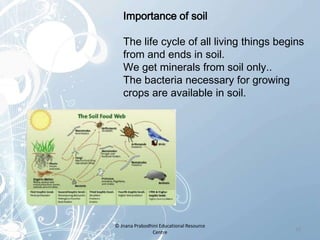
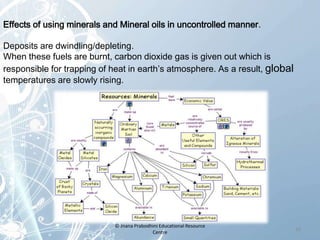
The document discusses natural resources and their classification. It defines natural resources as things through which man's basic needs are met, including air, water, soil, minerals, plants and animals. Renewable resources like plants and animals can reproduce and regrow when destroyed. Non-renewable resources like air, water and soil cannot be reproduced and their supplies are limited. The document emphasizes the importance of conserving both renewable and non-renewable natural resources and provides suggestions for reducing pollution and practicing sustainable use.