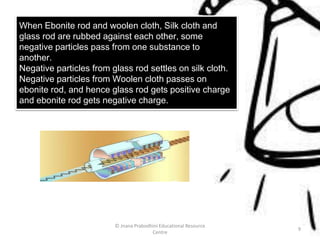
Static electric charge develops when objects are rubbed together, such as a plastic comb rubbed through hair. This causes an imbalance of electric particles between the two objects. Glass develops a positive charge when rubbed with silk, while ebonite becomes negatively charged when rubbed with wool. Like charges repel each other, while unlike charges attract. The electroscope can detect electric charge by the separation of its gold leaves when a charged object touches it.