Kyasanur Forest Disease virus, primarily transmitted to humans through tick bites. First identified in 1957 in Karnataka, India, the disease is monitored by the government due to its cyclical outbreaks linked to human activities in forests. Symptoms include fever, myalgia, and potential hemorrhage, with a case fatality rate of 5-10%, and while there is no specific treatment, supportive care and vaccination are available.