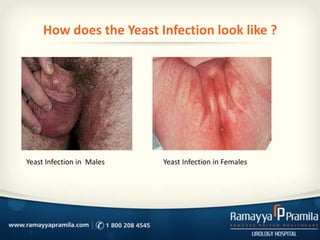
Yeast infections are caused by fungi that can cause infections in various parts of the body, especially the genital region. Common symptoms include redness, itching, burning sensations and thick white discharge. Diagnosis involves physical examination and testing of urine or discharge samples. Treatment depends on the location and severity of the infection, but typically involves antifungal creams, suppositories, or oral medications. While most infections can be treated, they sometimes recur or are difficult to fully eliminate in some patients.