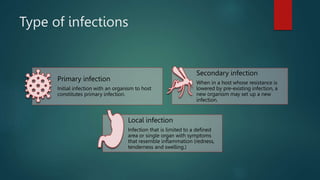
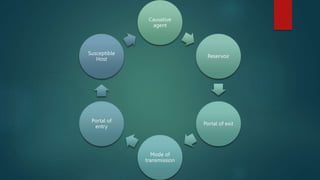
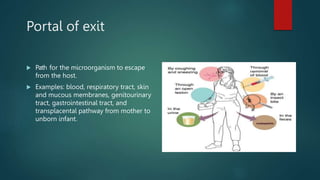
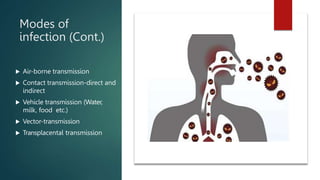
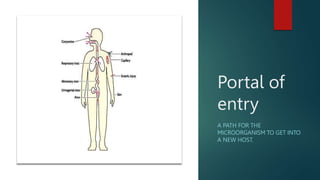
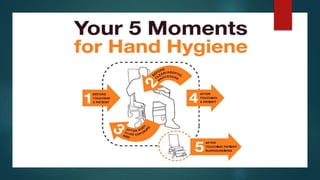
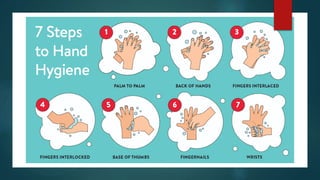
The document discusses infection control and prevention in healthcare settings, highlighting the significance of asepsis to reduce the spread of infections and unnecessary deaths. It outlines various types of infections, the chain of infection, and strategies for breaking the chain through hand hygiene, disinfection, environmental controls, and standard precautions. The importance of vaccination, regular health checks, and proper handling of contaminated materials is emphasized to protect both healthcare professionals and patients.