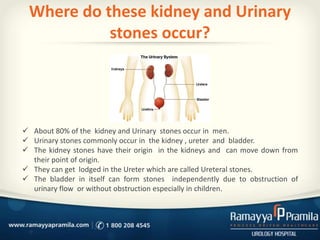
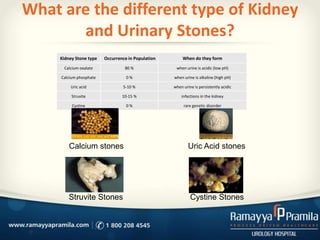
Kidney and urinary stones form when minerals in urine crystallize into solid formations. They most commonly occur in the kidneys and can then pass into the ureters or bladder. The three main types are calcium oxalate, uric acid, and struvite stones. Symptoms include flank or abdominal pain, nausea, blood in the urine, and painful urination. Diagnosis involves physical exam, urinalysis, and imaging tests. Prevention focuses on drinking plenty of fluids to dilute urine and reducing dietary intake of minerals that contribute to stone formation, depending on the type of stones.