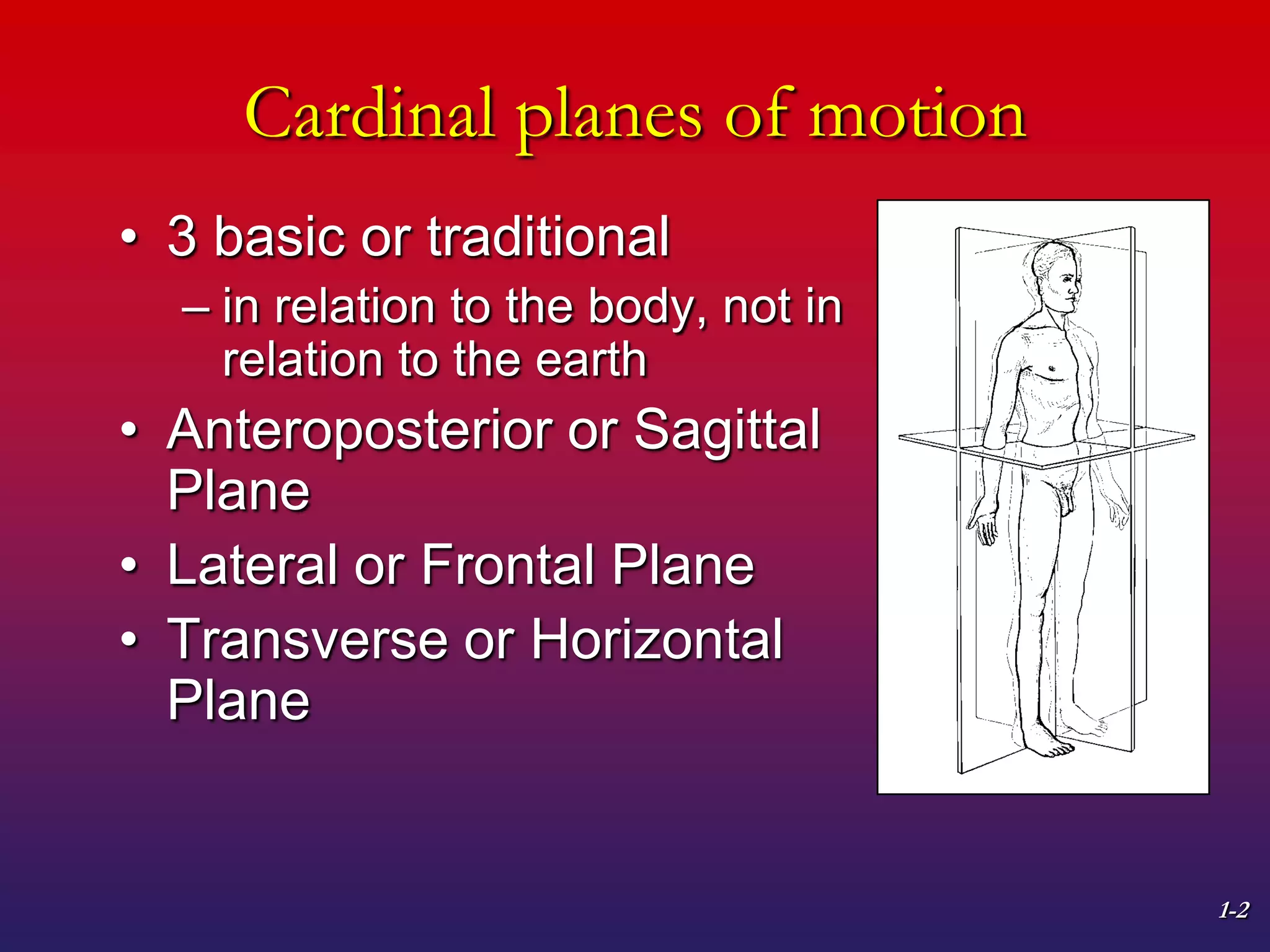
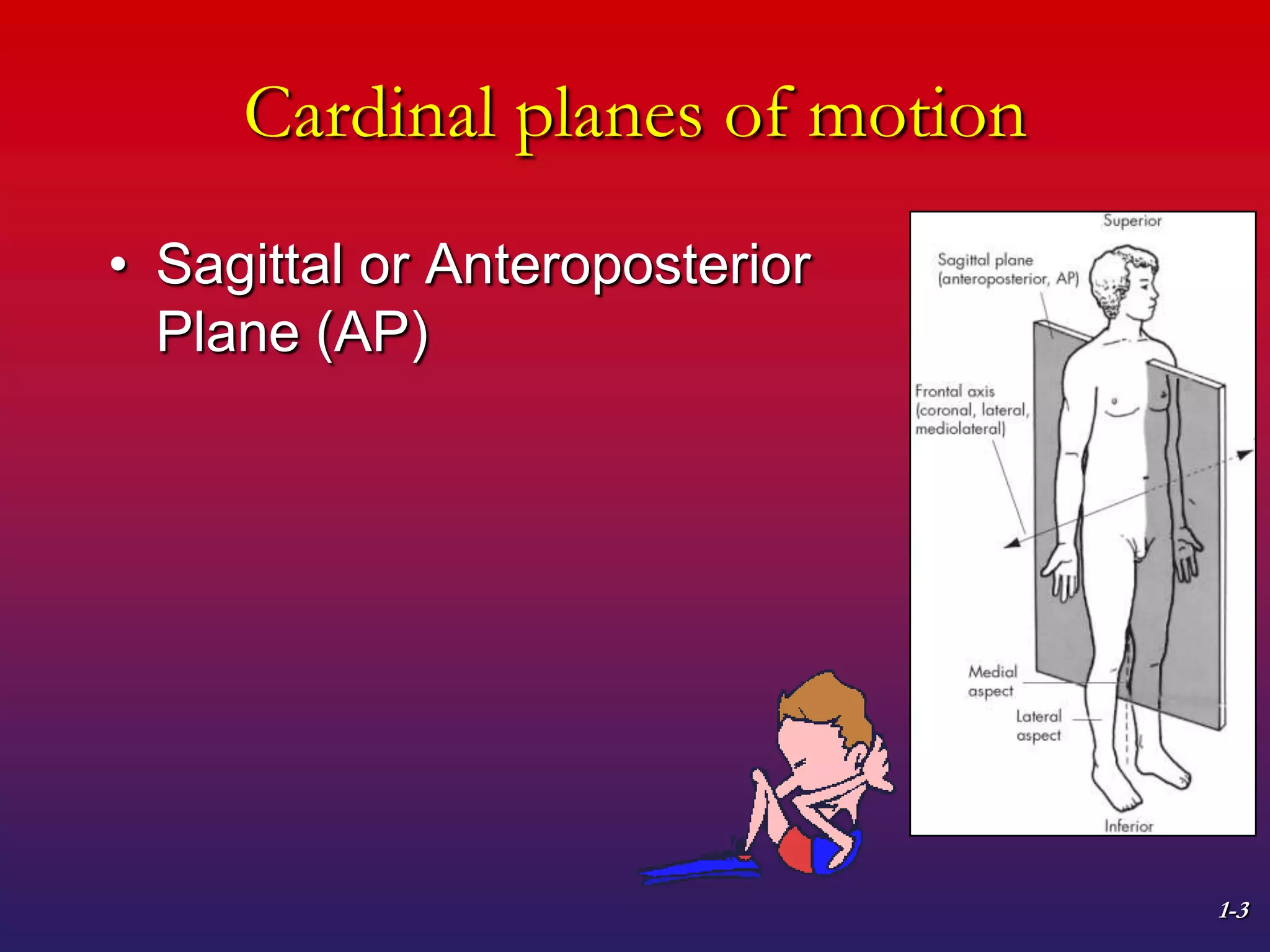
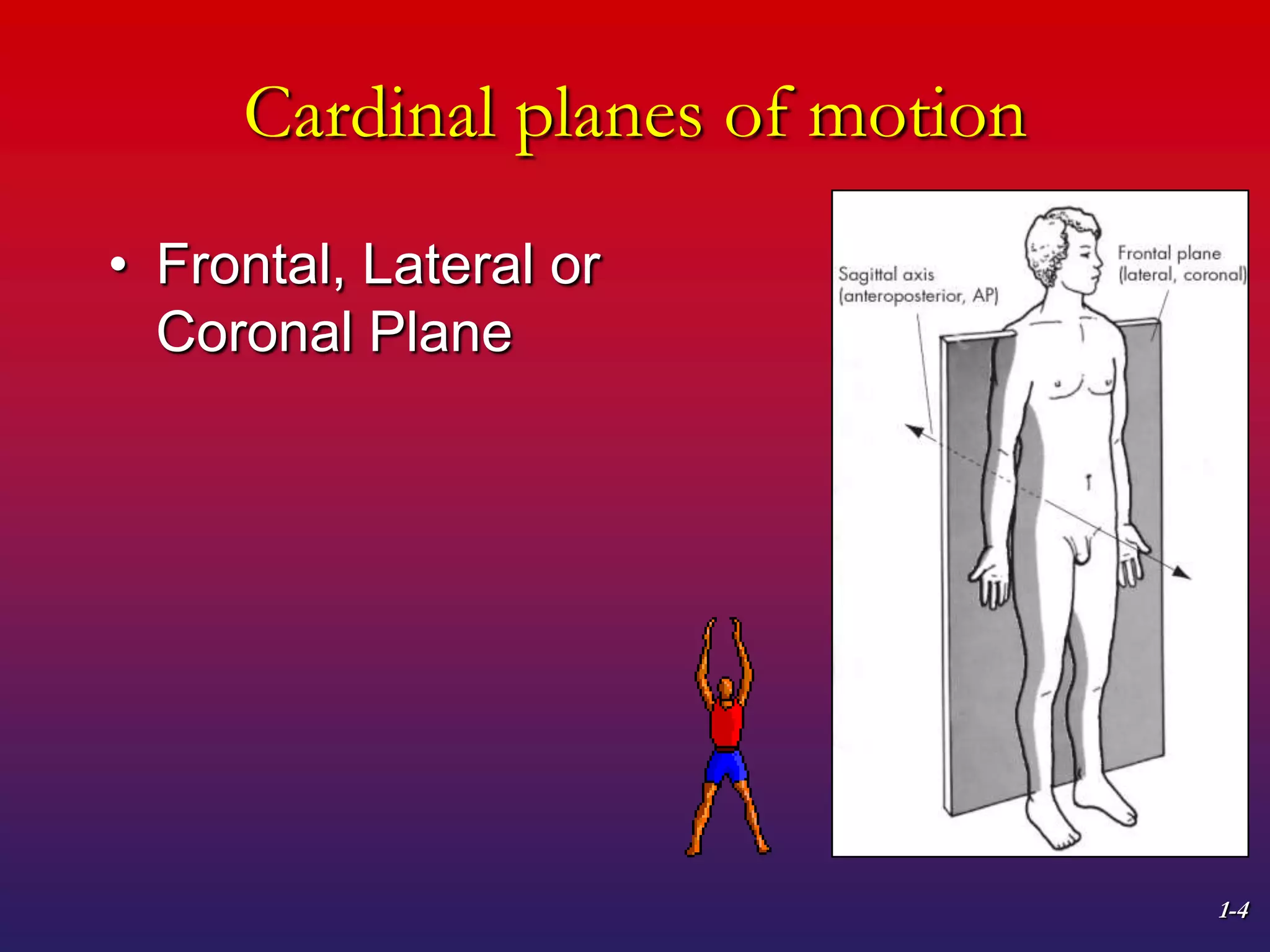
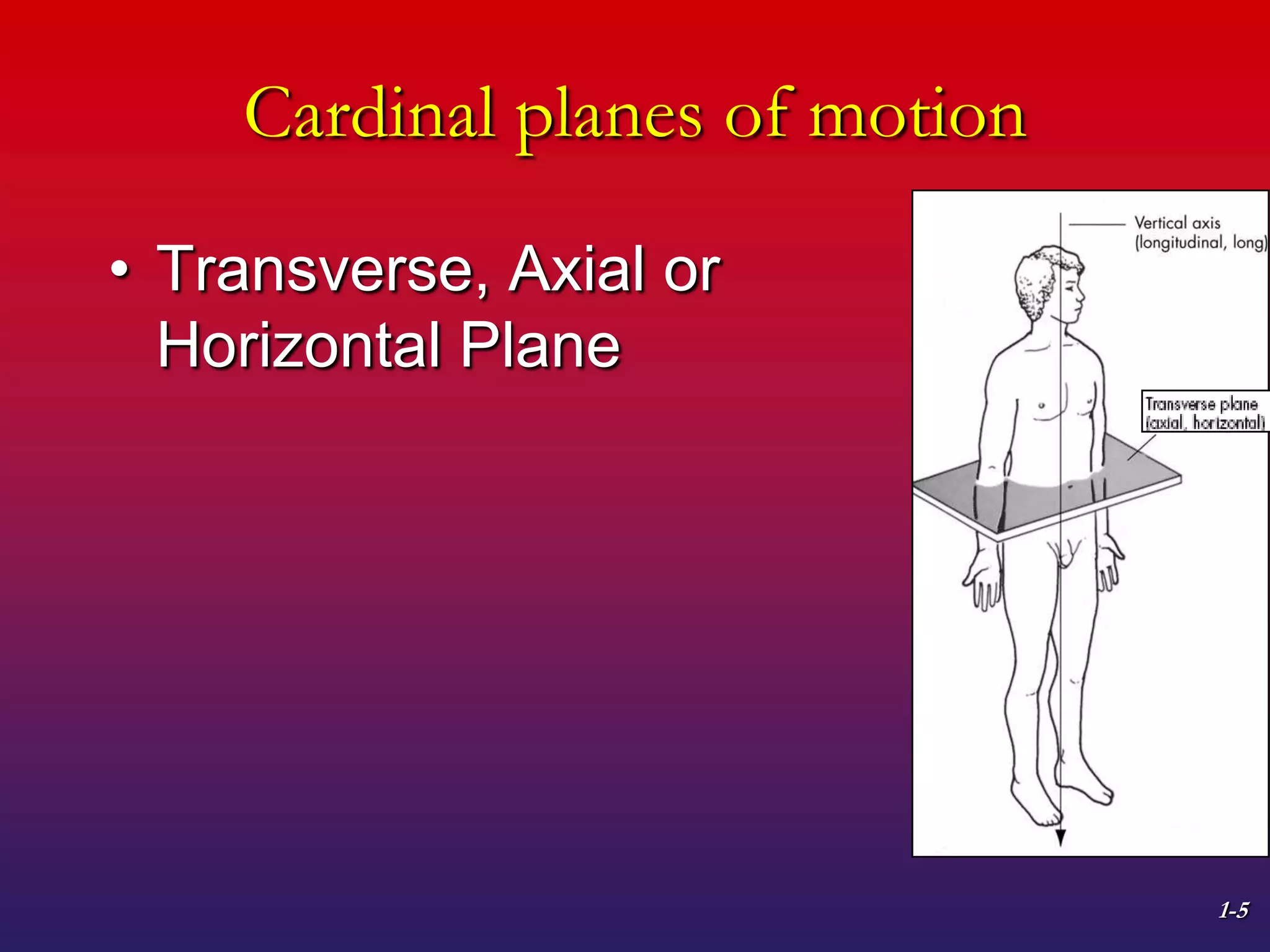
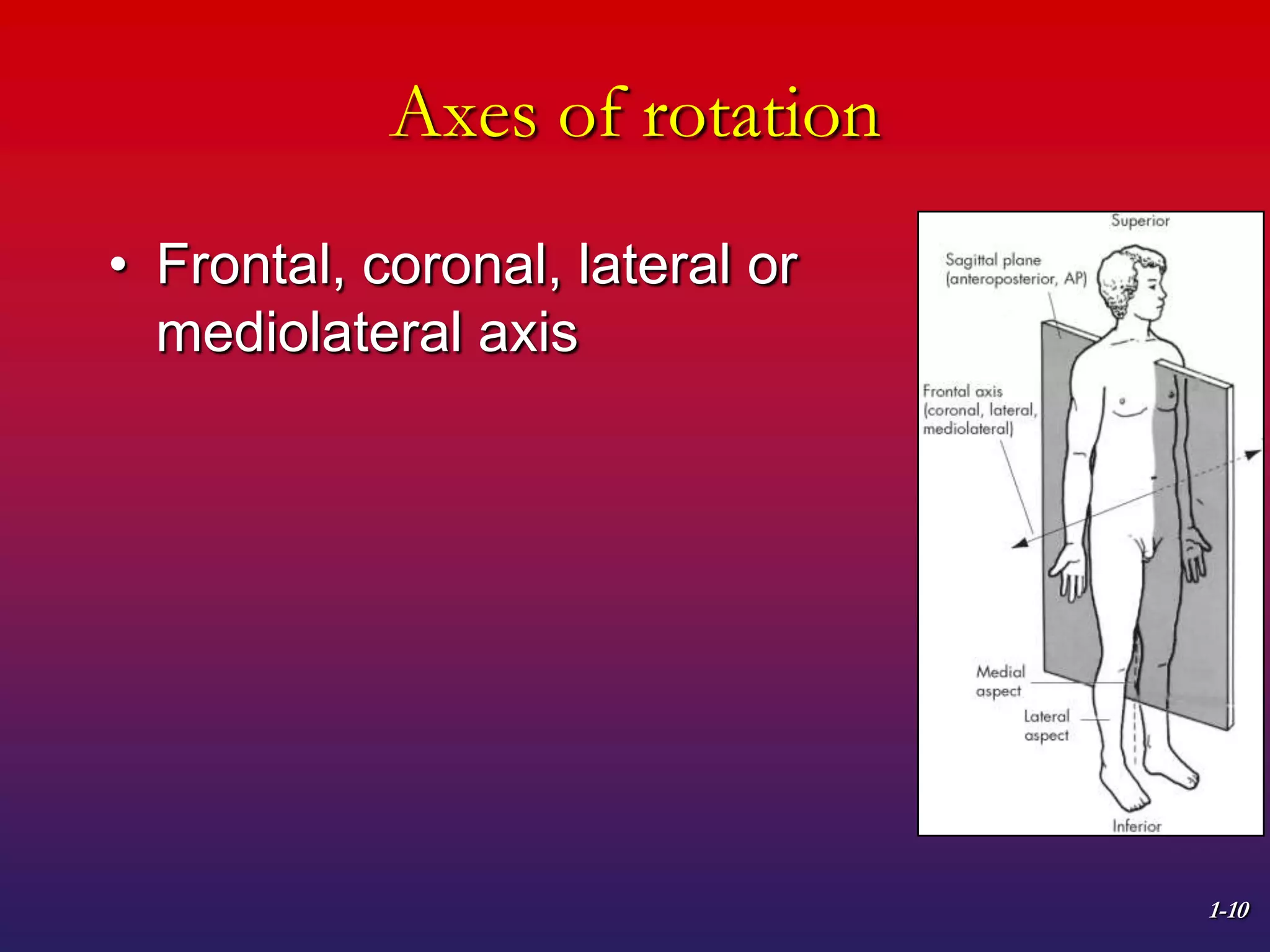
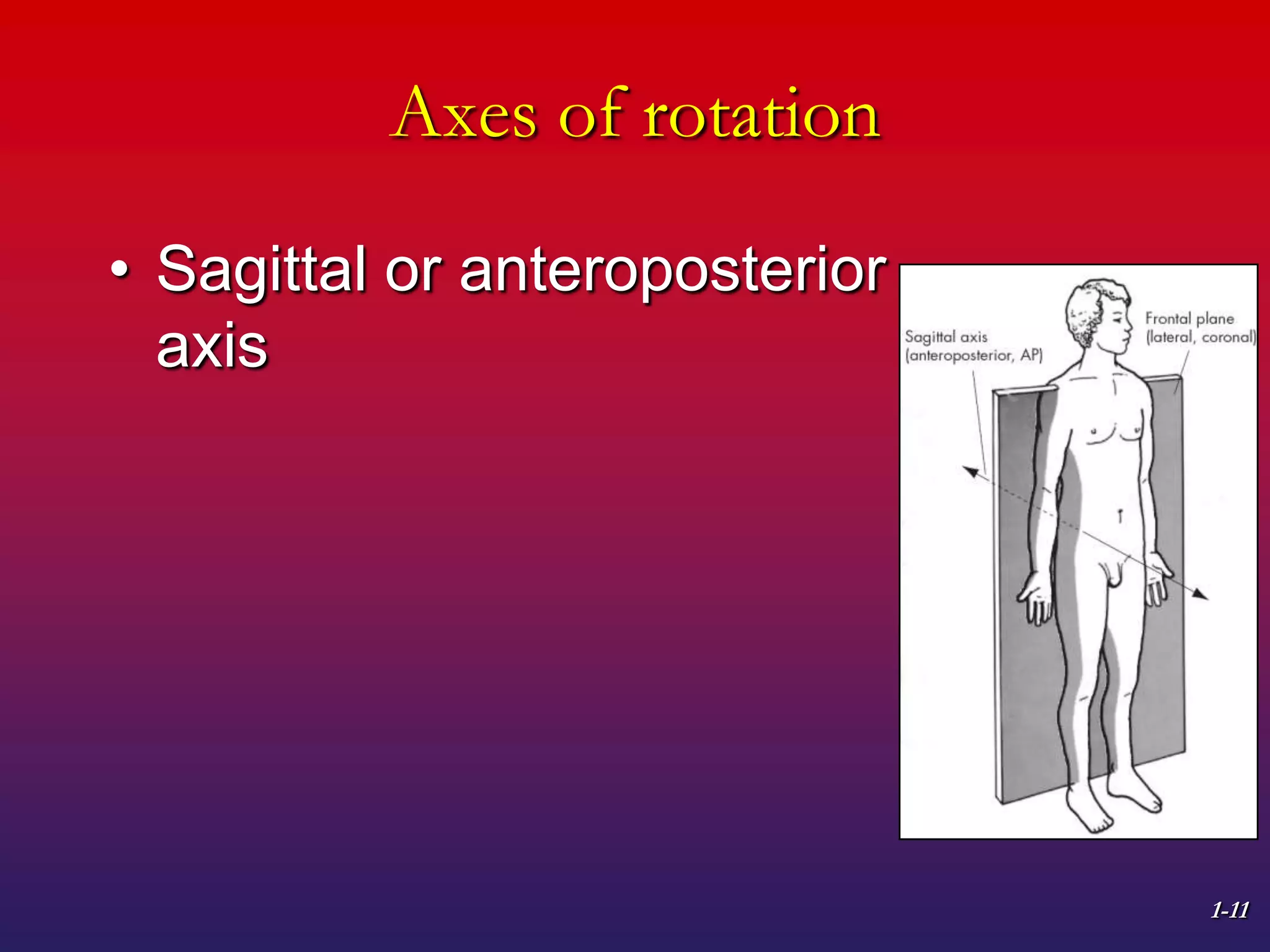
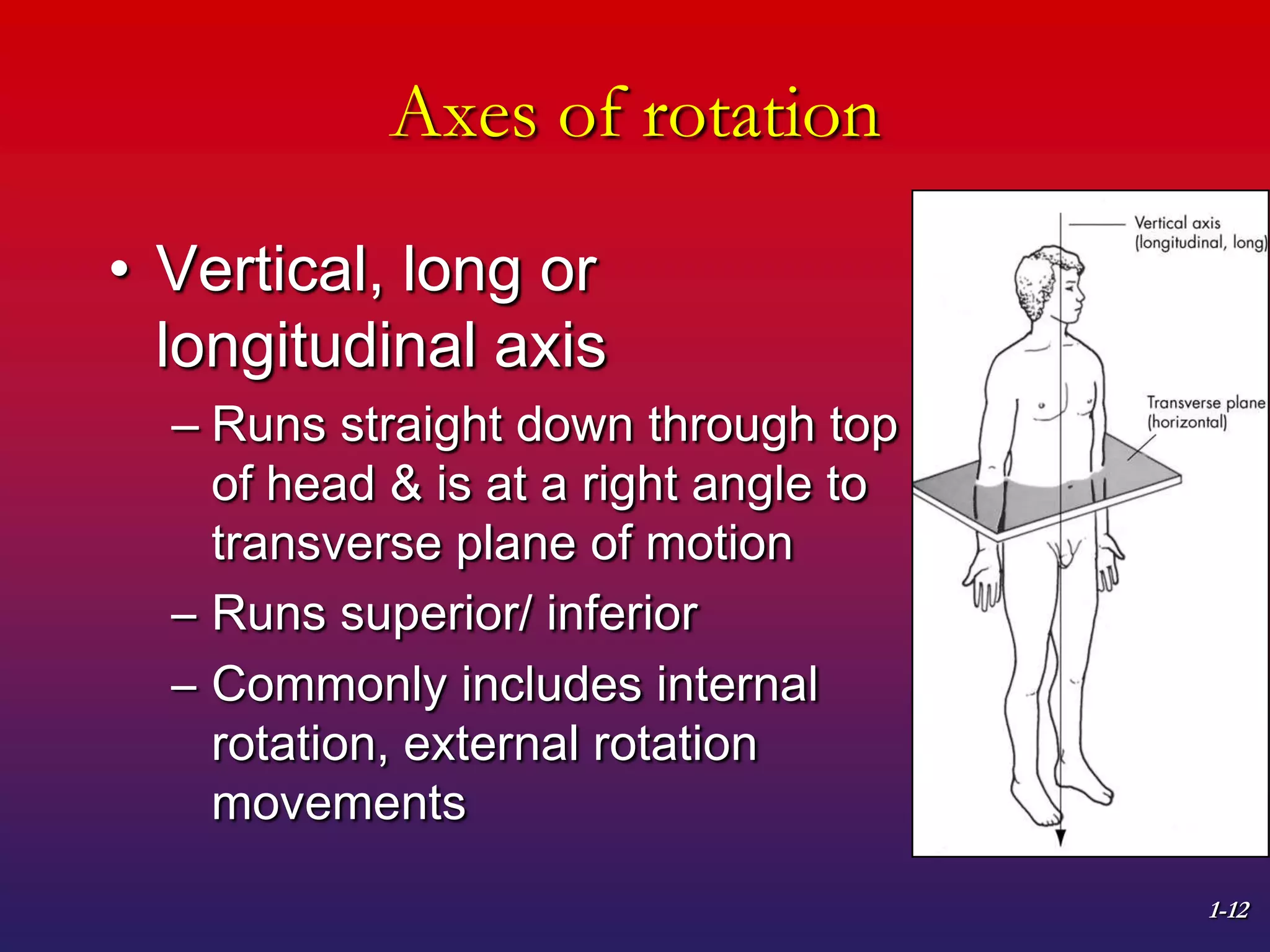
1. The document discusses planes of motion, axes of rotation, and the cardinal planes which are the three basic planes used to describe human movement.
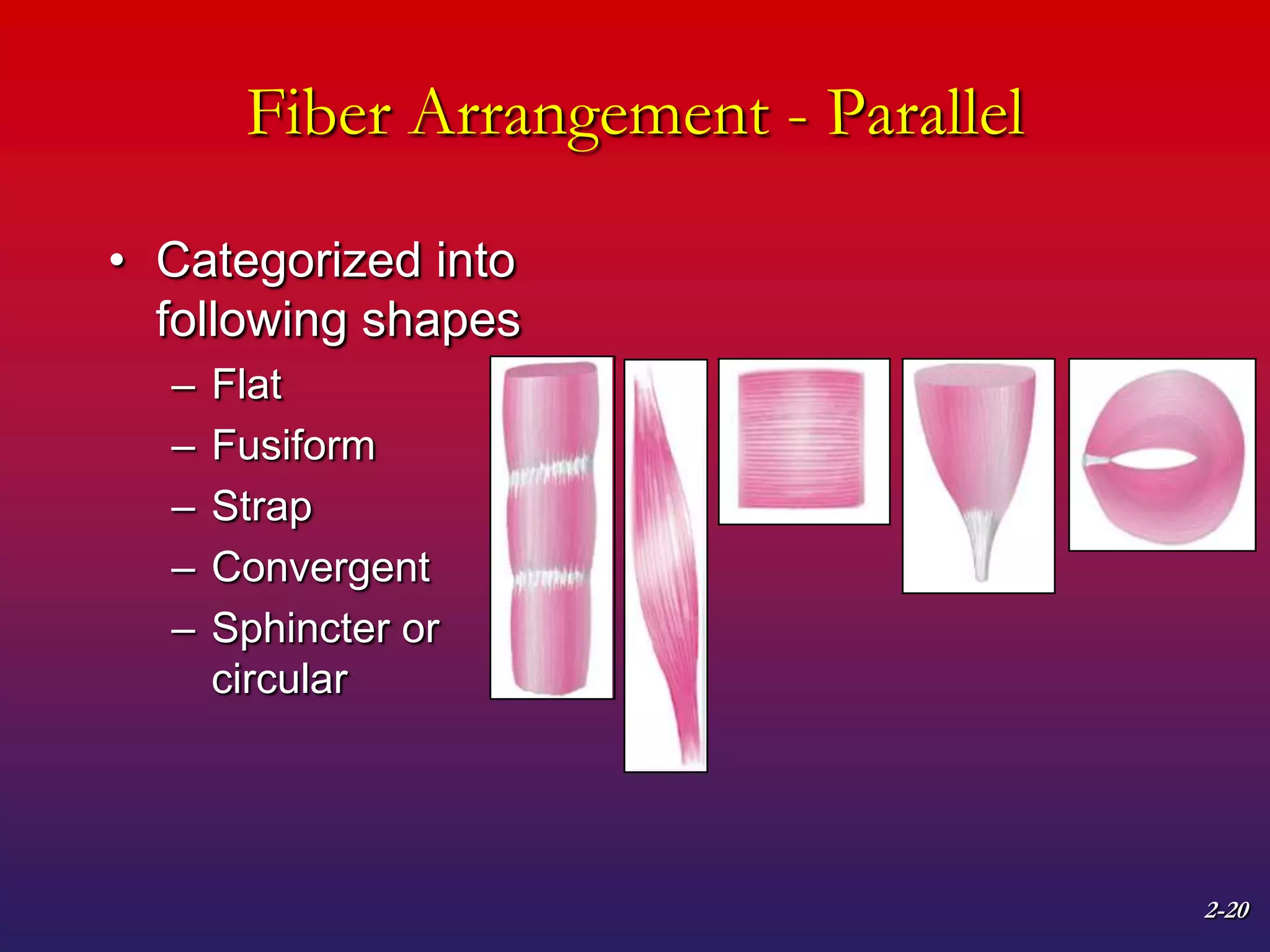
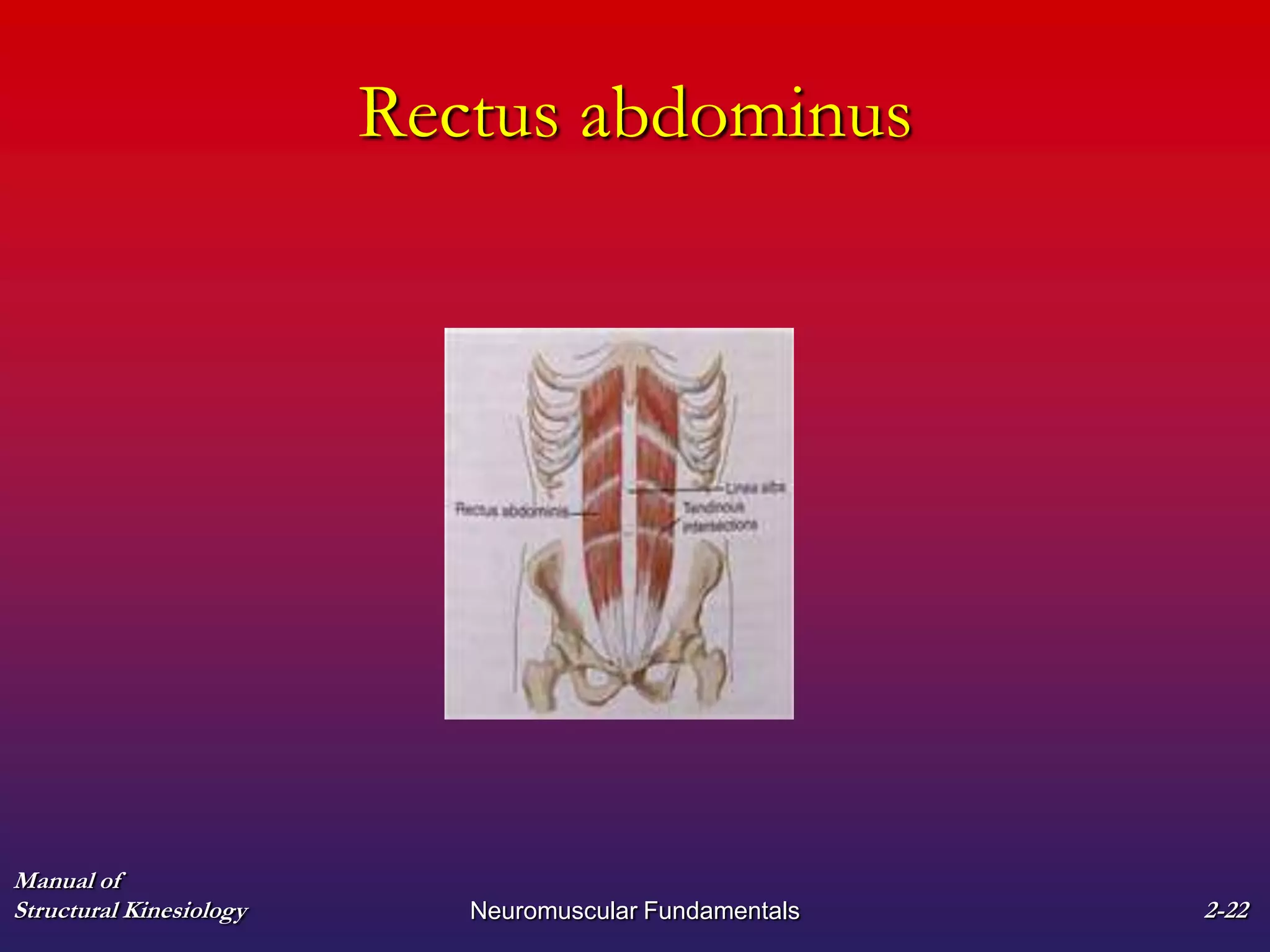
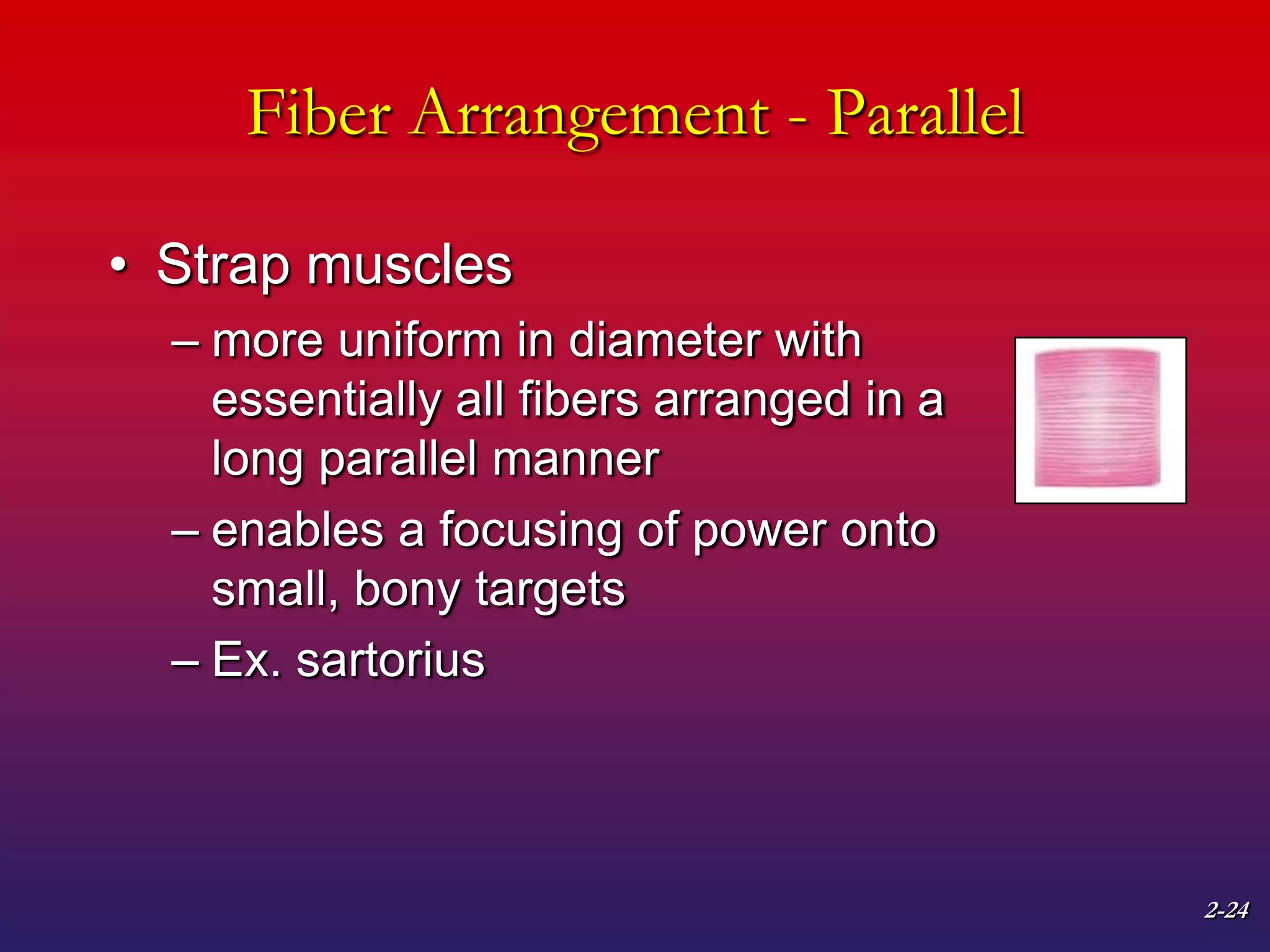
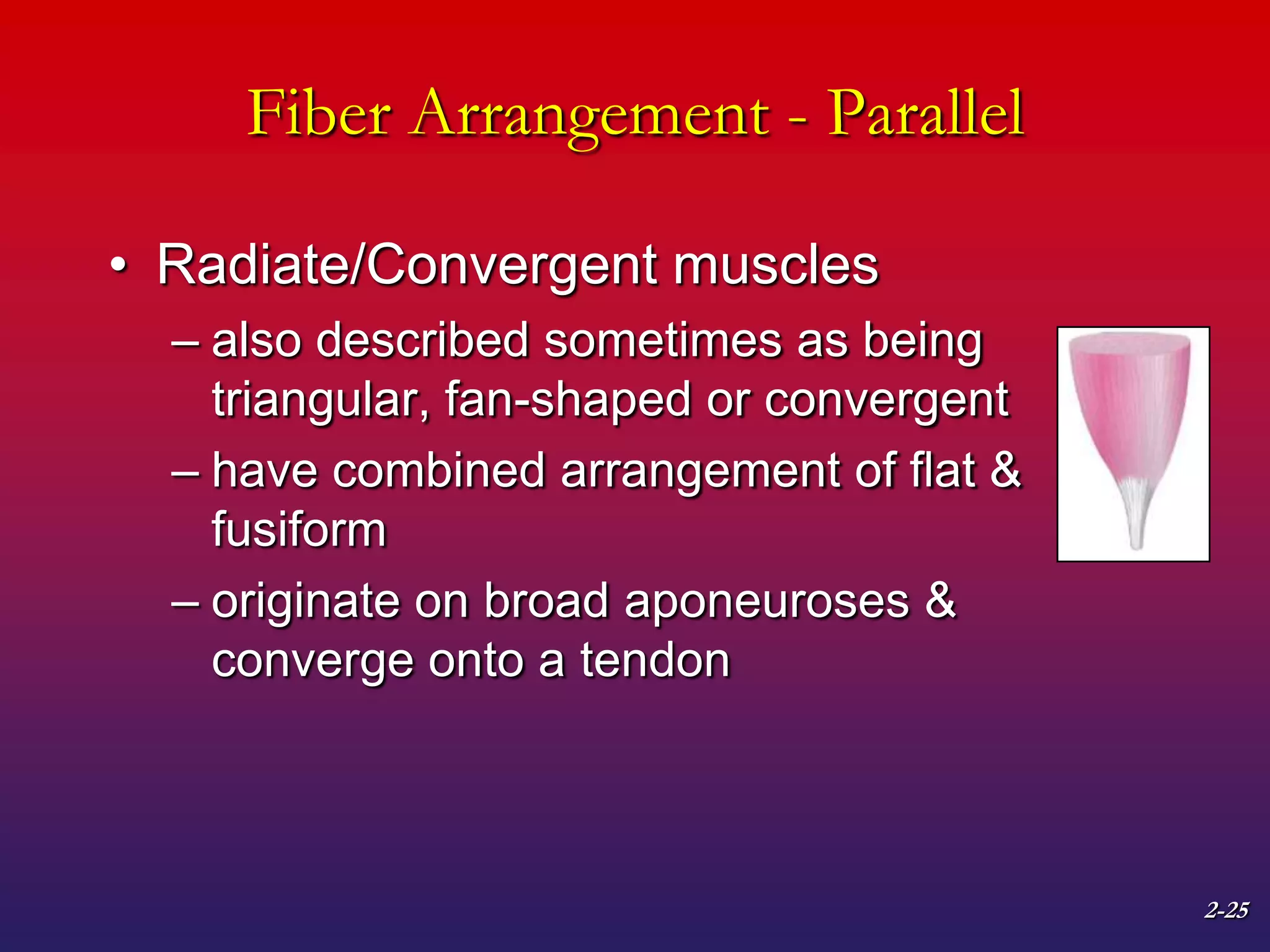
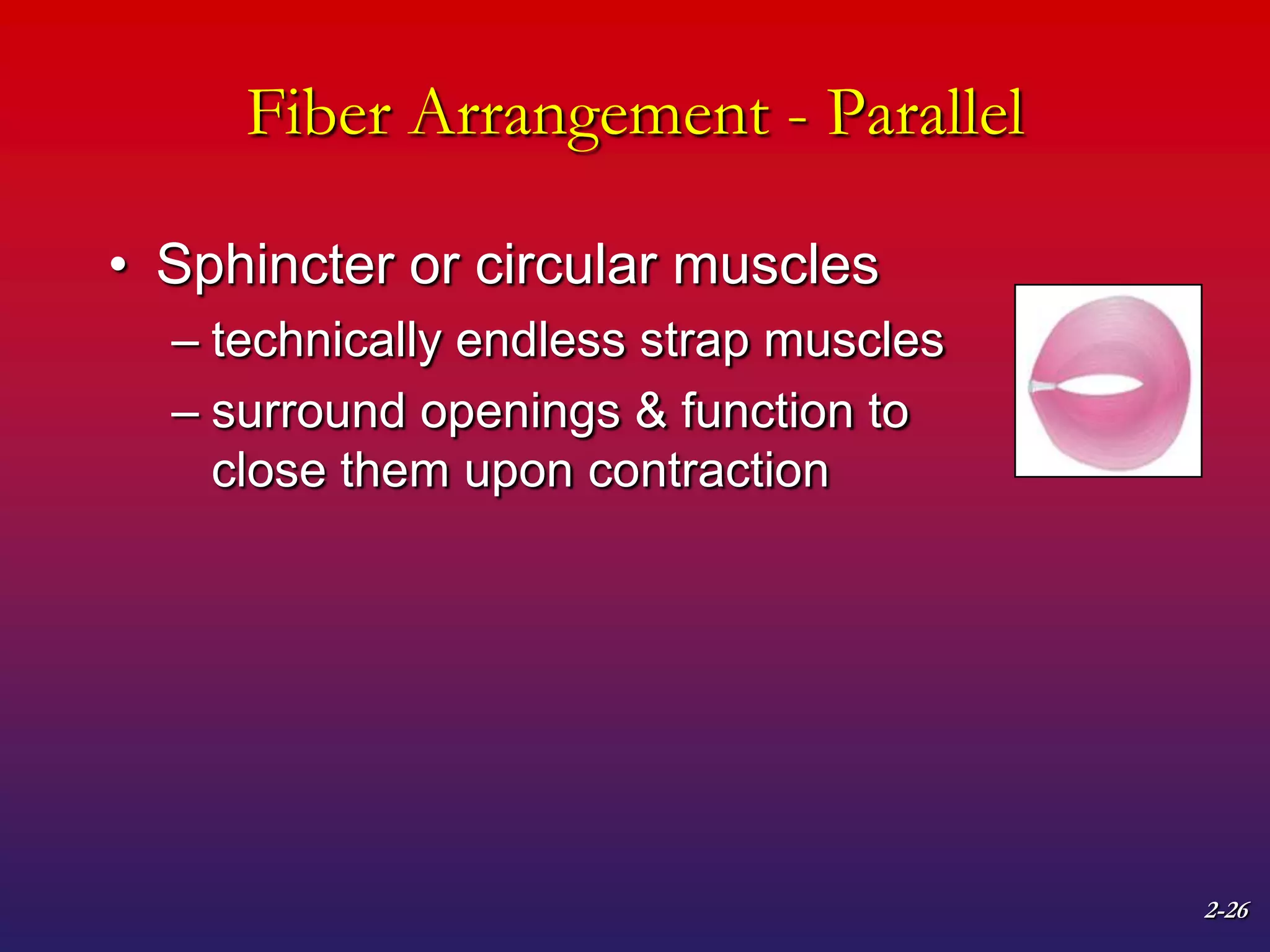
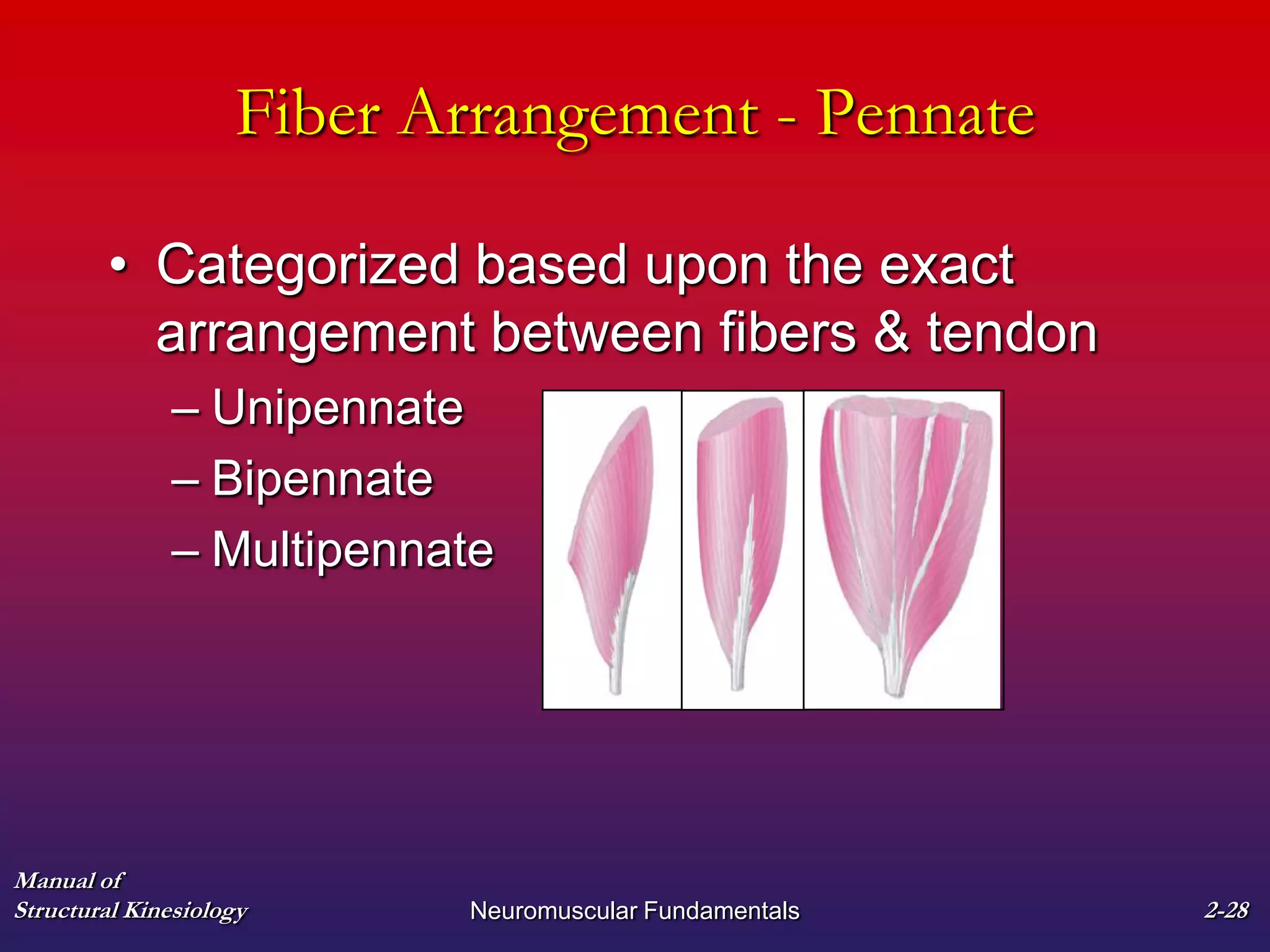
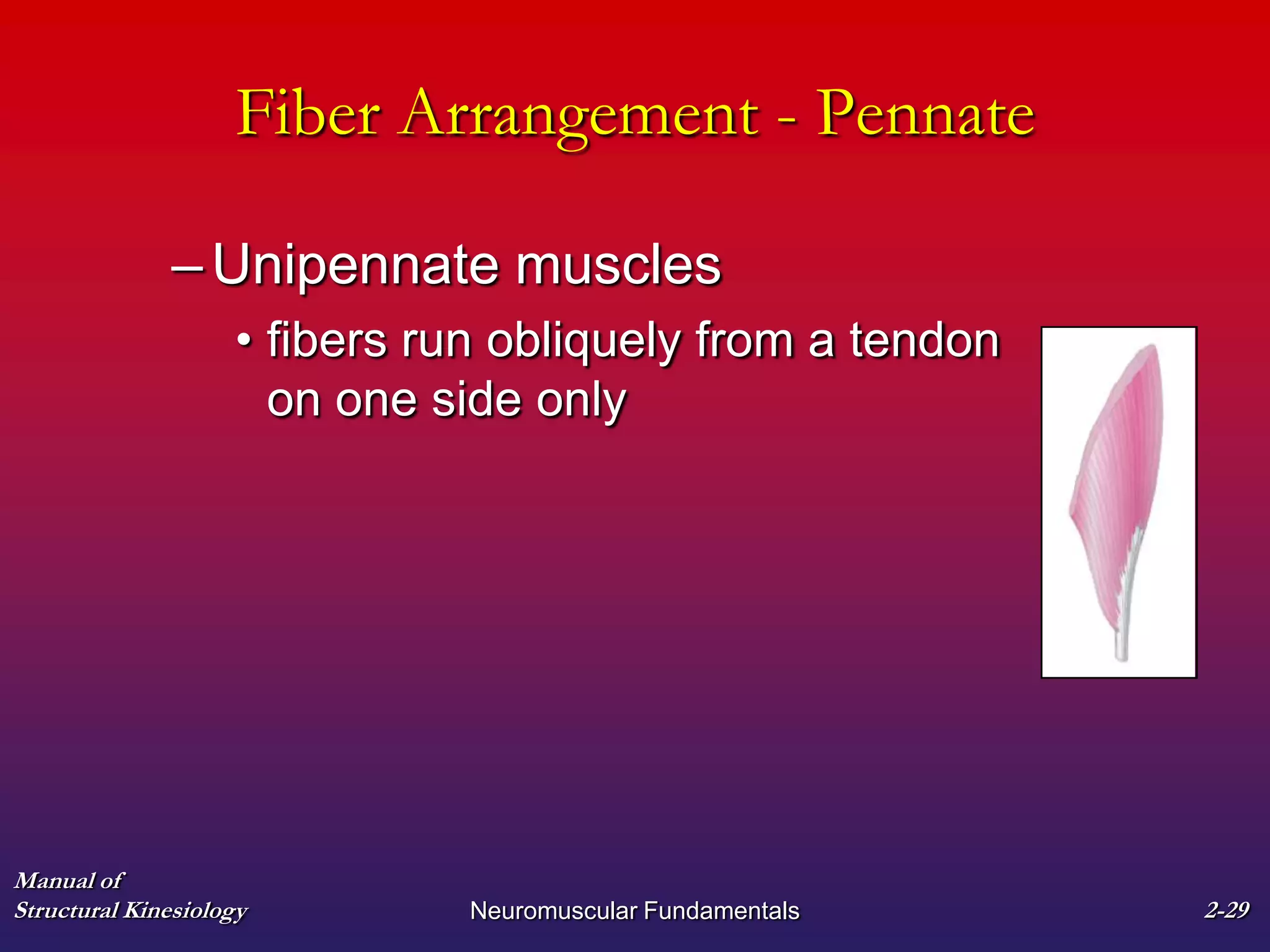
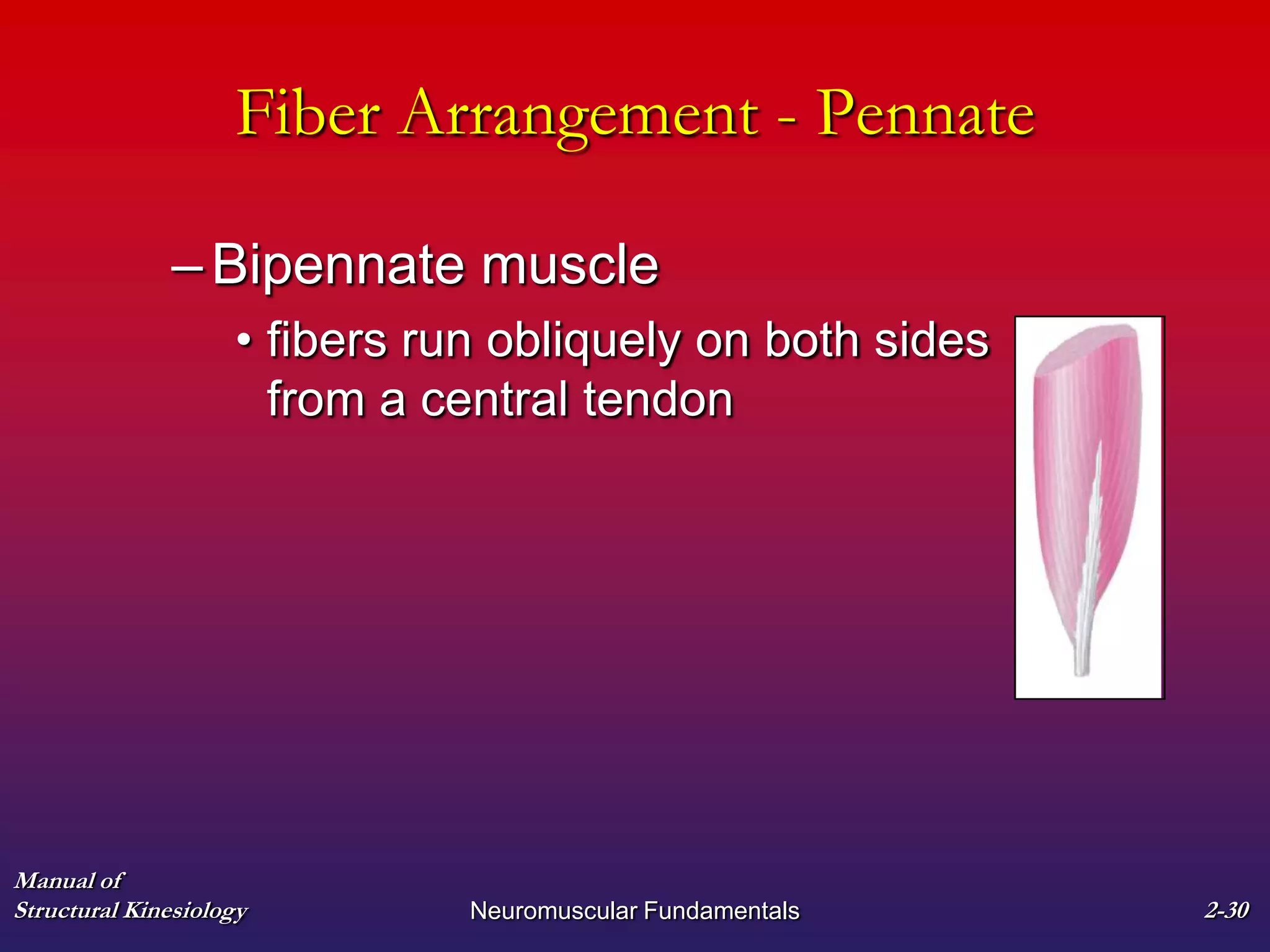
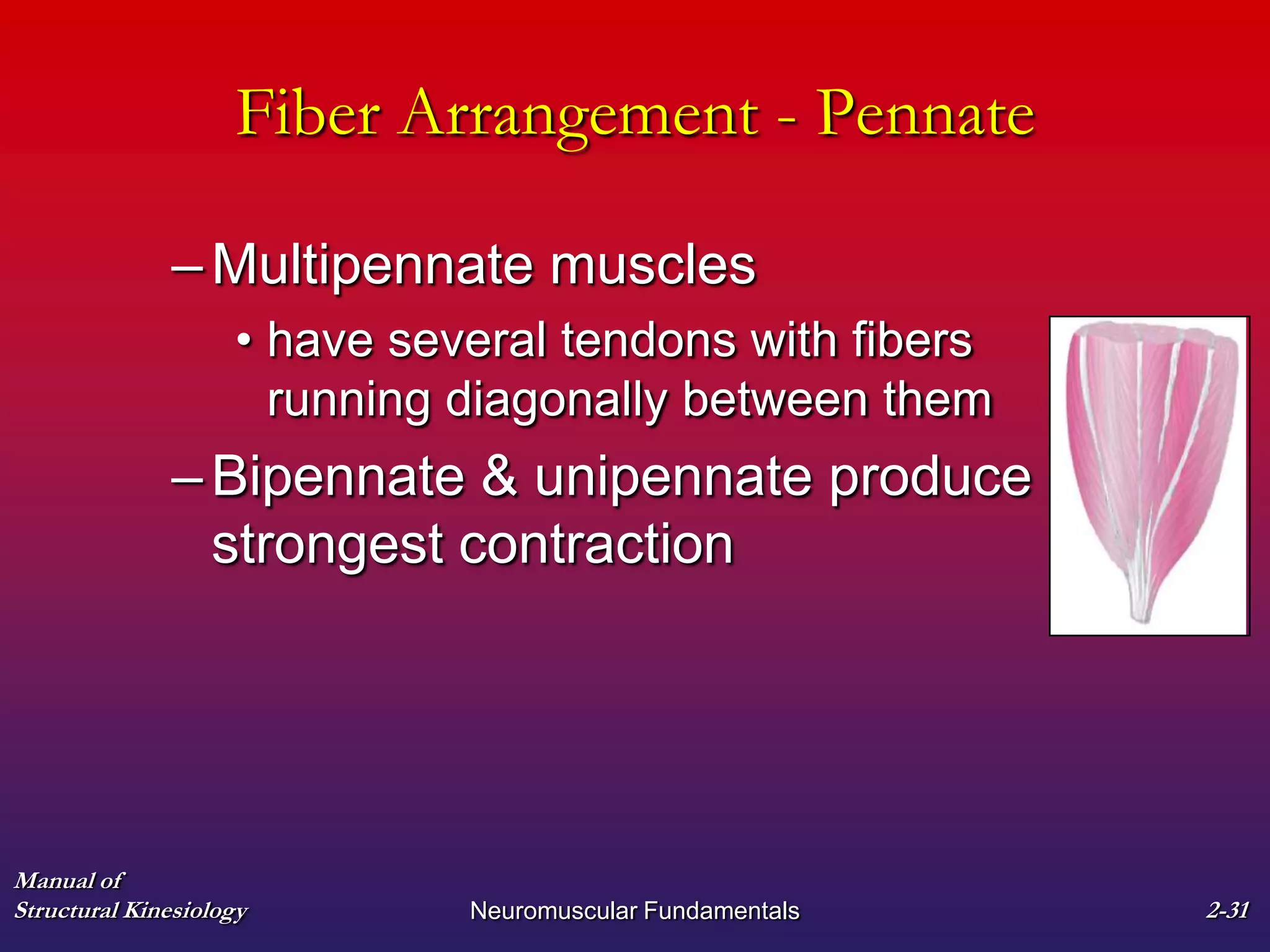
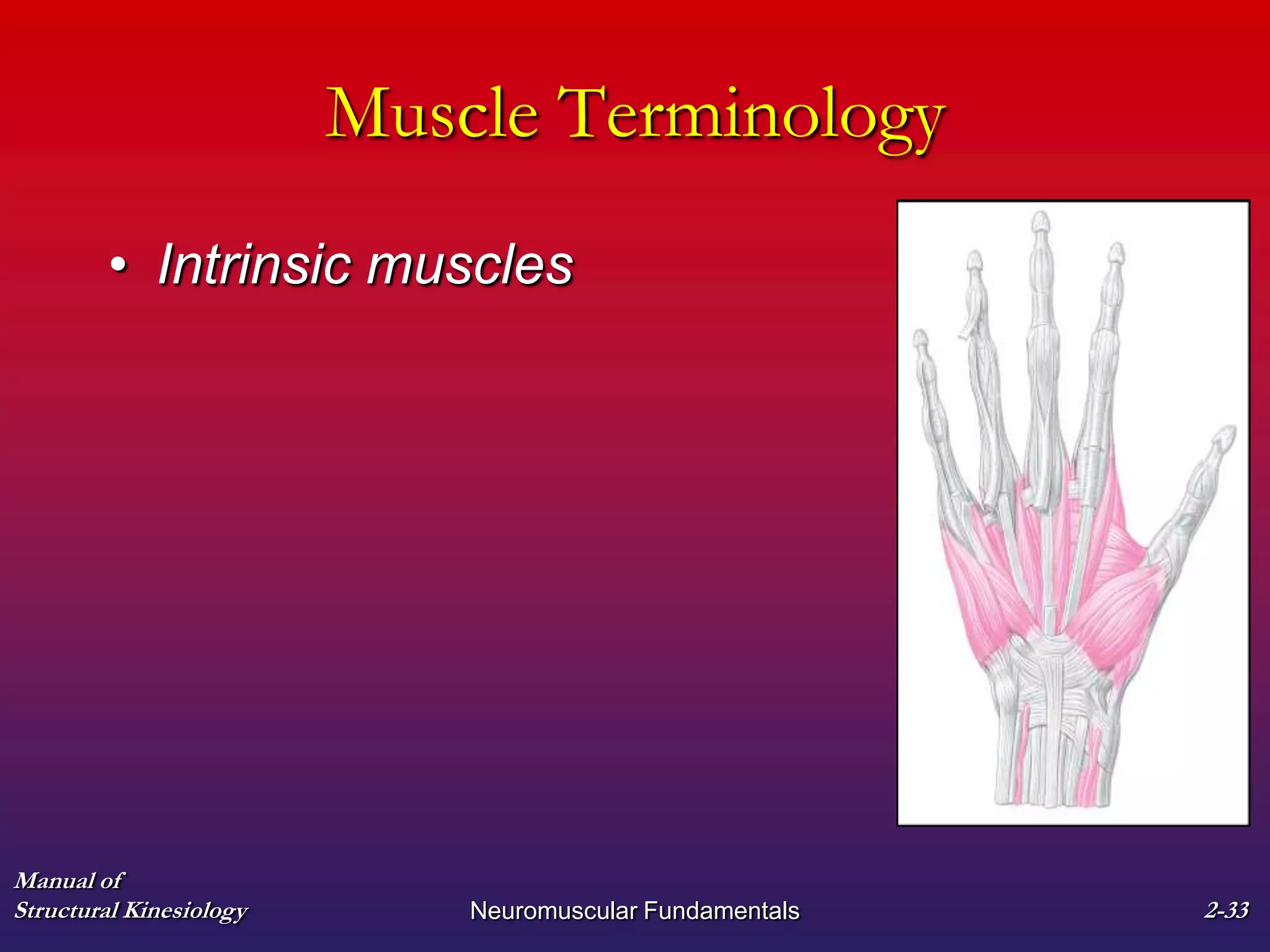
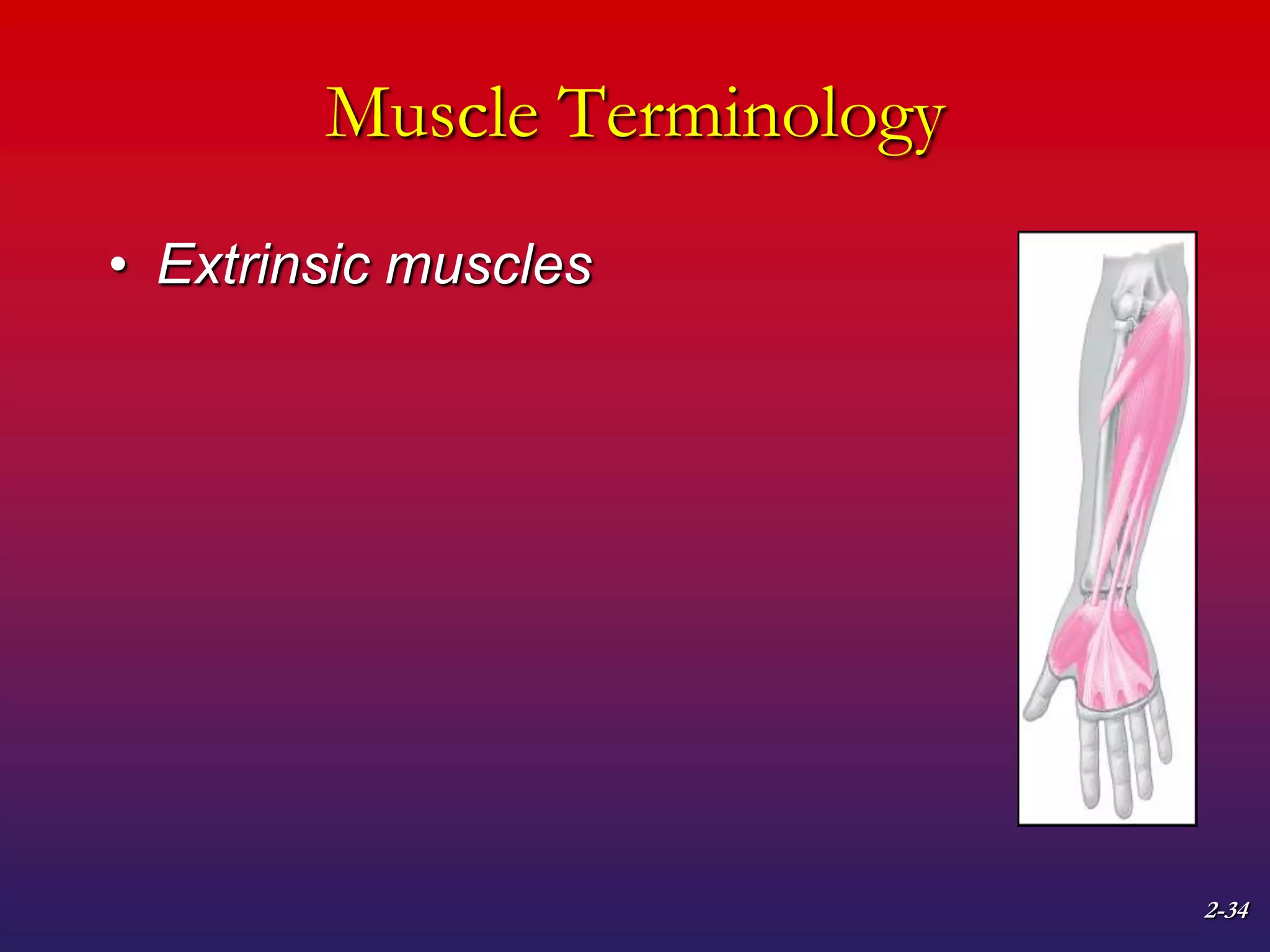
2. It also covers muscle terminology including names based on appearance, location, function, and fiber arrangement of muscles.
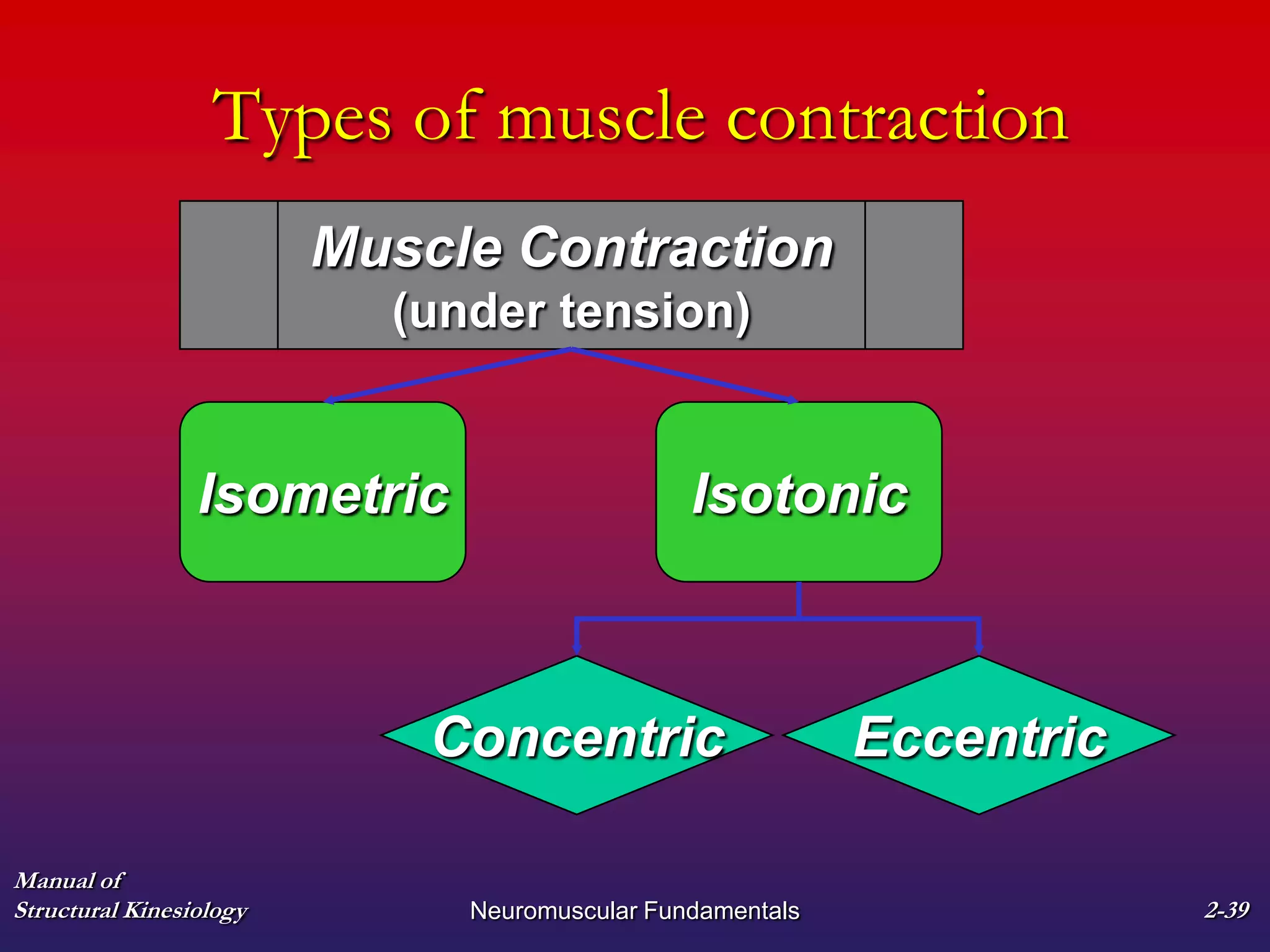
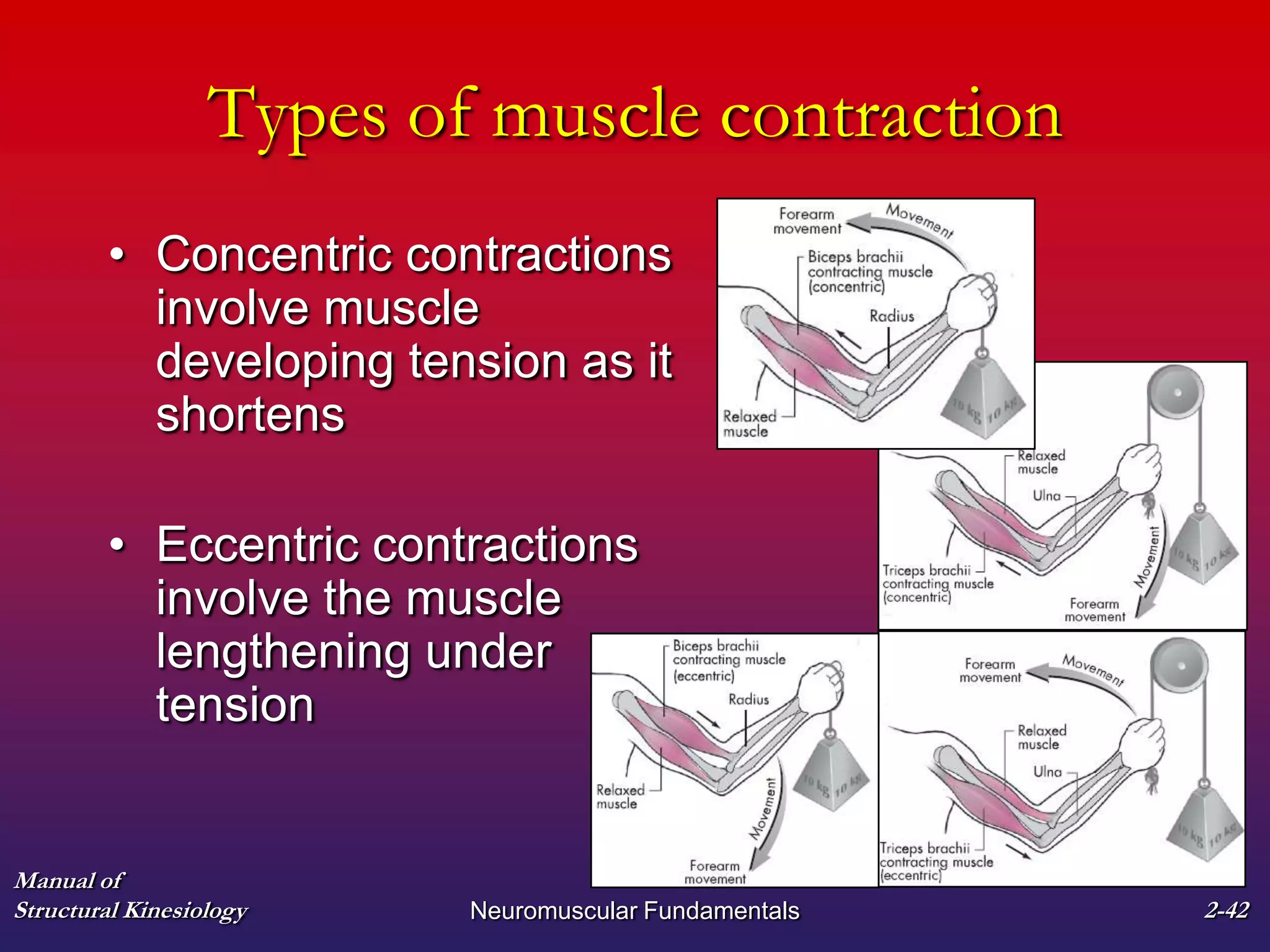
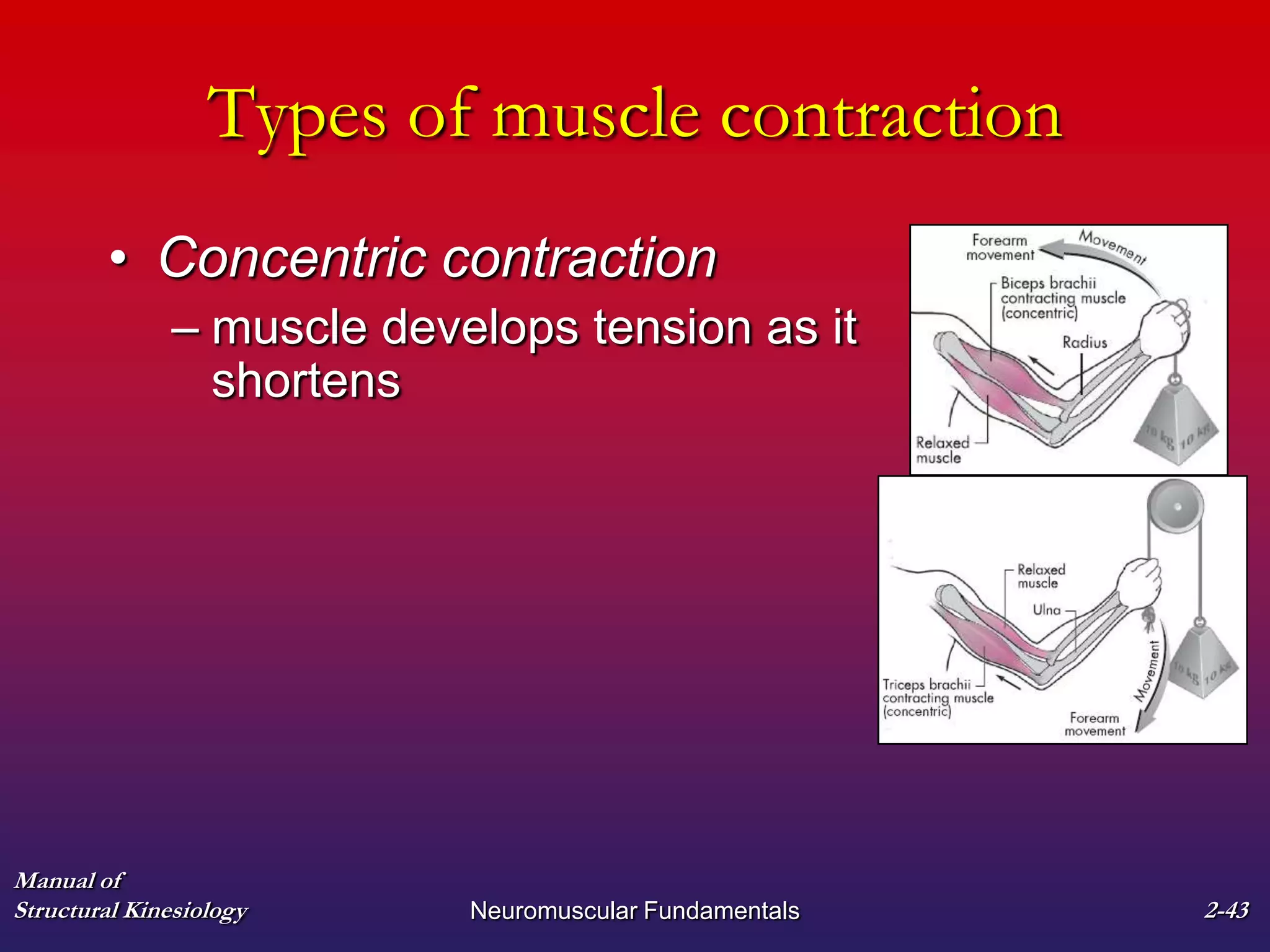
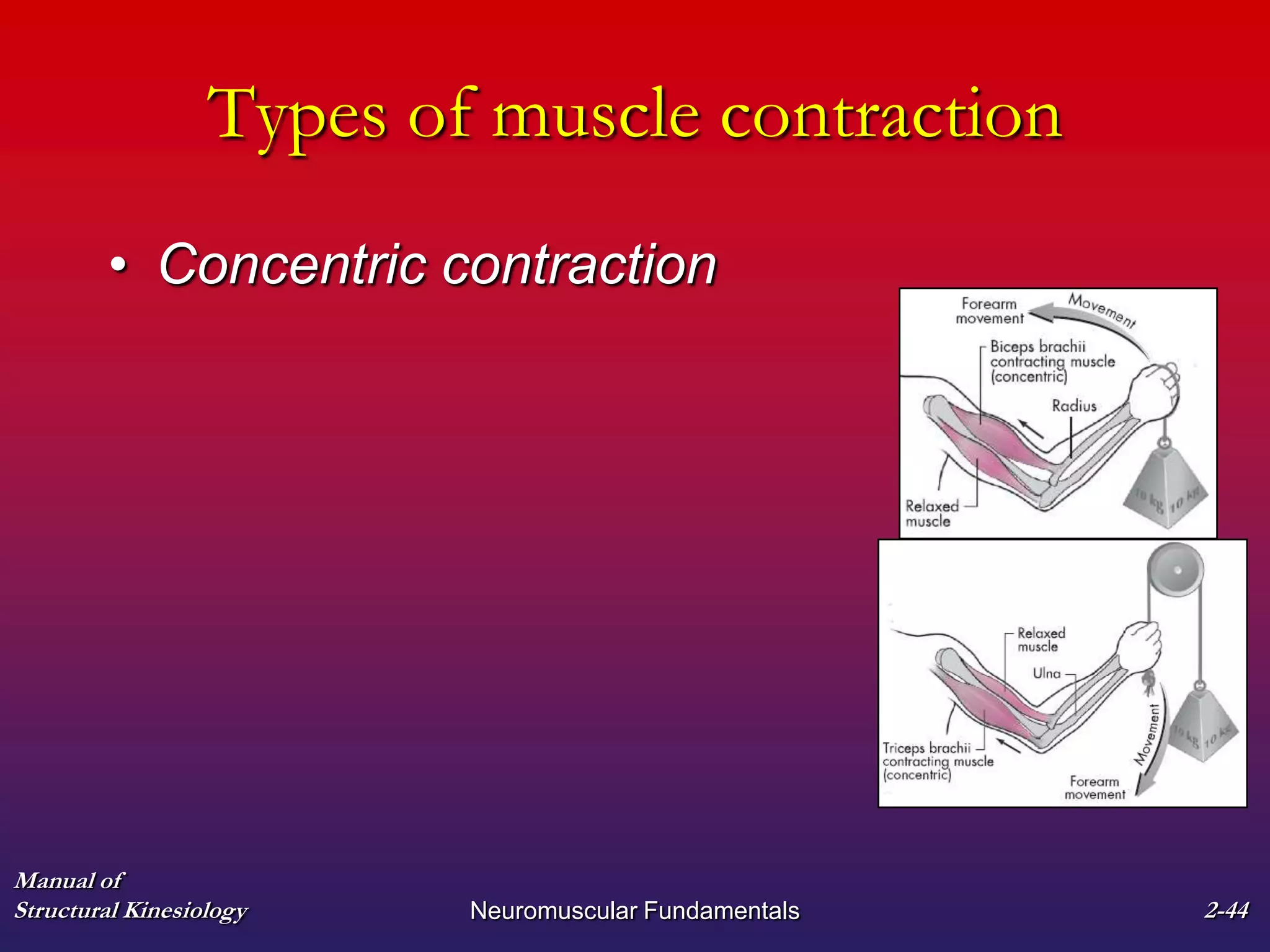
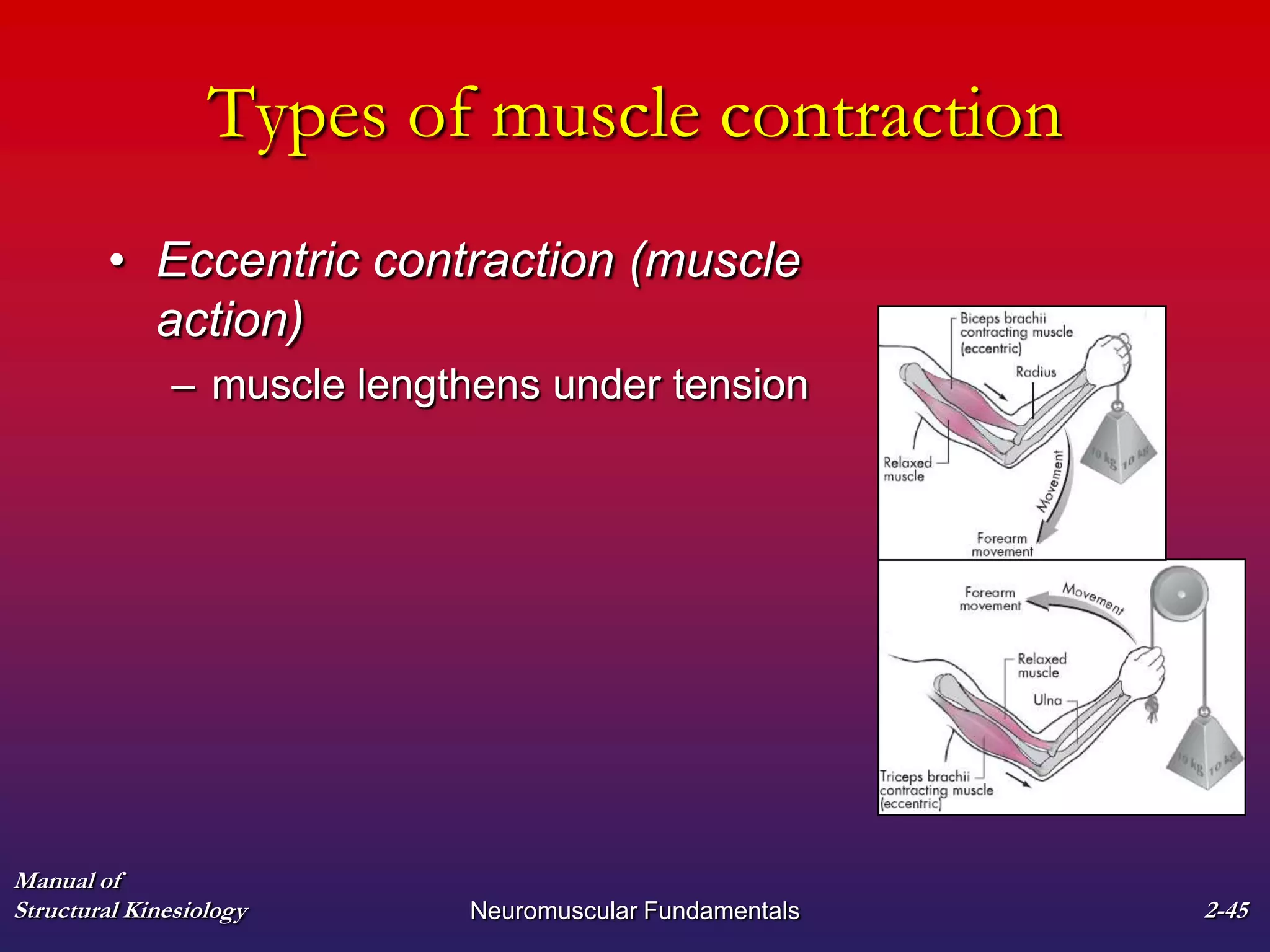
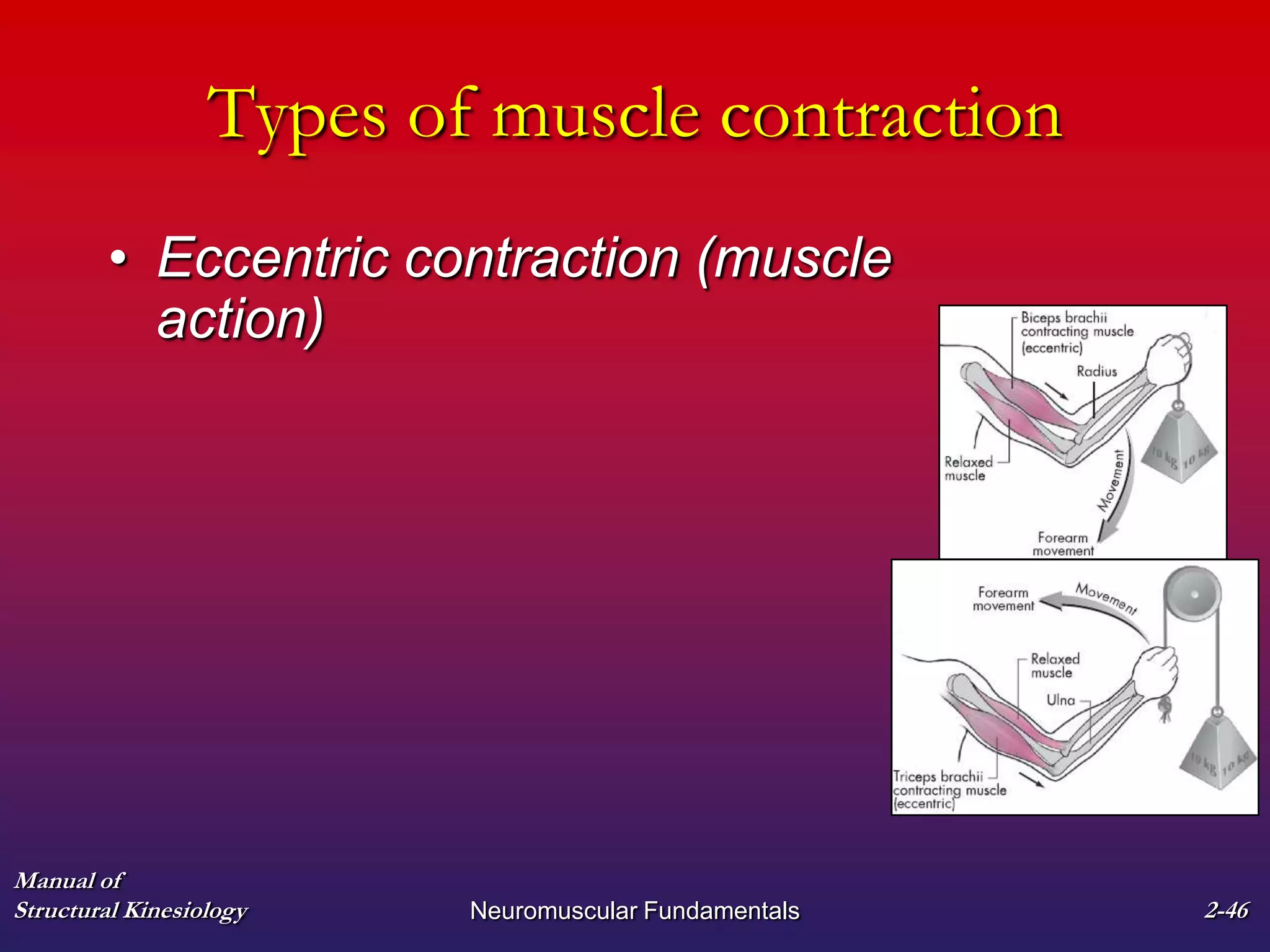
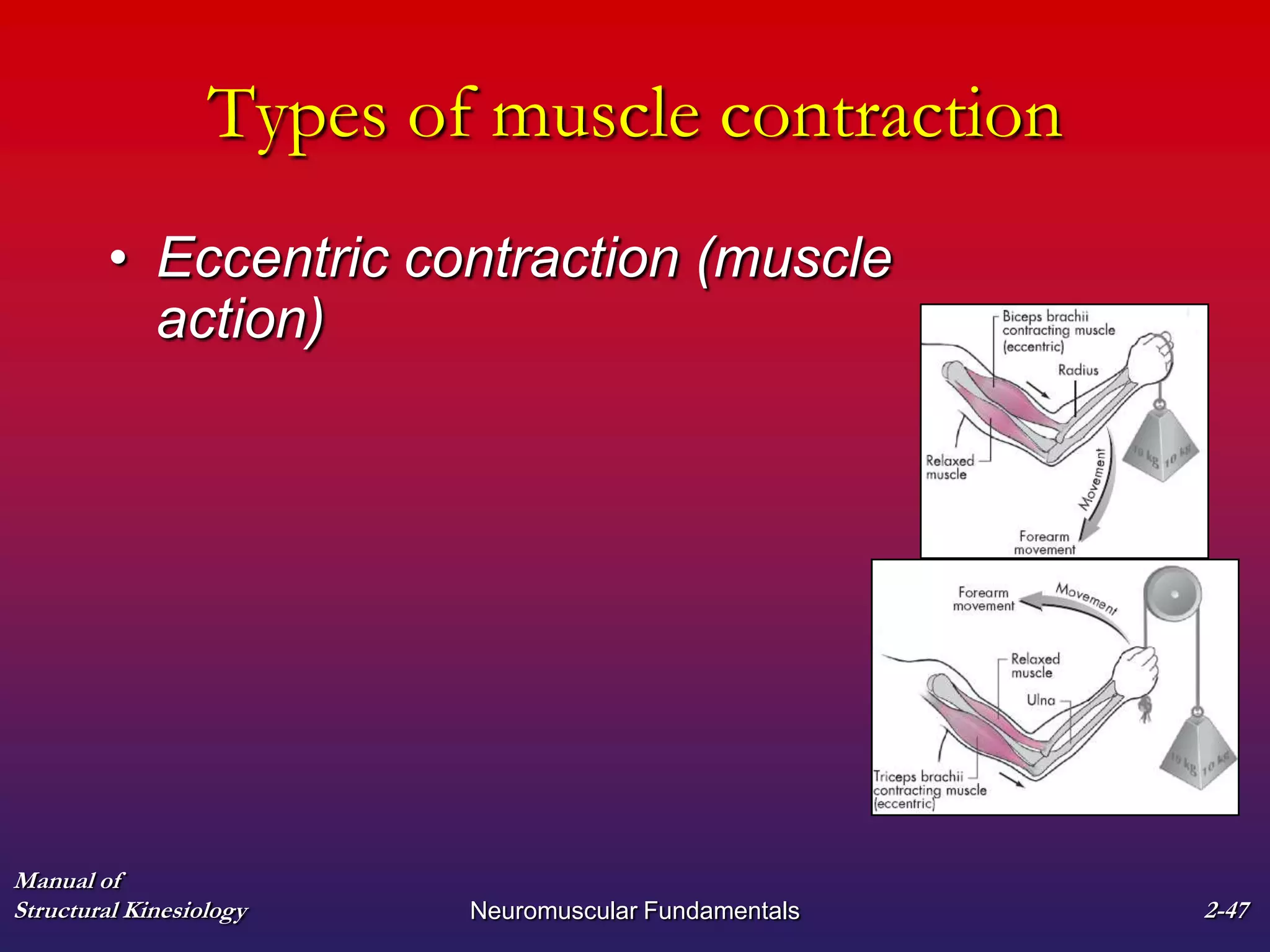
3. The types of muscle contractions - isometric, concentric, and eccentric - and the roles of agonist, antagonist, synergist and other muscles are defined.