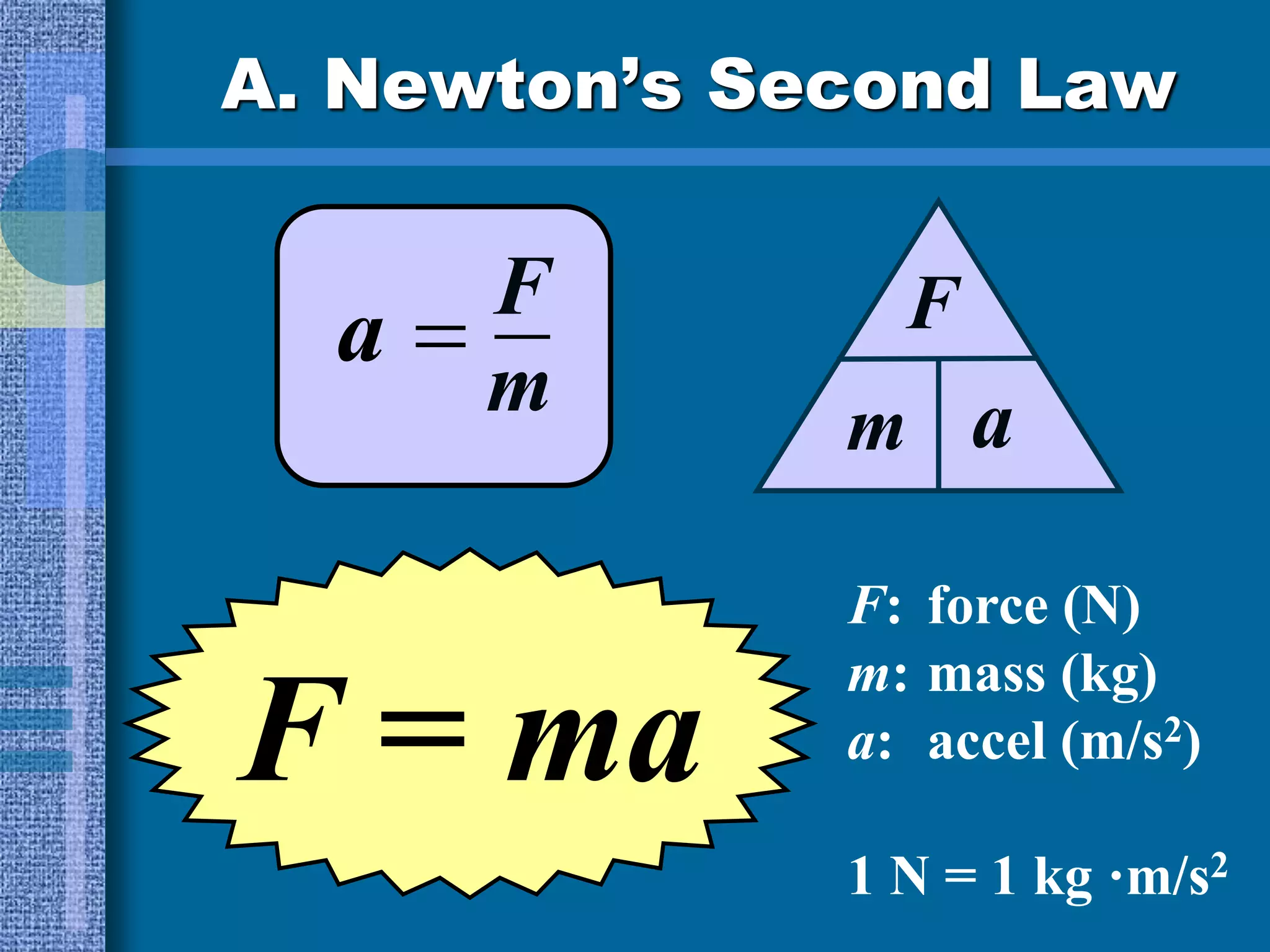
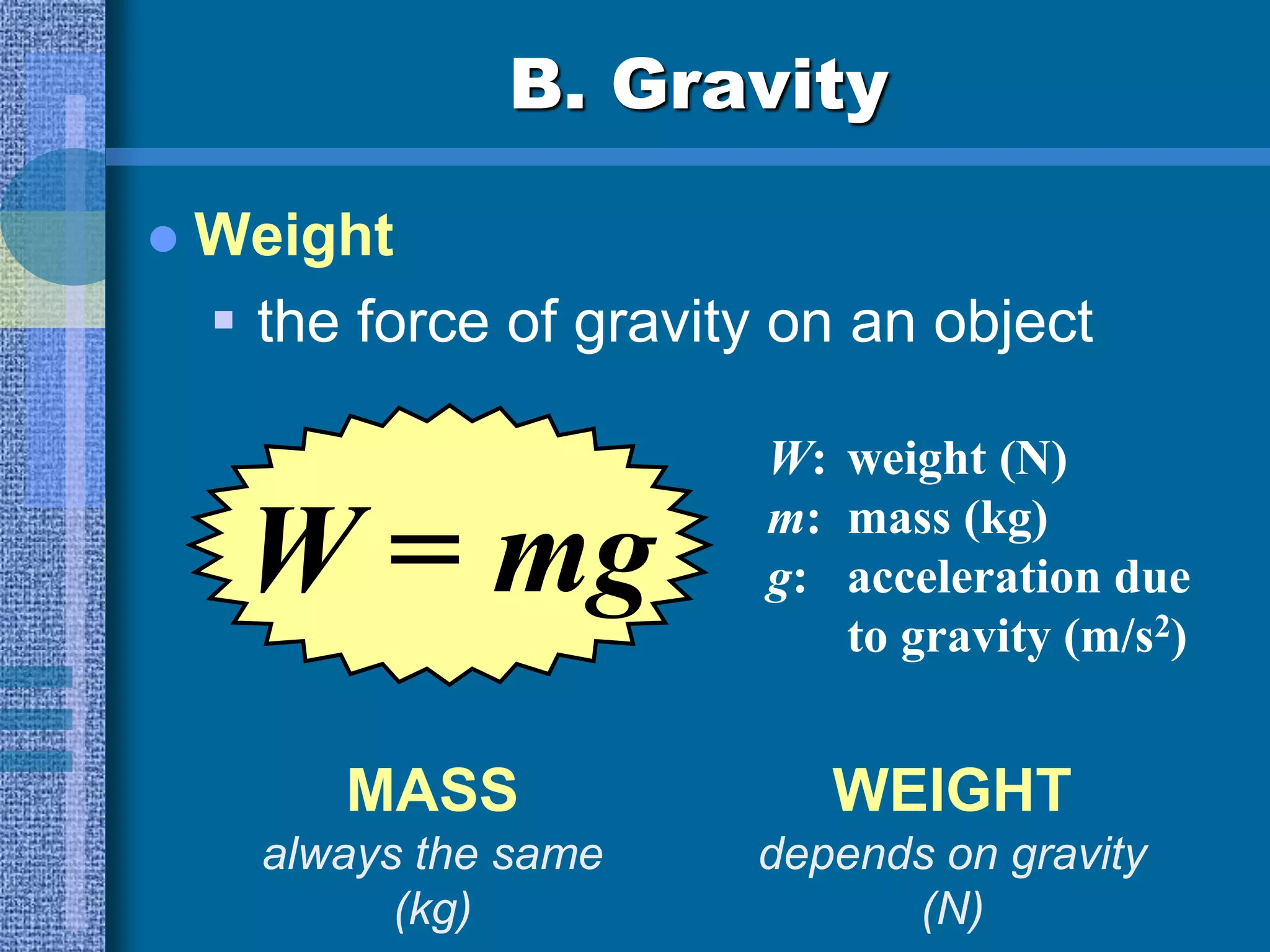
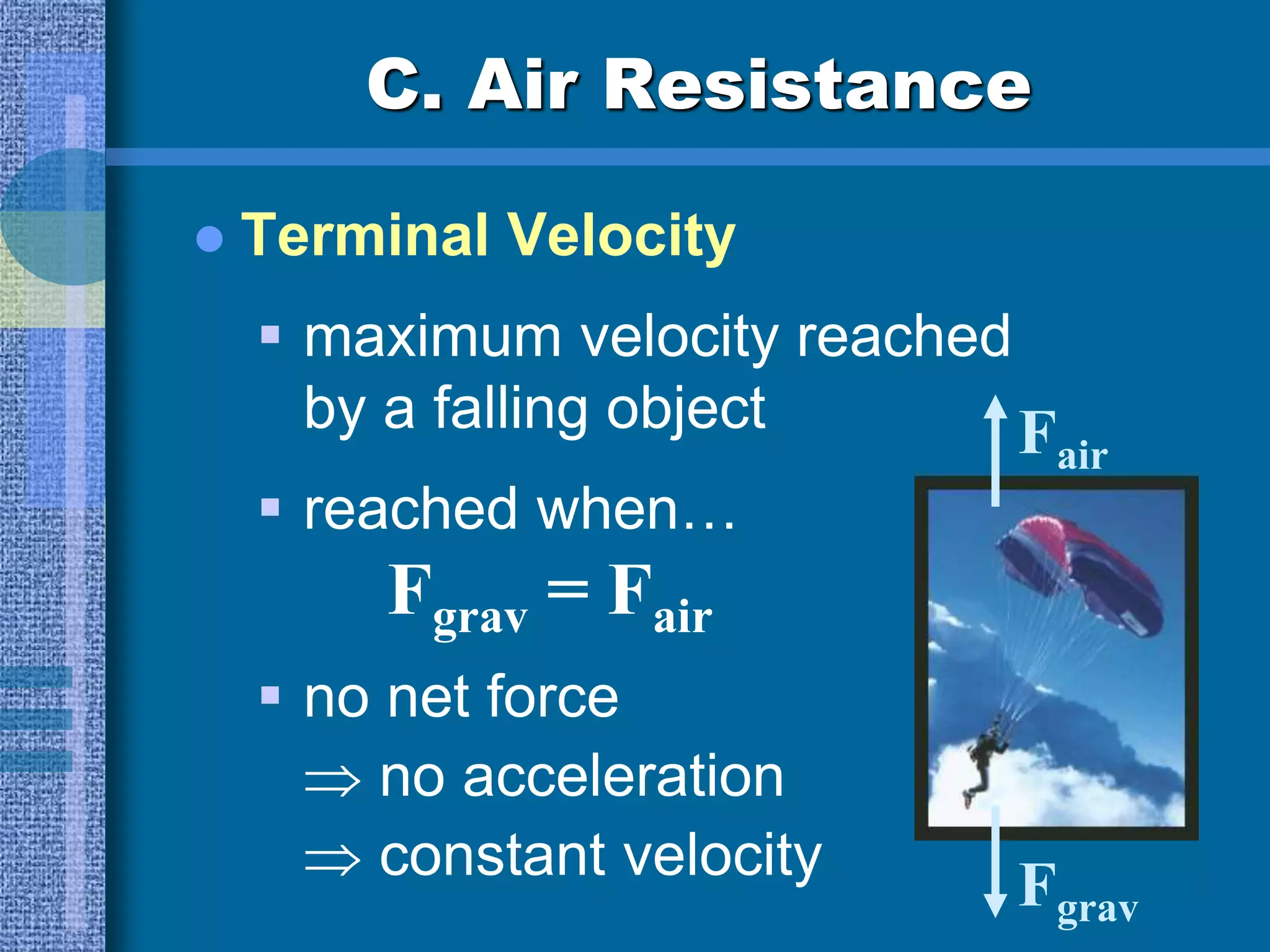
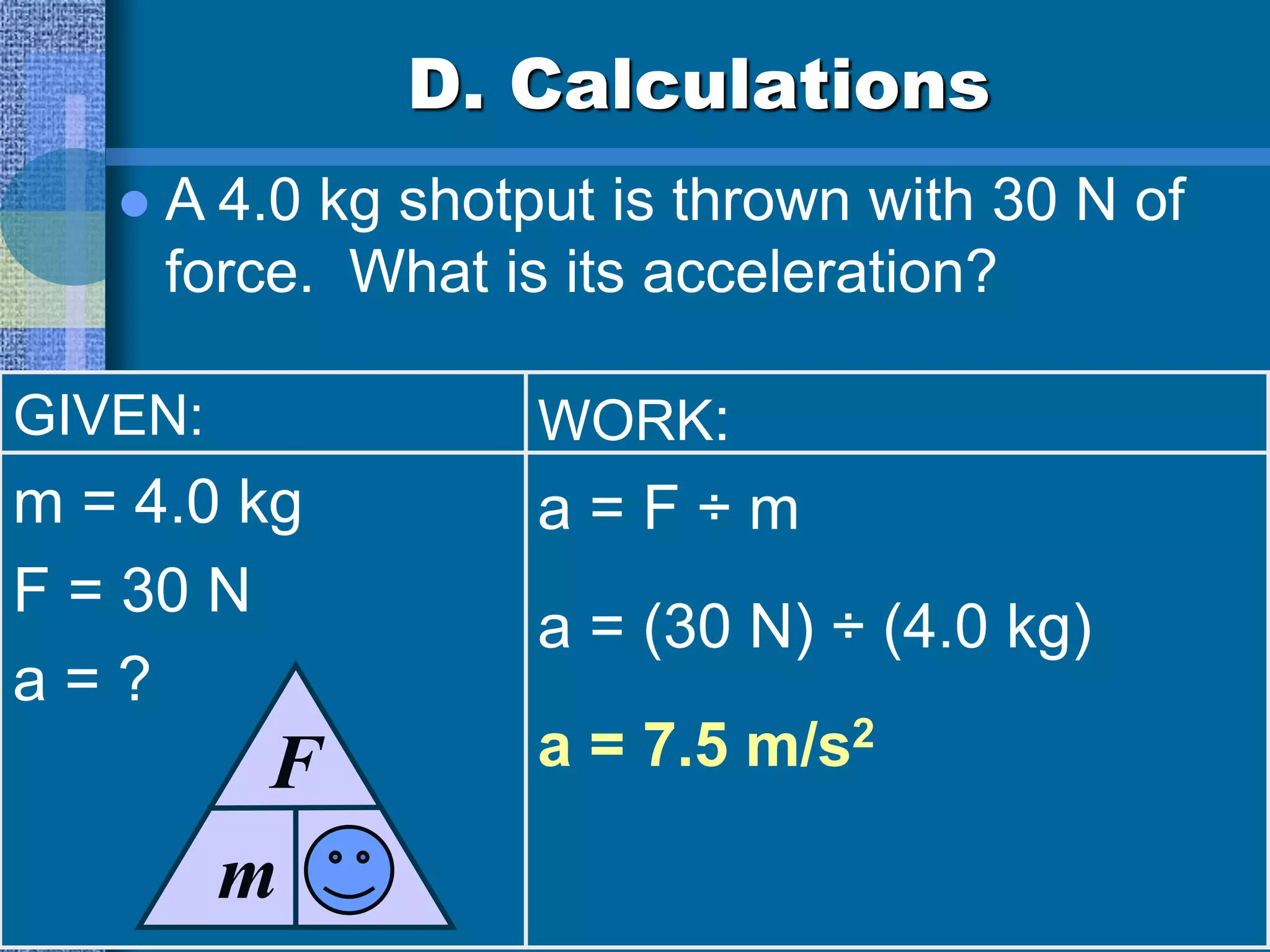
This document discusses motion and forces, including Newton's Second Law of motion, gravity, air resistance, and sample calculations. Newton's Second Law states that force is equal to mass times acceleration. Gravity is a force that attracts all objects and increases with greater mass or shorter distance. Air resistance opposes the motion of falling objects and depends on factors like speed, surface area, and fluid density. Terminal velocity is reached when gravitational and air resistance forces balance. Sample calculations demonstrate using equations like Force = mass x acceleration to solve for unknown values.