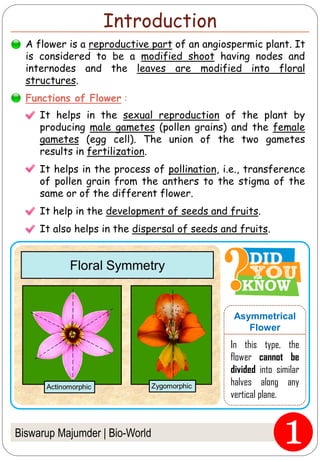
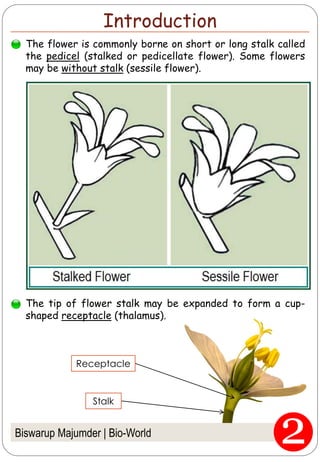
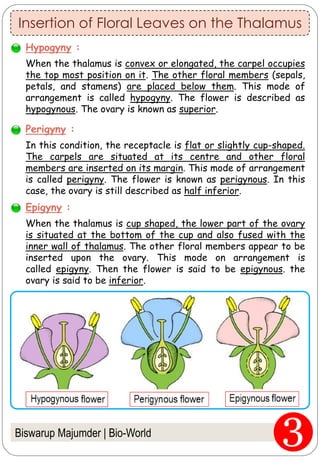
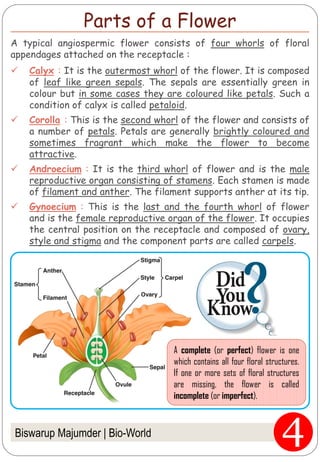
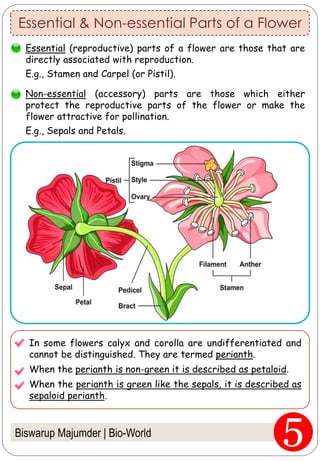
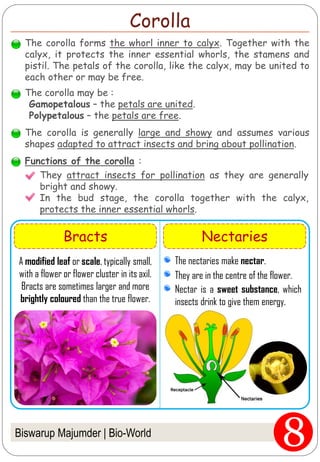
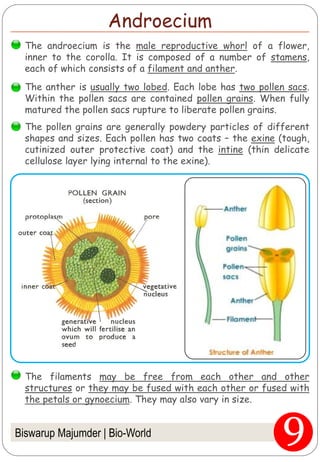
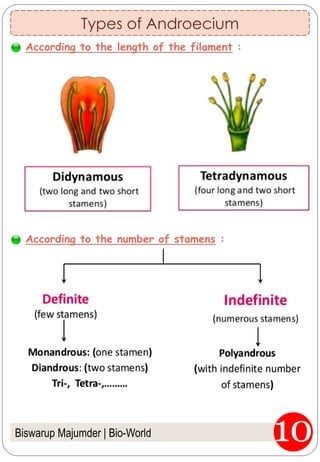
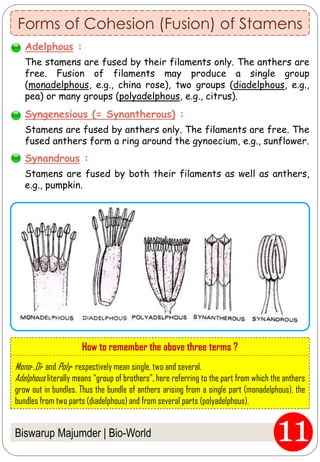
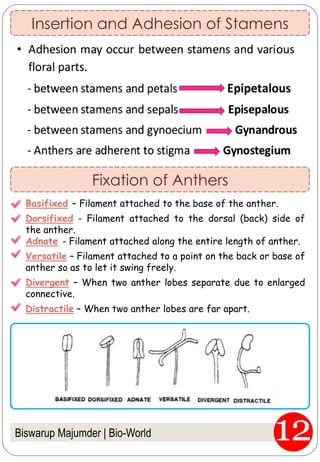
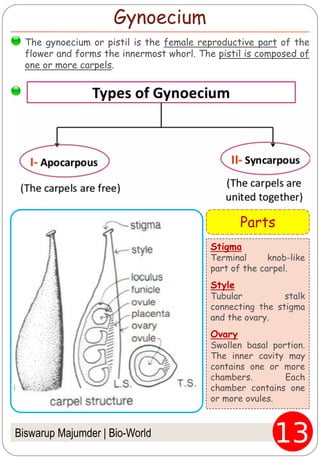
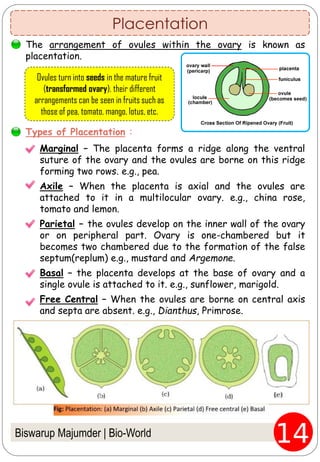
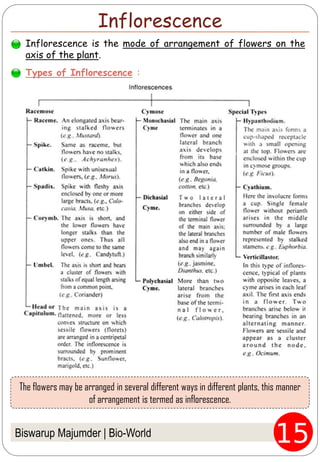
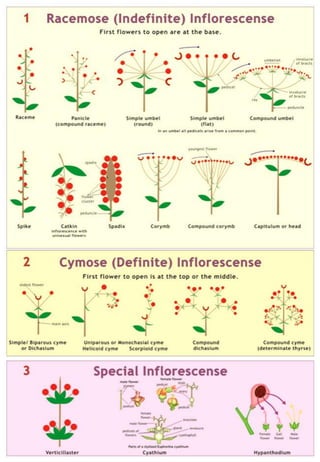
The document provides an in-depth overview of flowers, detailing their structure, functions, and types. It describes the various components of flowers, including the calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium, while explaining their roles in reproduction and pollination. Additionally, it addresses the concepts of complete versus incomplete flowers, as well as the different arrangements of floral structures and inflorescence patterns.