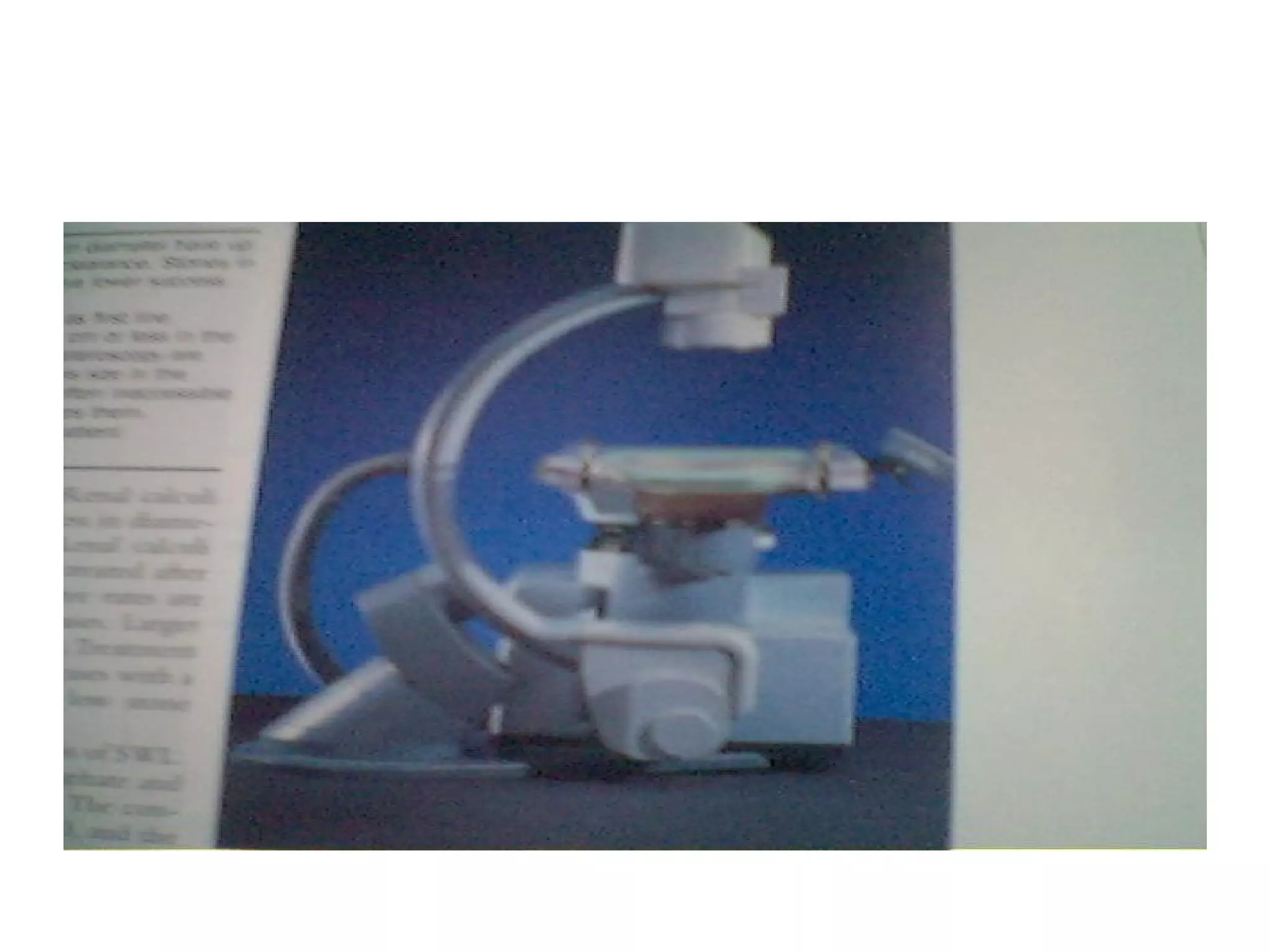
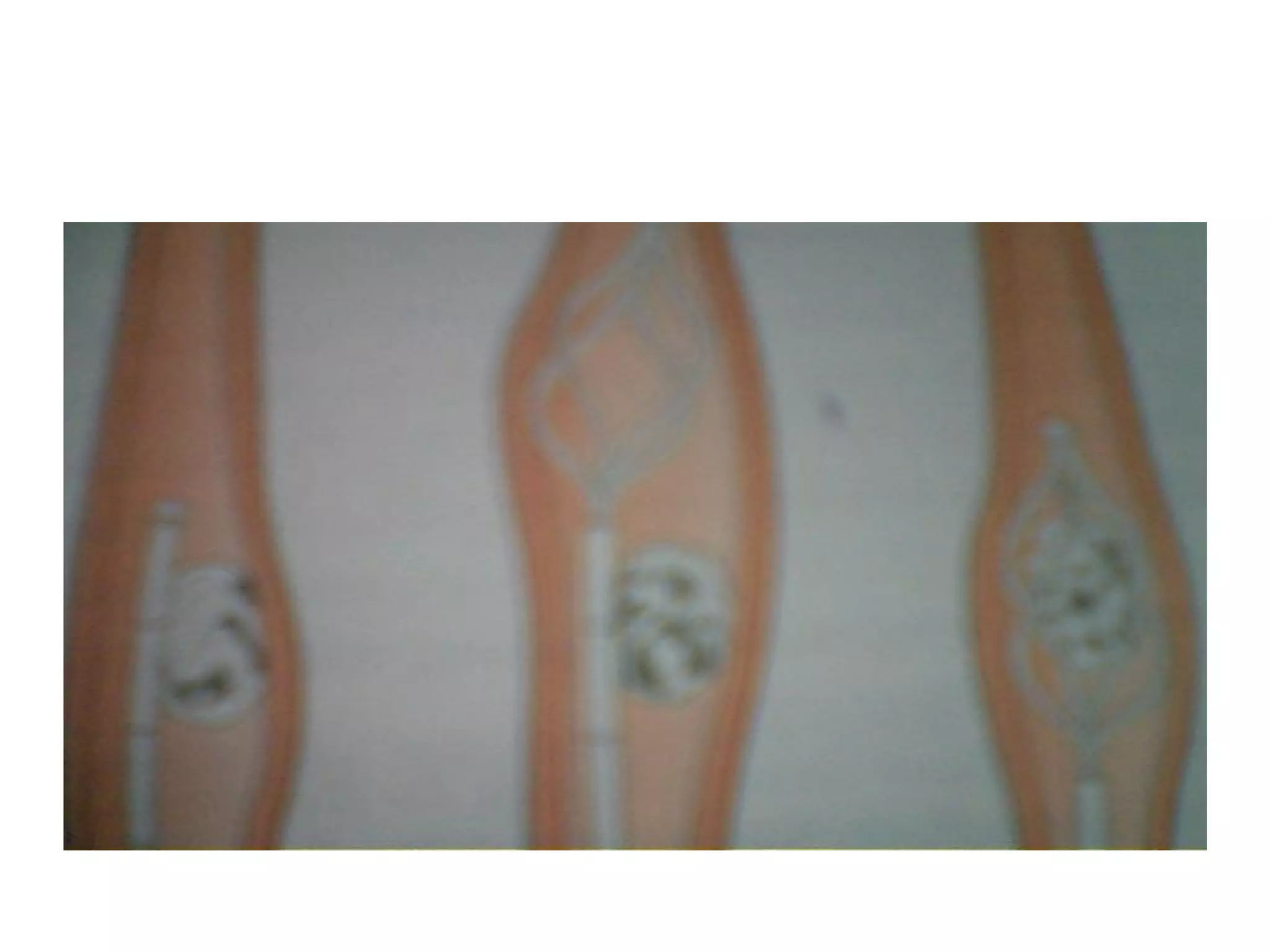
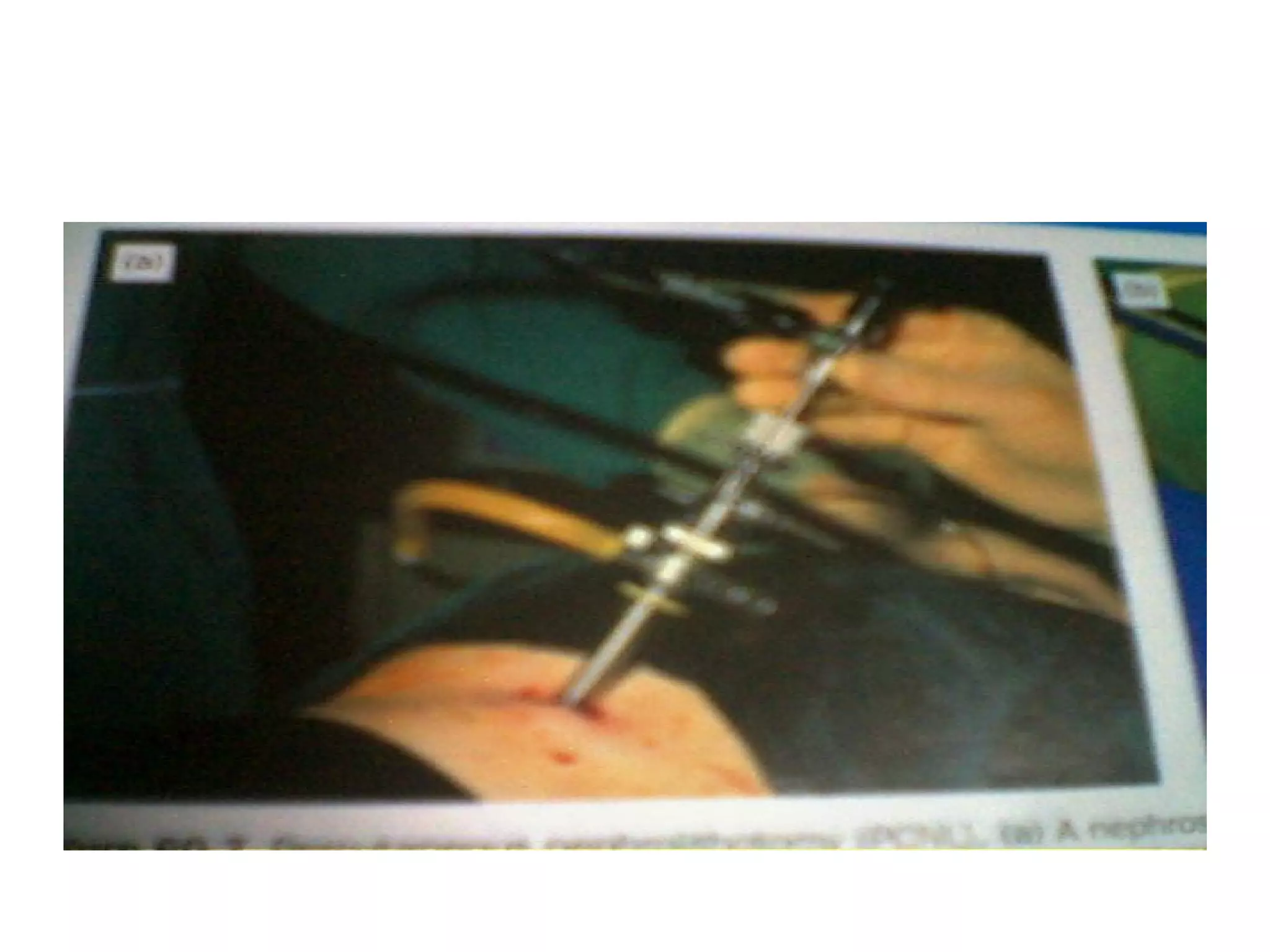
This document discusses upper urinary tract calculi (kidney stones). It notes that kidney stones are common in Pakistan and are caused by many factors. The document describes the types of stones, risk factors like diet and climate, and the multi-step process of stone formation. It outlines evaluations for stones and treatments options ranging from conservative management to procedures like ESWL, ureteroscopy, and surgery depending on the stone size, location, and other factors.