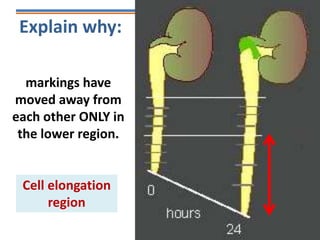
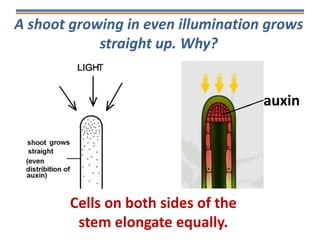
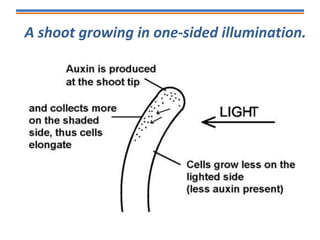
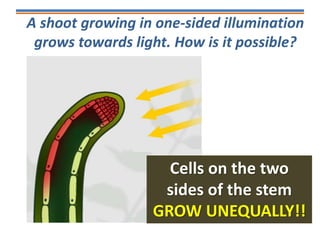
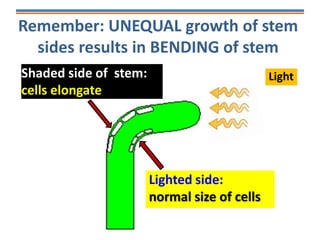
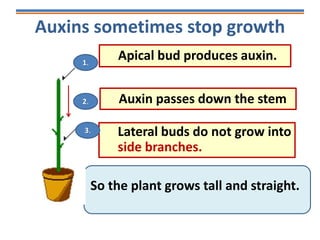
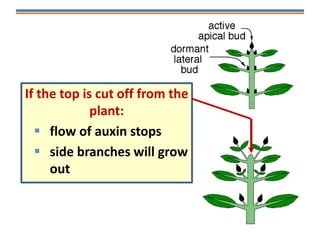
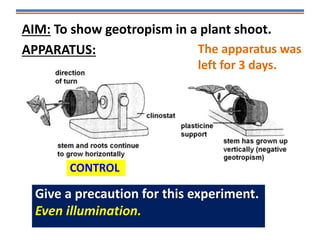
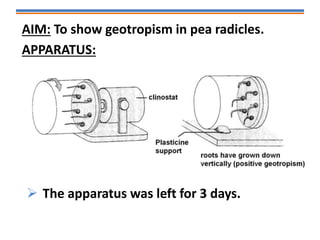
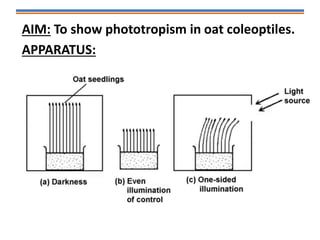
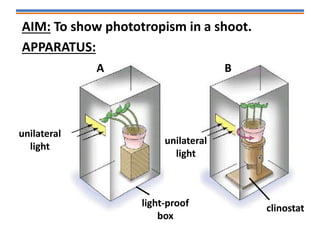
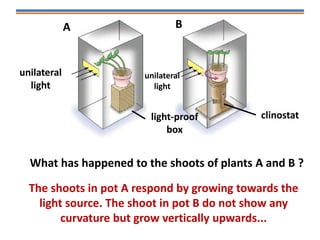
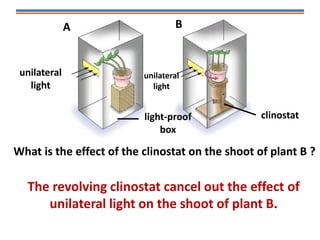
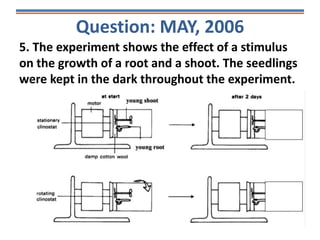
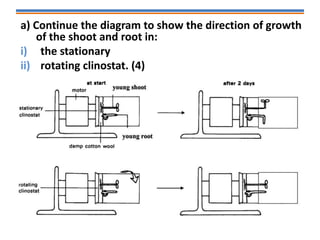
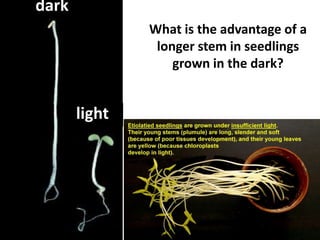
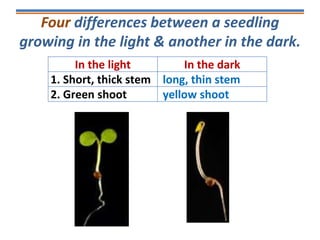
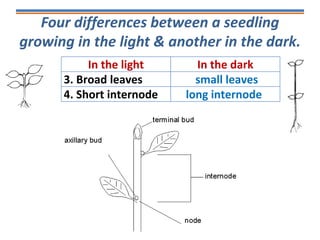
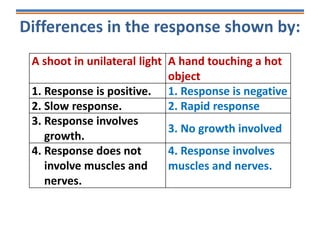
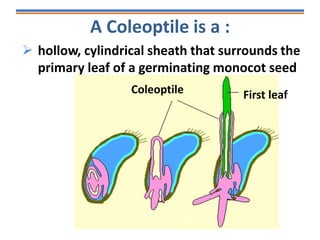
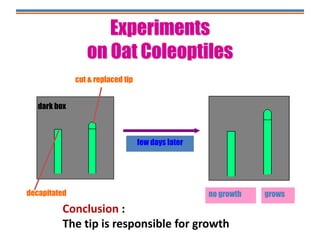
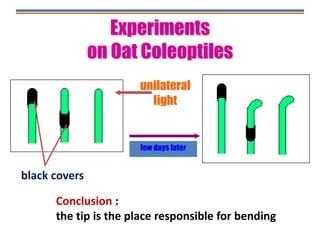
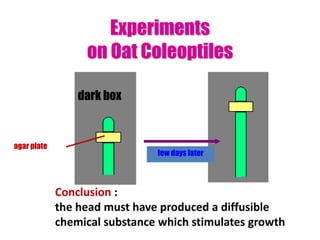
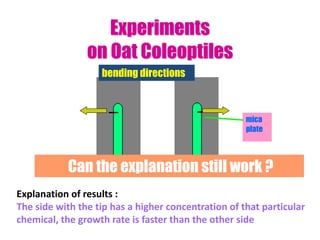
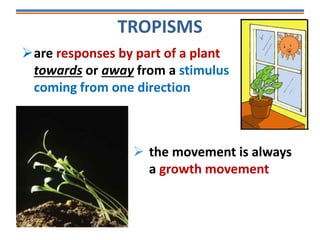
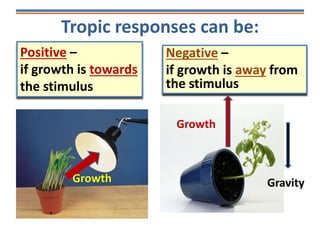
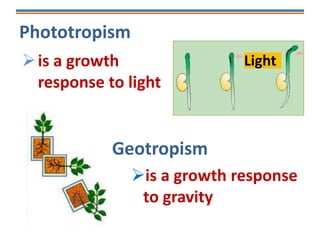
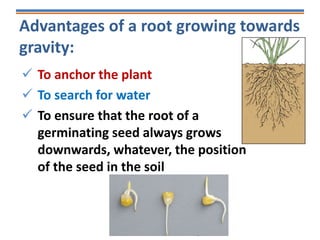
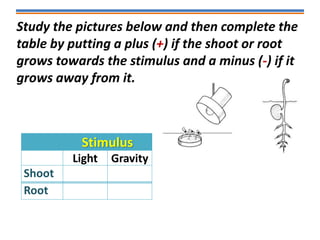
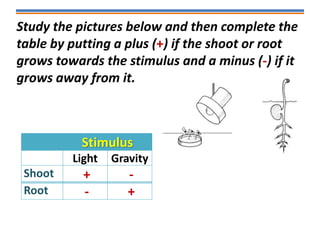
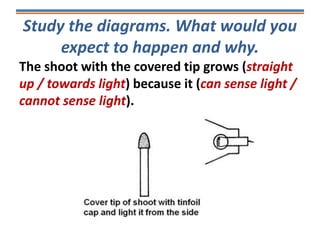
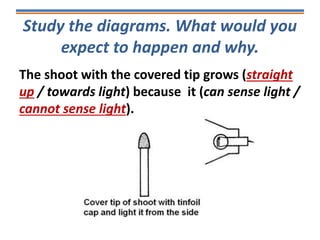
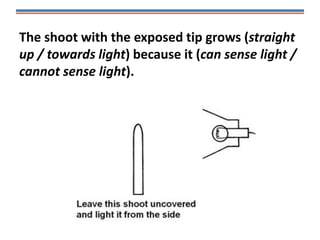
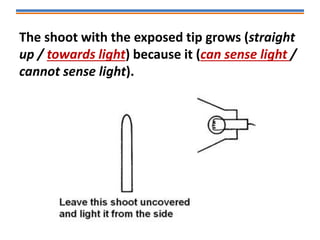
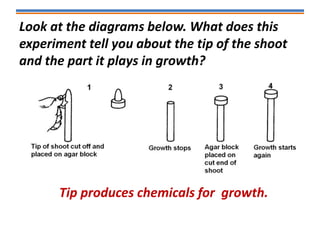
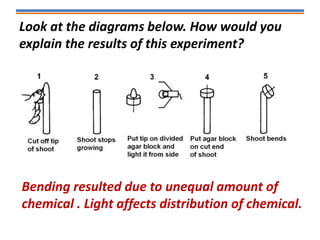
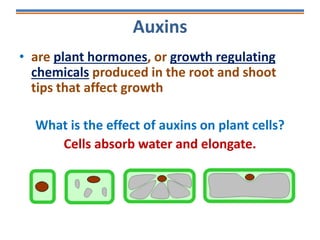
Tropisms refer to directional growth responses in plants. These include phototropism, the growth response to light, and geotropism, the growth response to gravity. In phototropism, shoots grow towards light (positive phototropism) while roots grow away from light (negative phototropism). In geotropism, shoots grow away from gravity (negative geotropism) while roots grow towards gravity (positive geotropism). These directional growth responses are regulated by the plant hormone auxin.







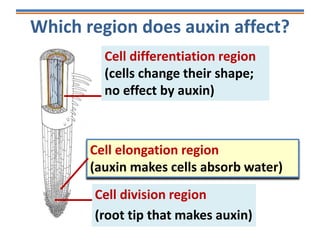
![Three regions of a root tip
Cell division region
Cell
differentiation
region
Cell elongation
region
[Cells become specialised]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tropisms-150215093929-conversion-gate02/85/Tropisms-21-320.jpg)