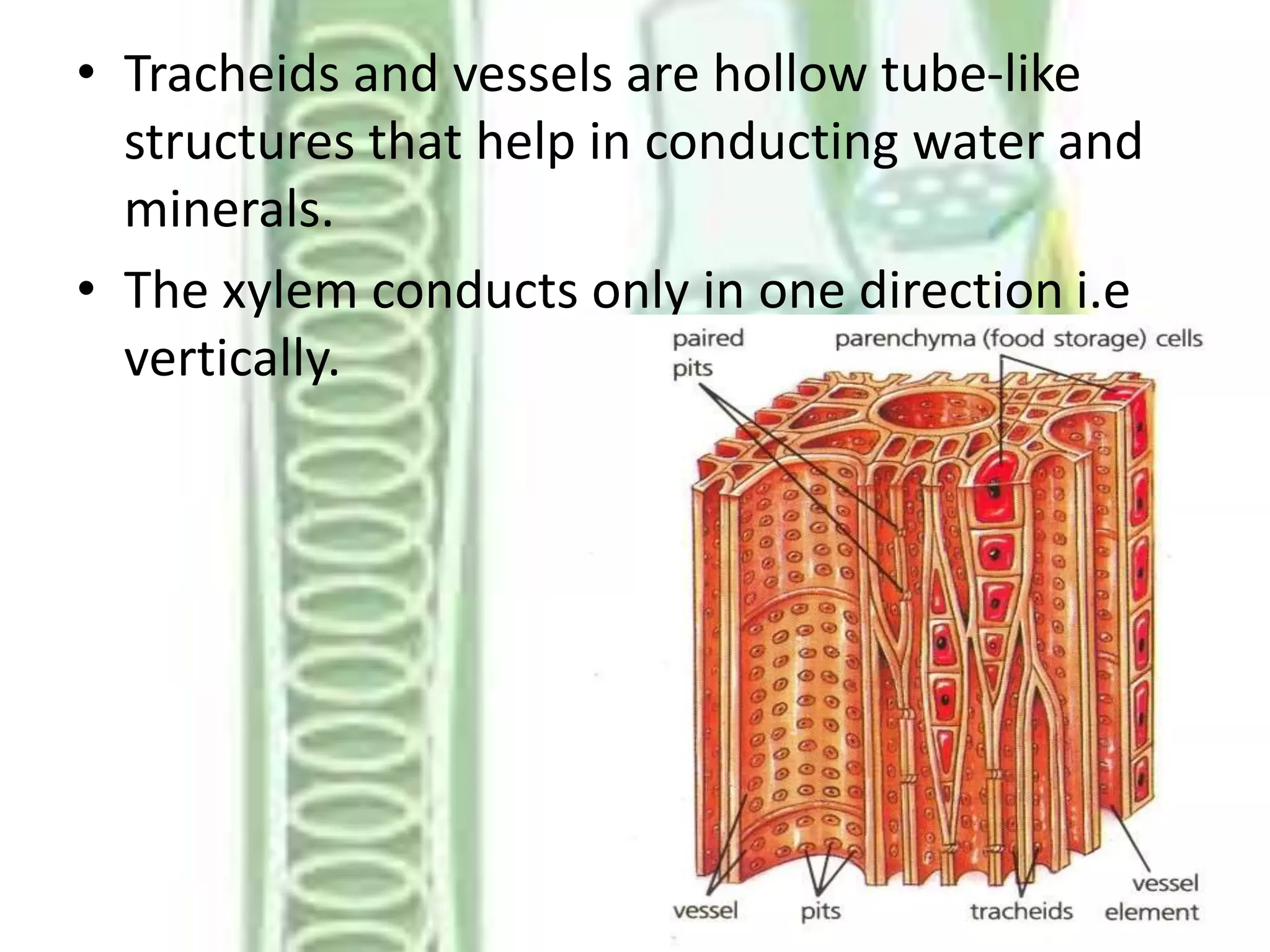
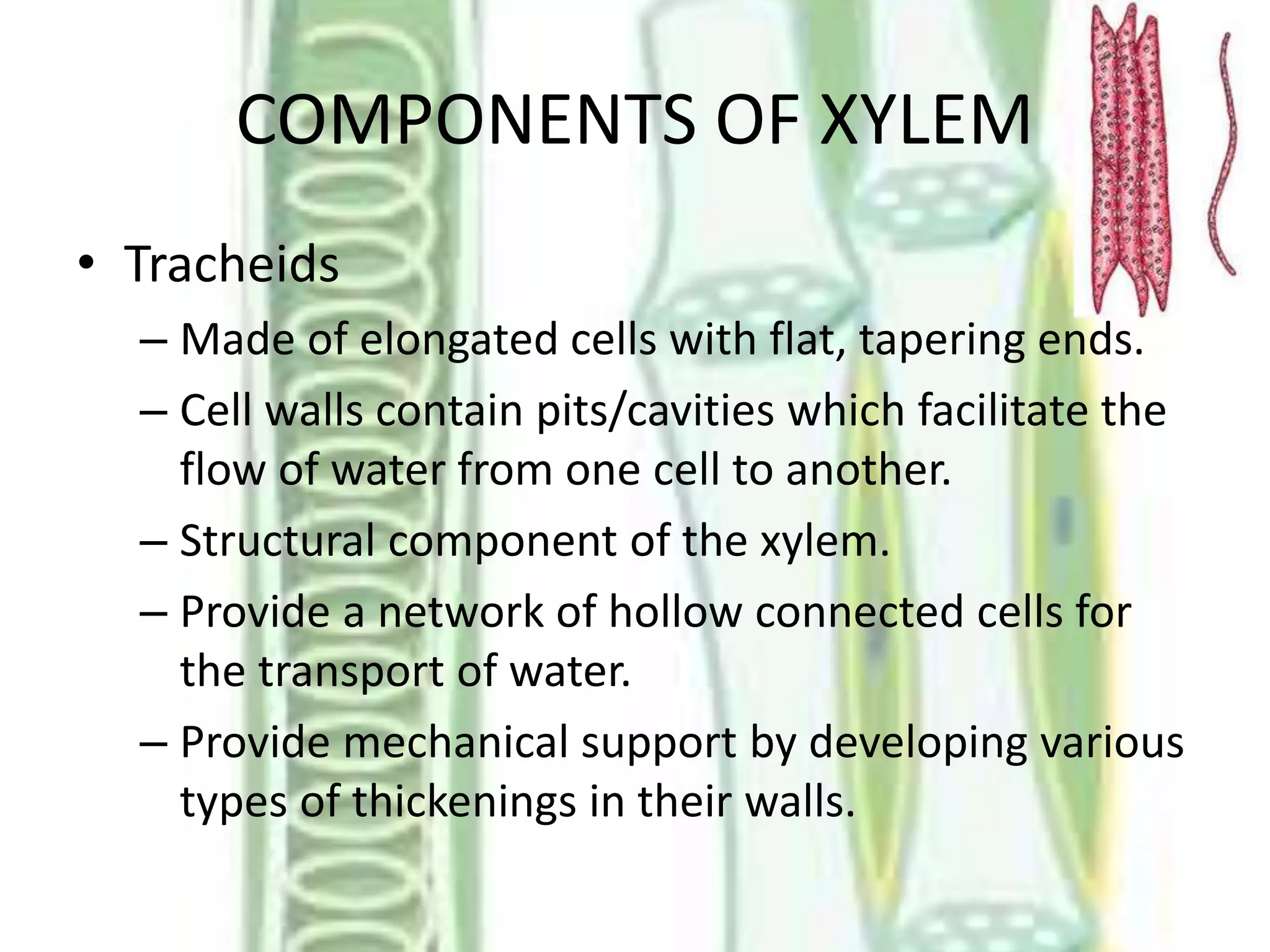
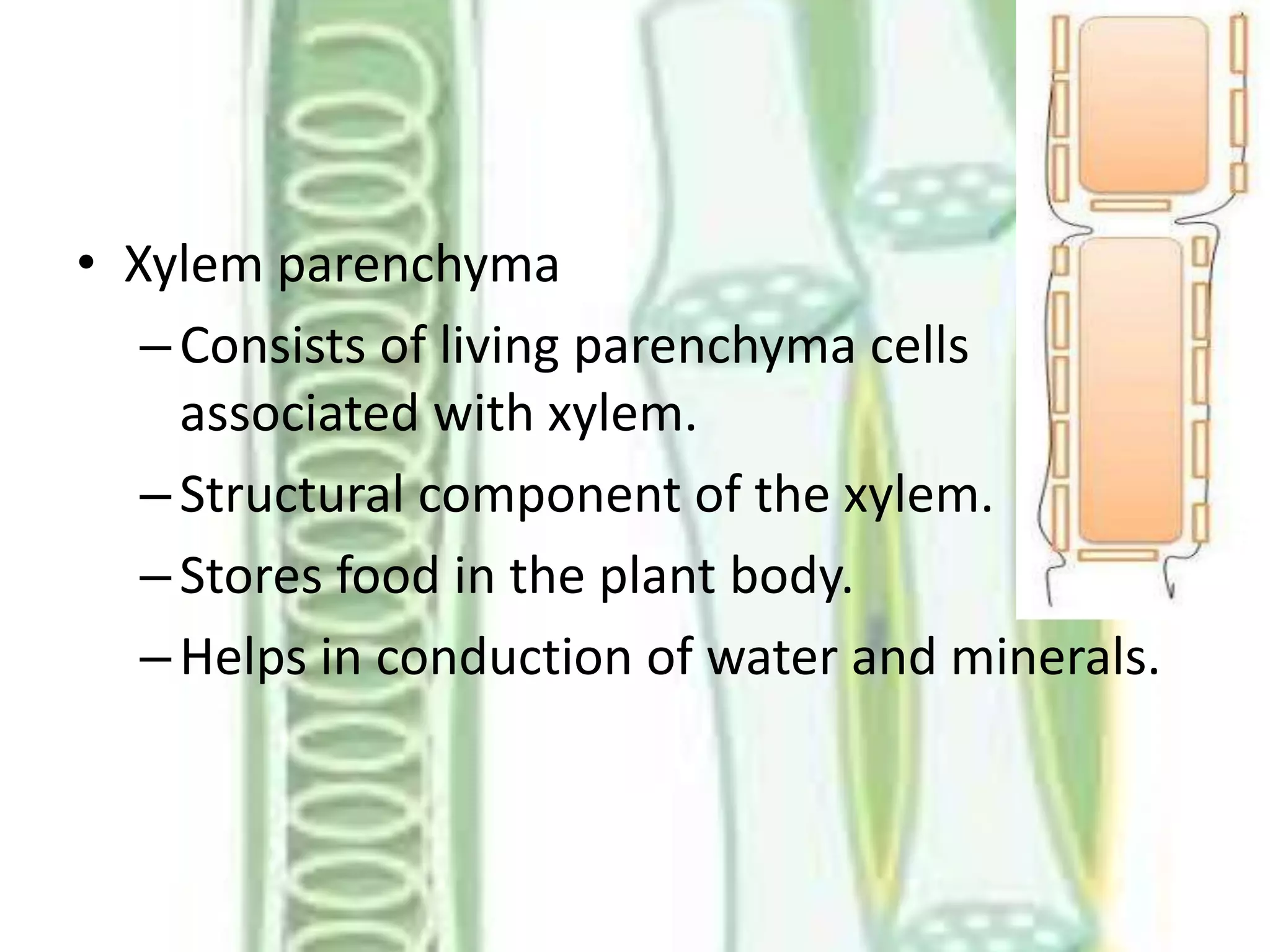
This document summarizes the components of xylem and phloem in vascular plants. It describes that xylem consists of tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres which help conduct water and minerals. Tracheids and vessels are hollow tubes, while xylem parenchyma stores food and helps conduct water. Phloem consists of sieve elements, companion cells, phloem parenchyma, and phloem fibres. Sieve elements conduct organic food, companion cells maintain pressure gradients, and phloem fibres provide mechanical strength. Both xylem and phloem work together to conduct water, minerals and food throughout vascular plants.