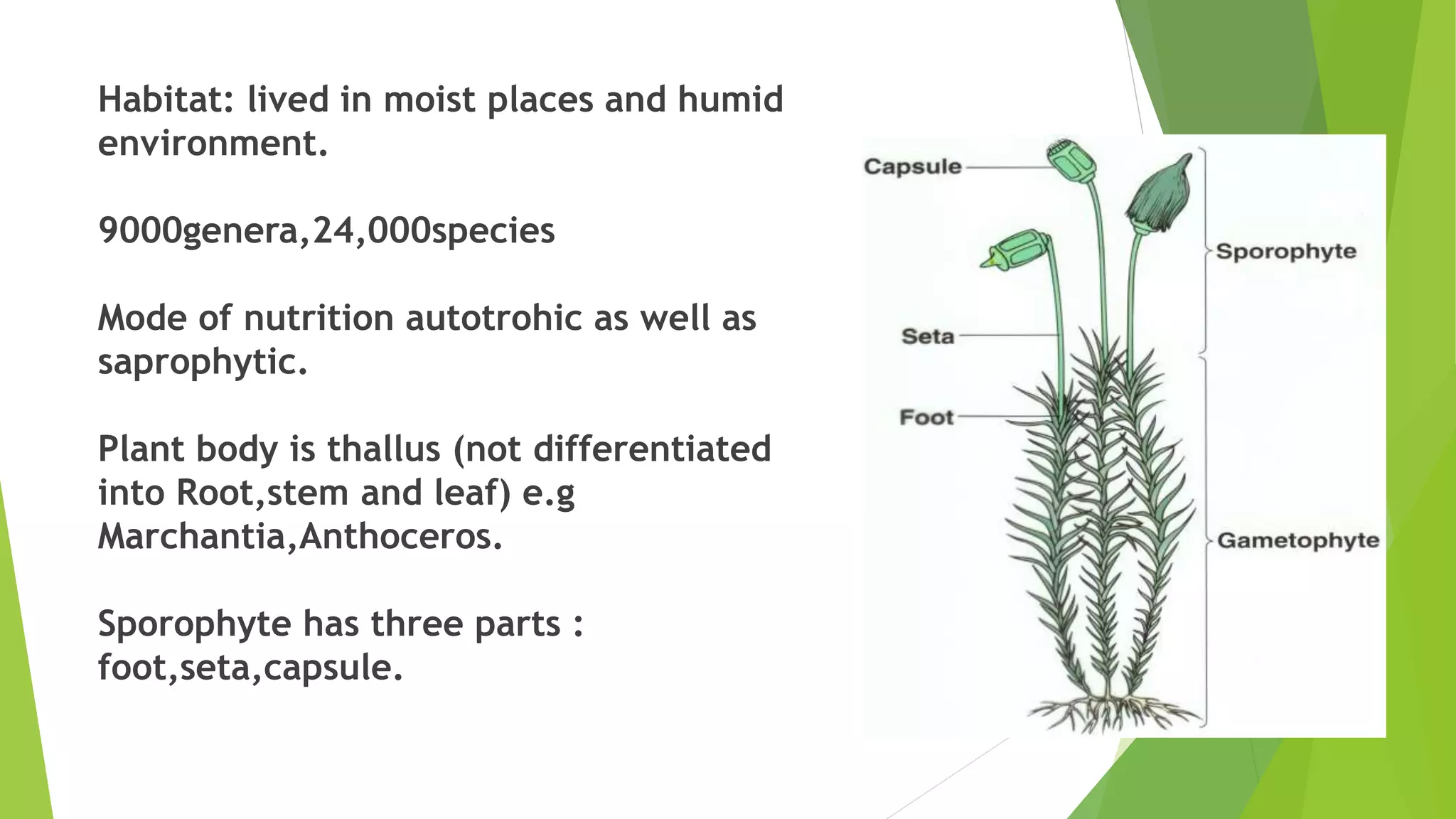
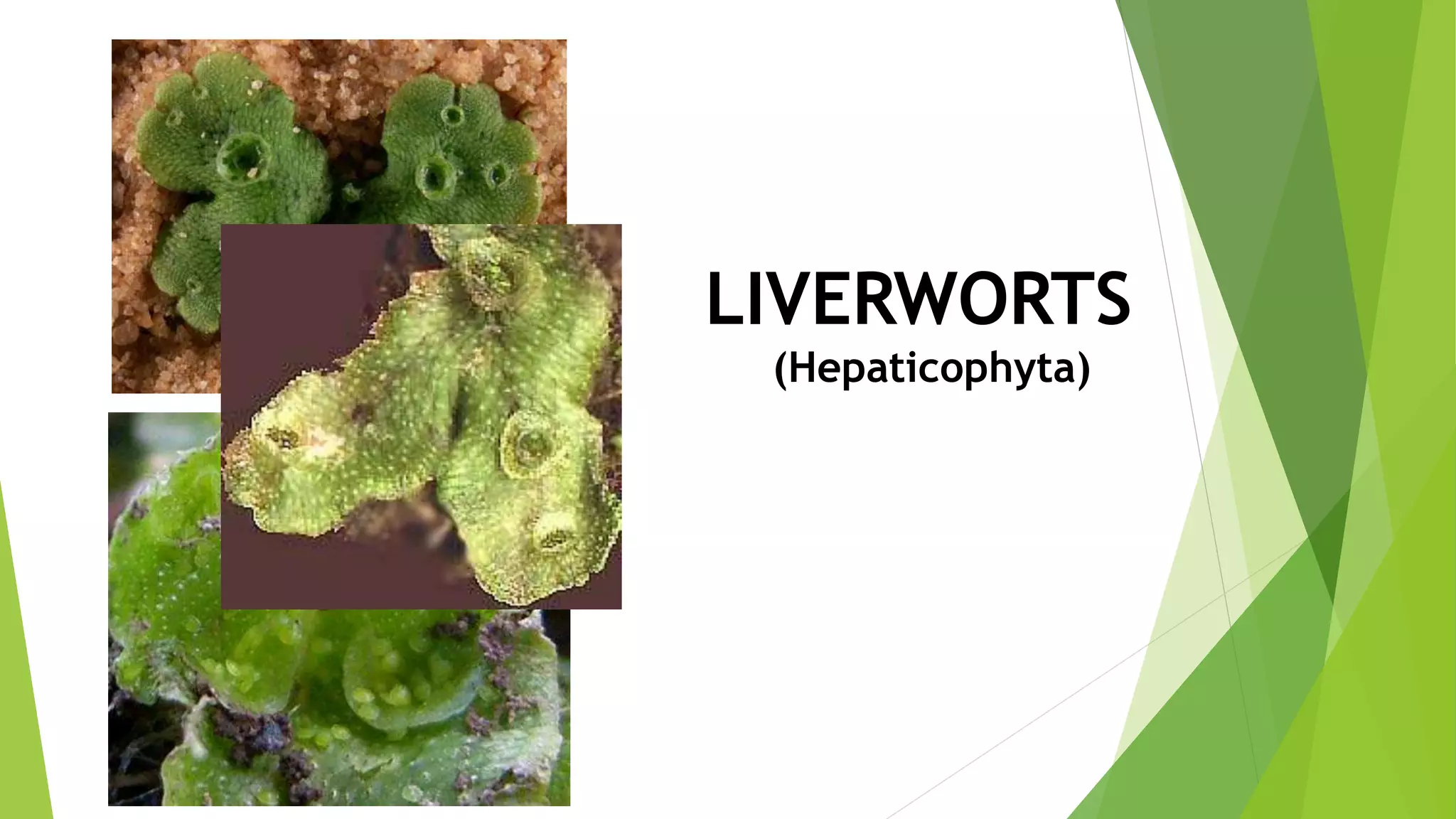
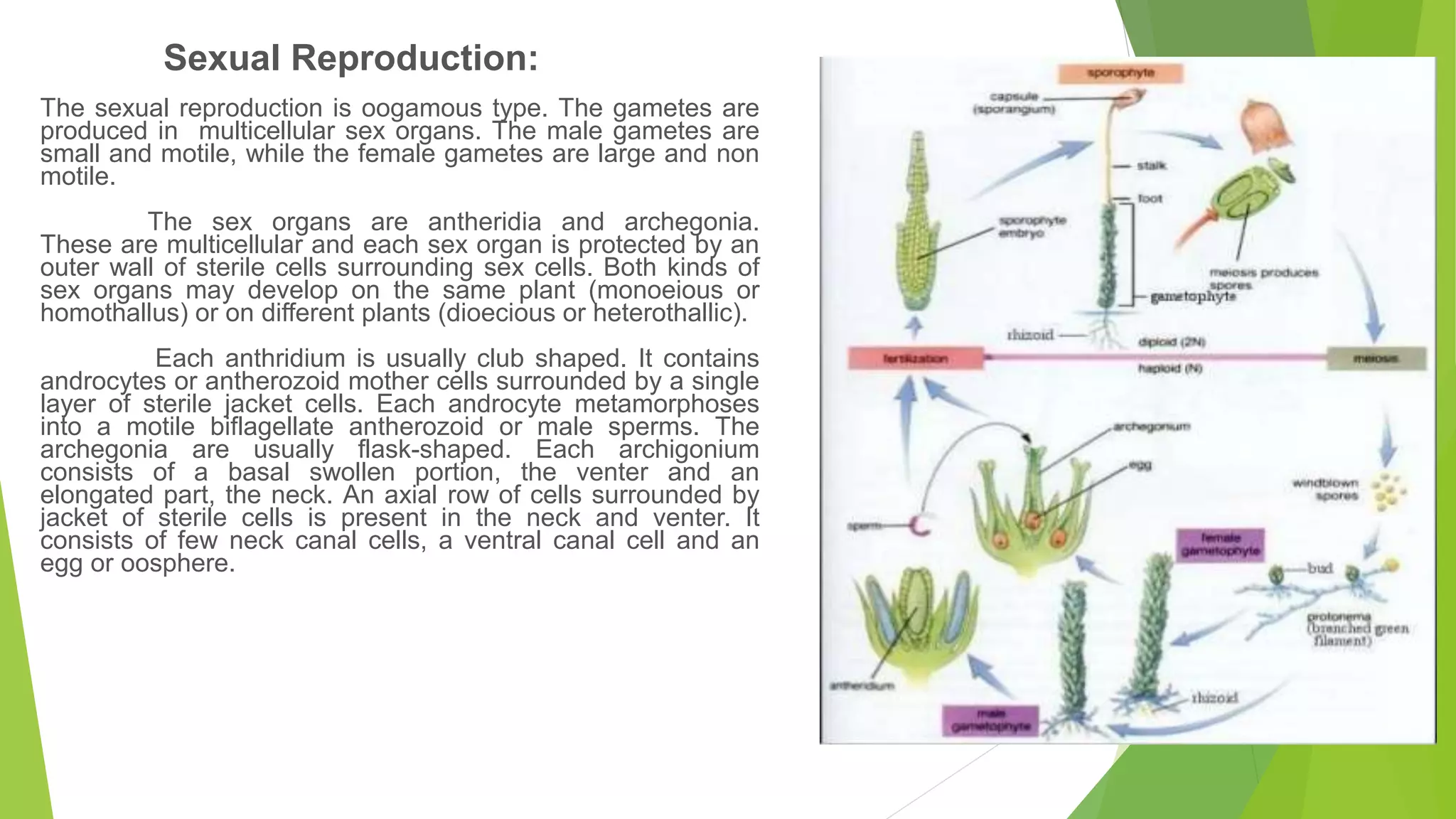
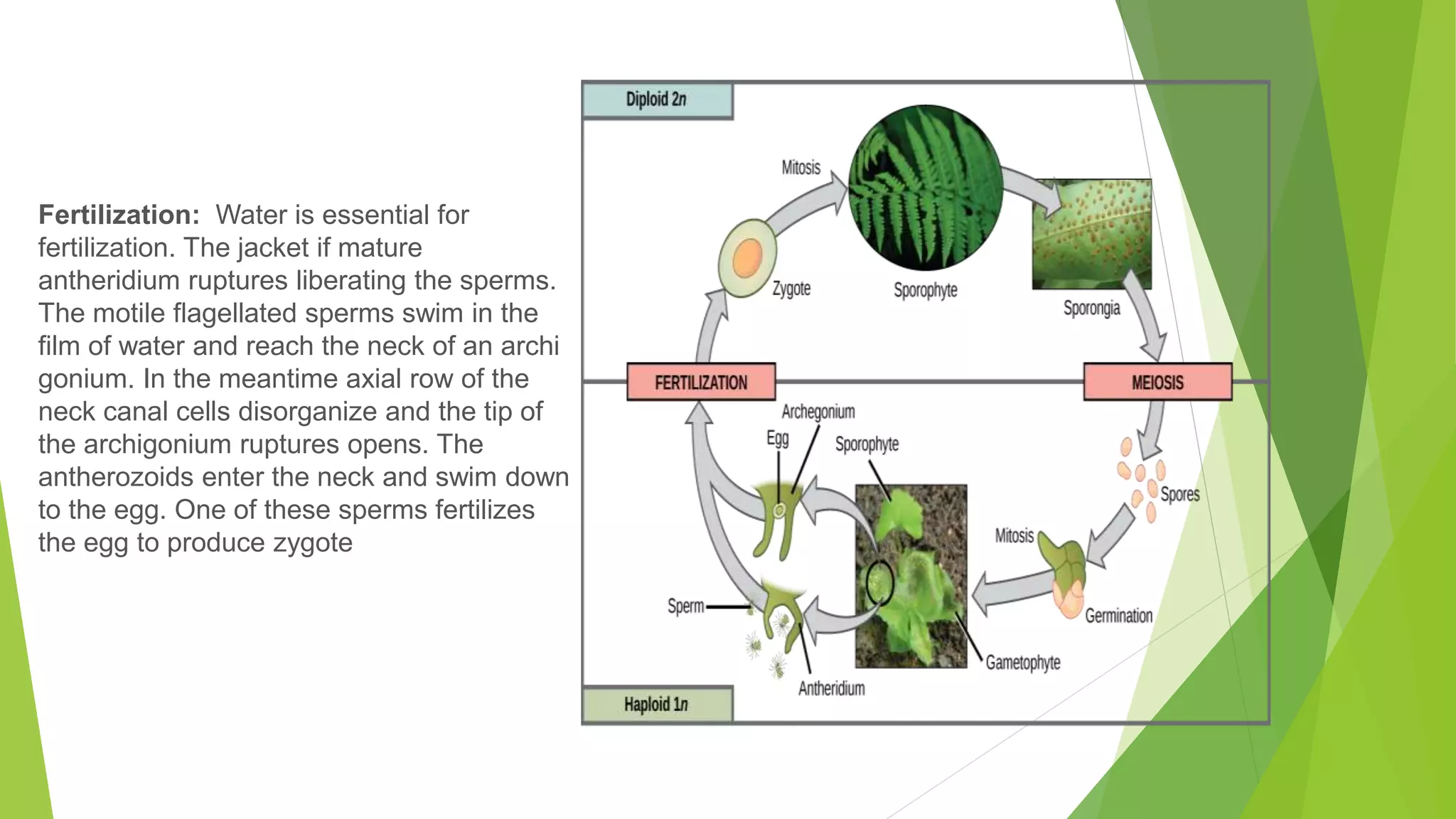
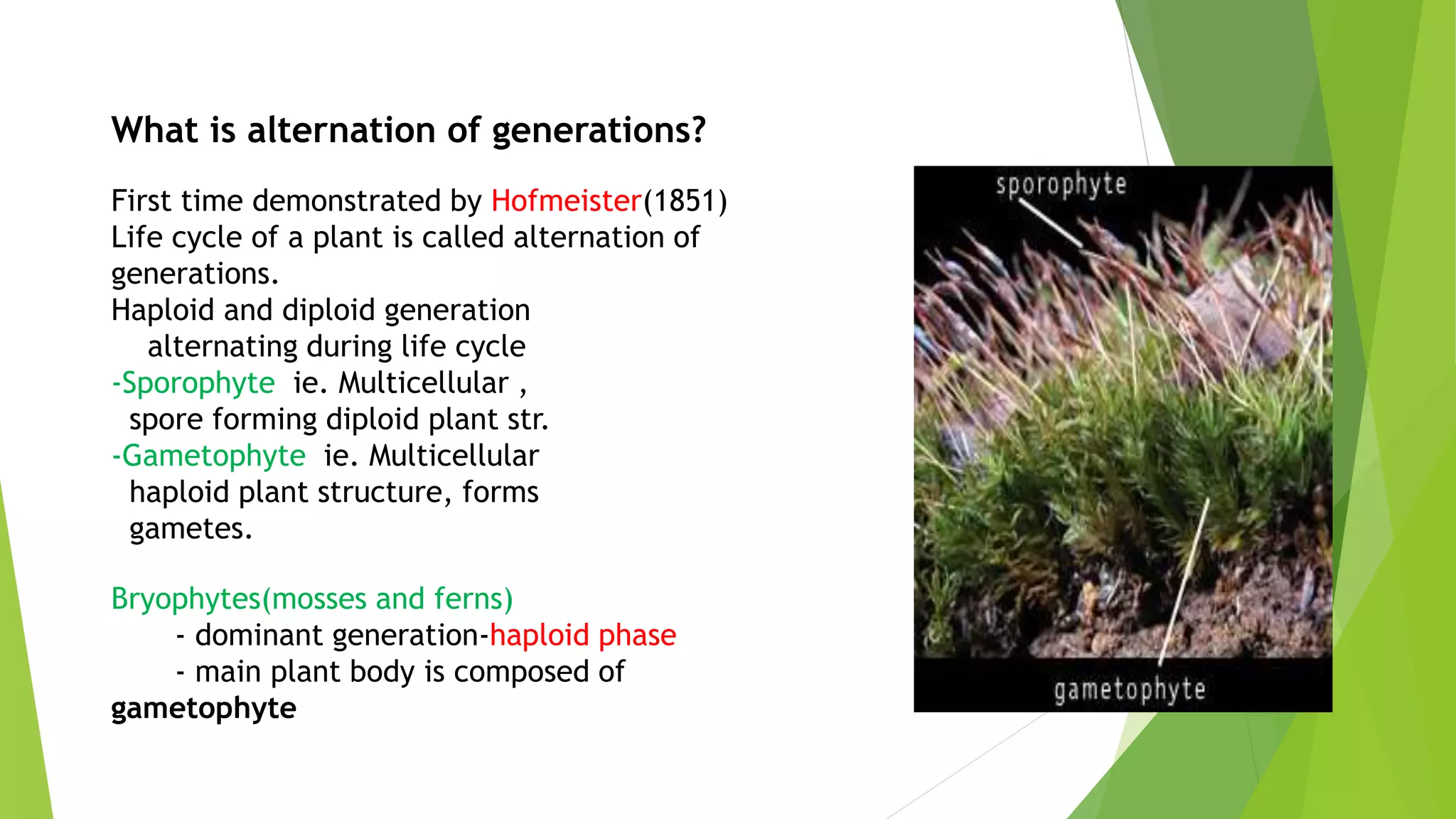
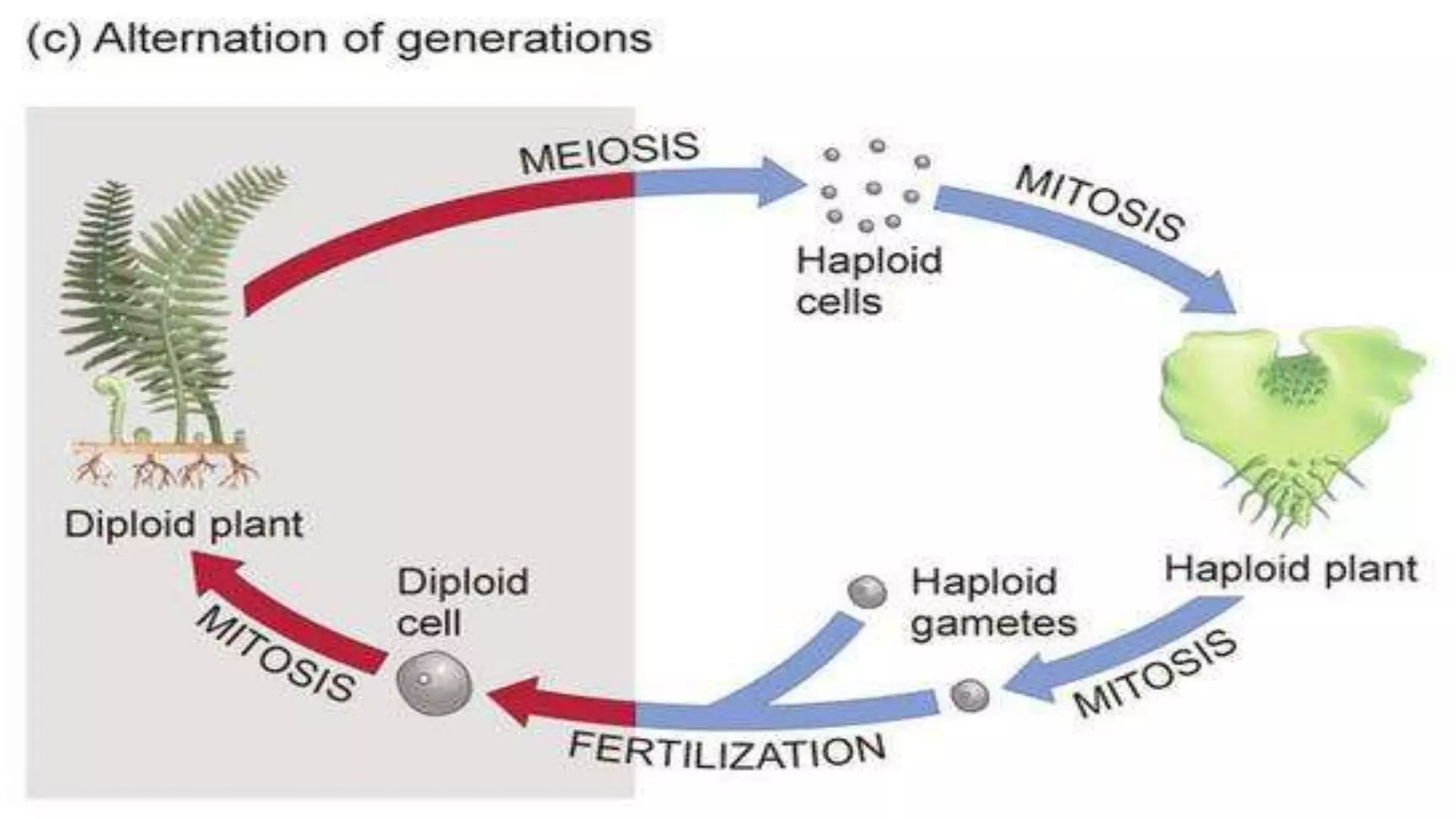
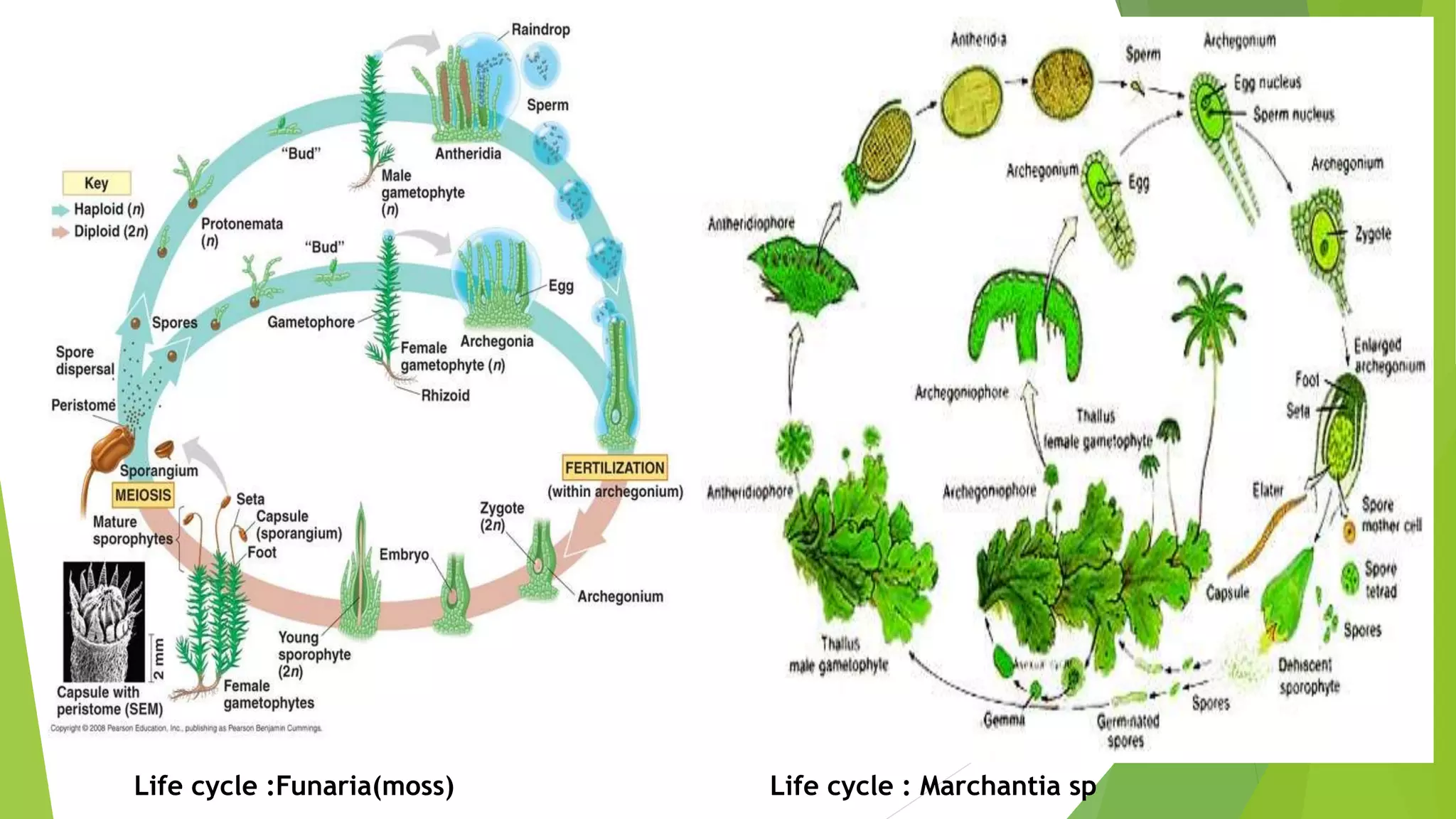
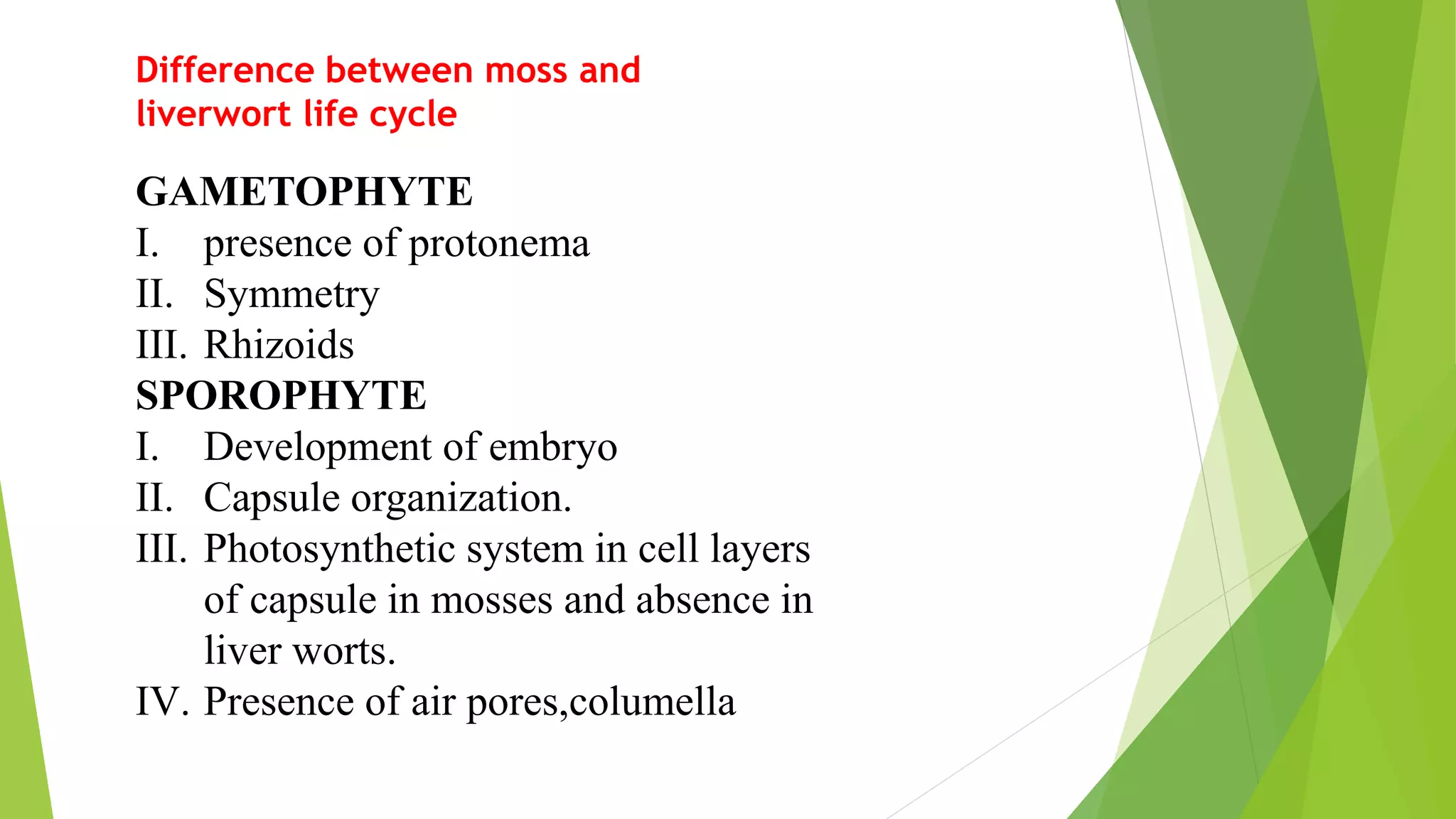
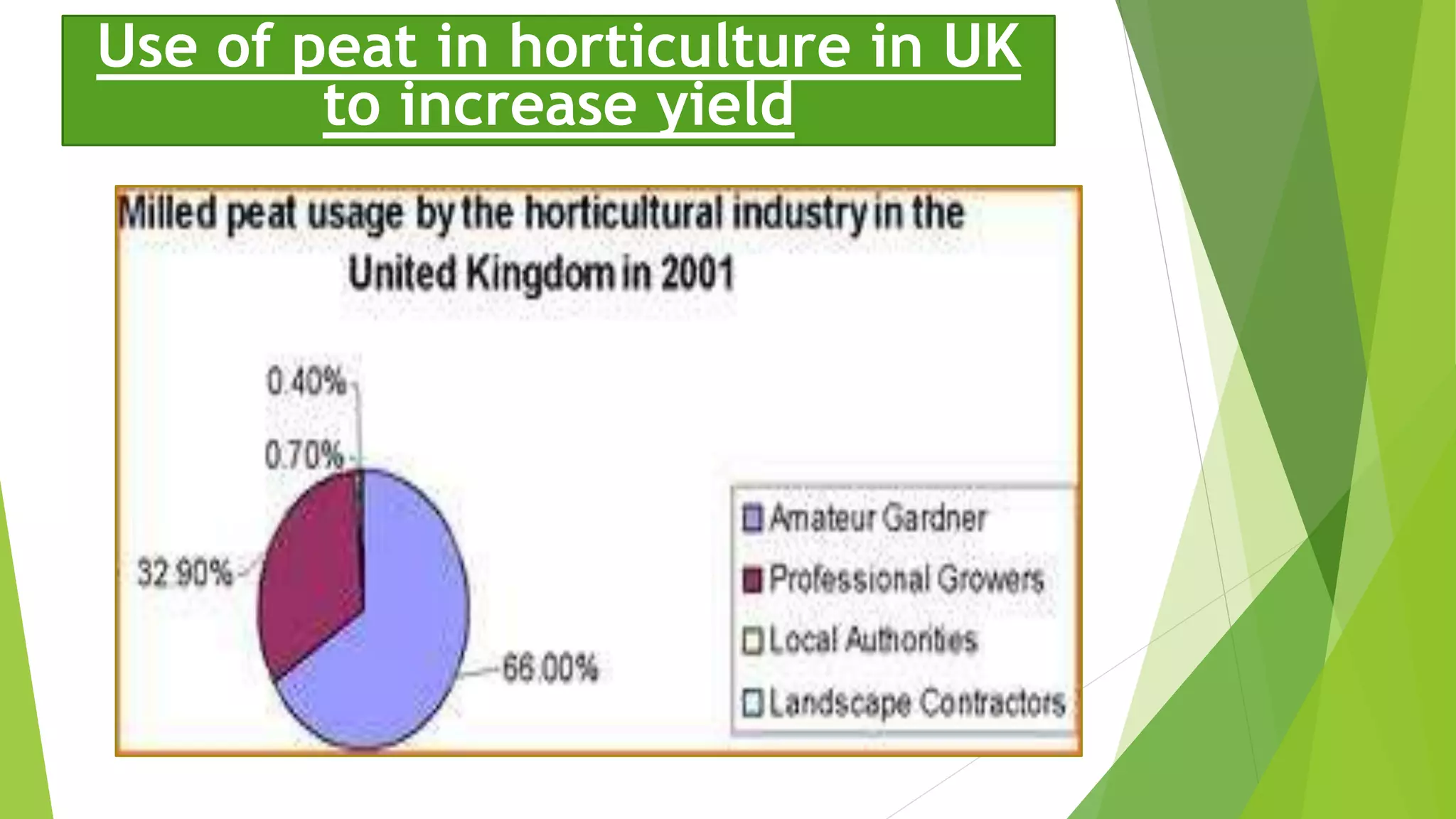
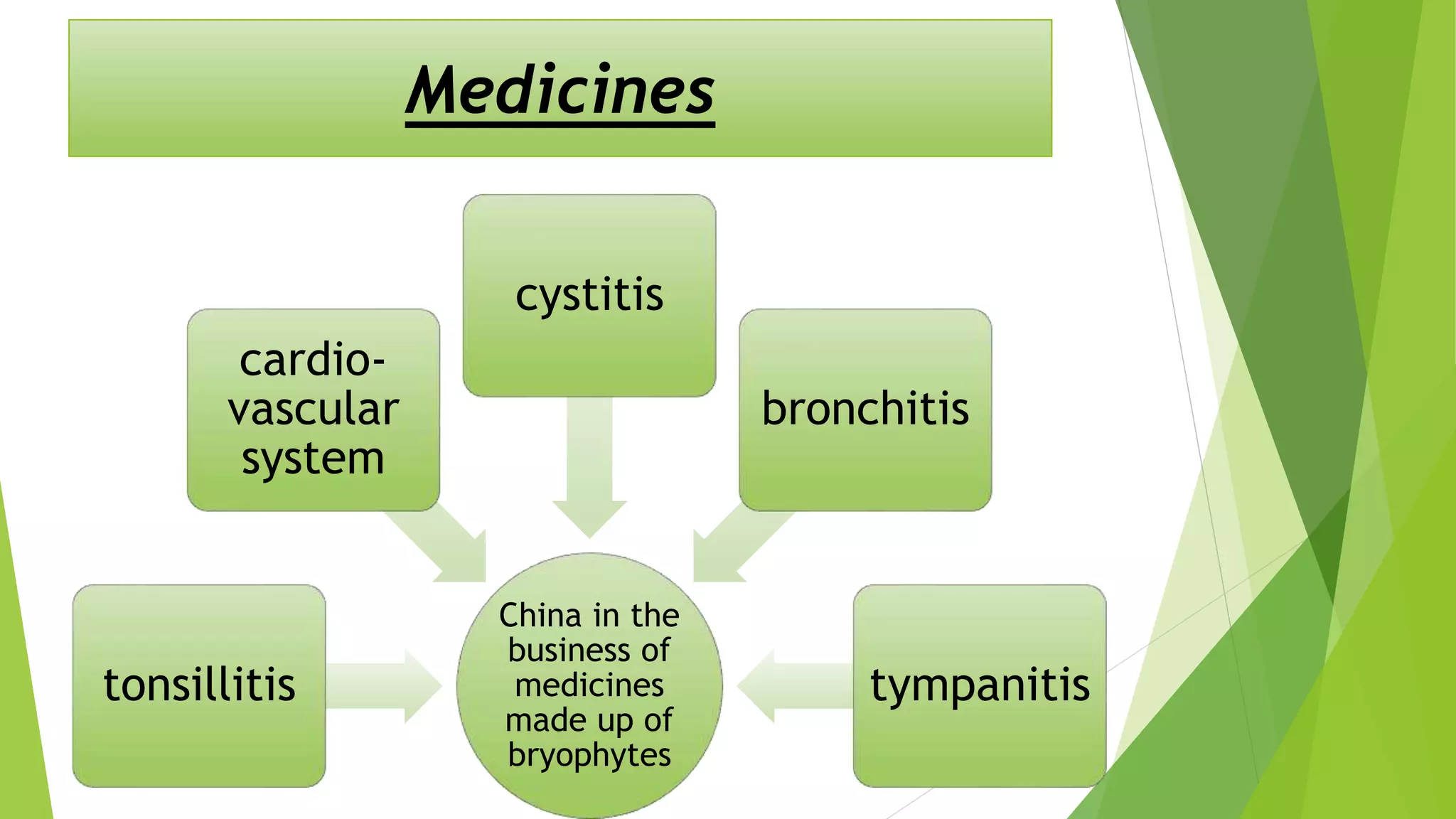
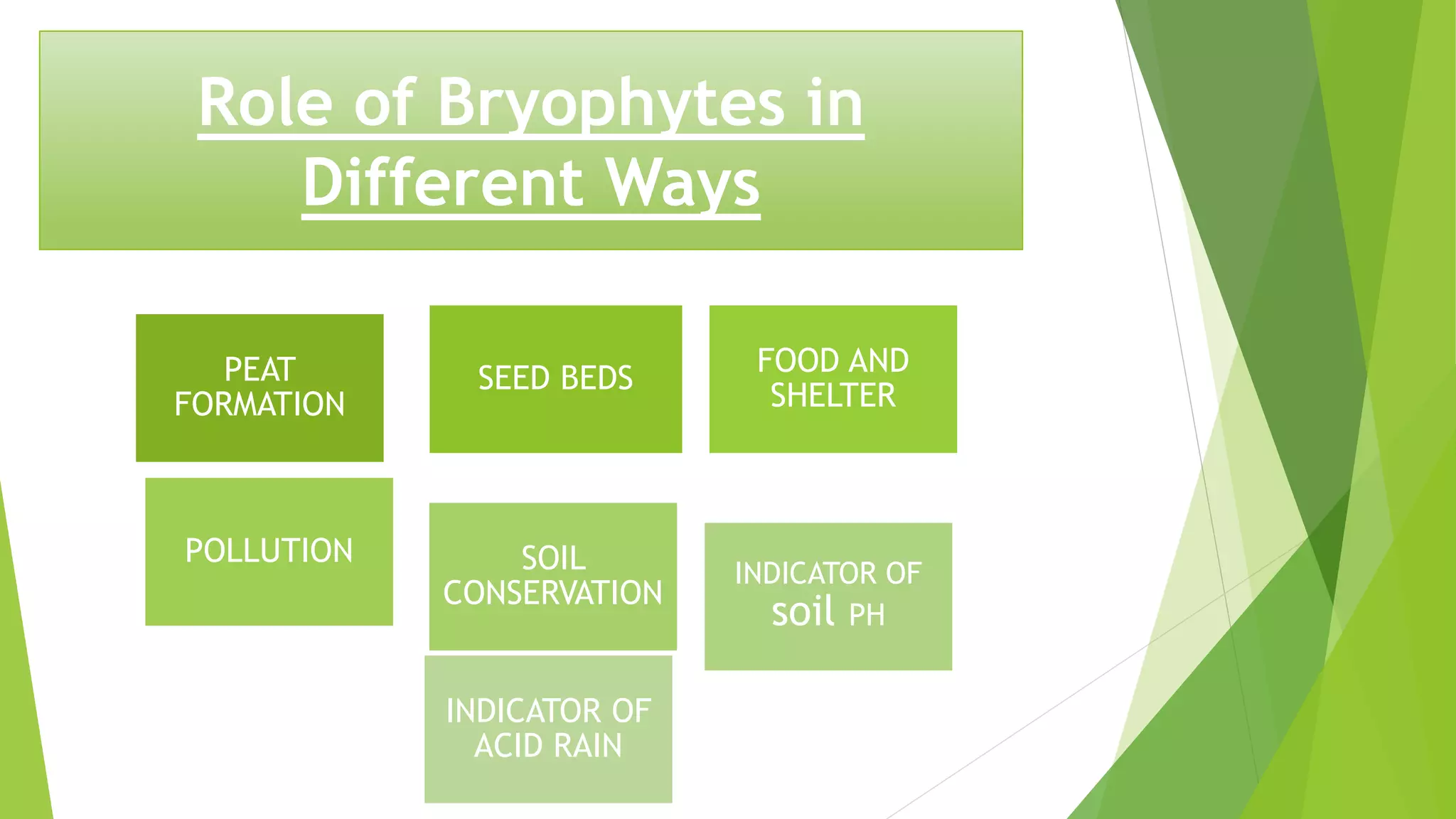
Bryophytes are the oldest land plants and include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. They lack true vascular tissues and have non-lignified structures like rhizoids instead of roots. Bryophytes reproduce both sexually through the formation of gametes and asexually by forming spores. They exhibit alternation of generations where the haploid gametophyte generation is dominant. Bryophytes are ecologically important in forming peat, providing food and shelter, and indicating soil pH and acid rain levels. They also have economic uses as fuel, horticultural additives, preservatives, construction materials, and traditional medicines.