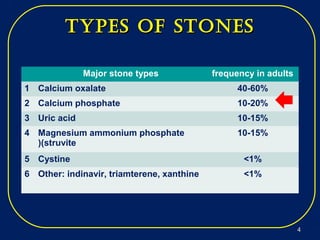
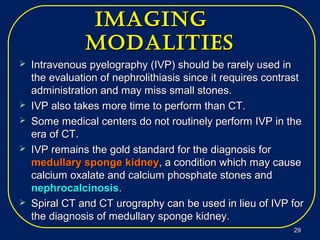
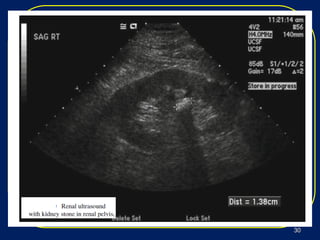
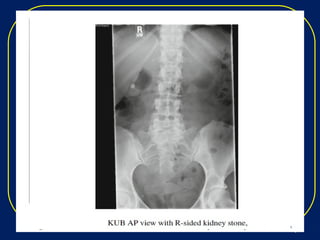
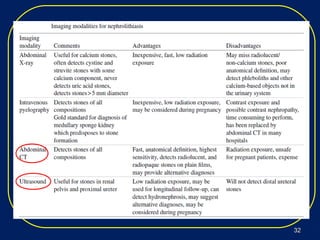
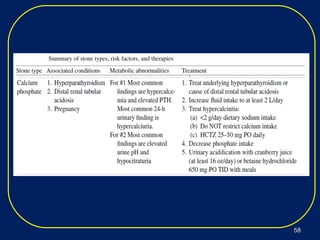
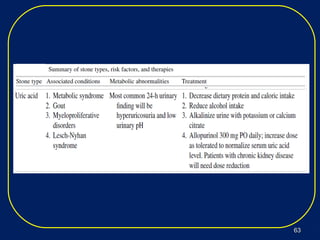
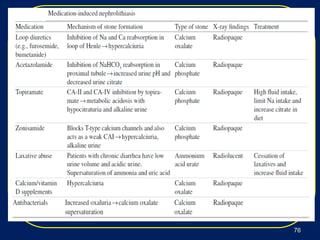
Nephrolithiasis, or kidney stones, is a common condition where stones form in the kidneys or urinary tract. The prevalence increases with age, affecting 11% of men and 5.6% of women in the US by age 70. Calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate are the most common stone types. Risk factors include genetics, medical conditions like obesity and hyperparathyroidism, dietary factors high in sodium and animal protein, and low urine volume. Patients typically present with sudden severe flank or abdominal pain known as renal colic. Diagnosis involves urinalysis, blood tests, abdominal imaging like CT, and stone analysis if a sample can be obtained. Treatment depends on factors like stone size,