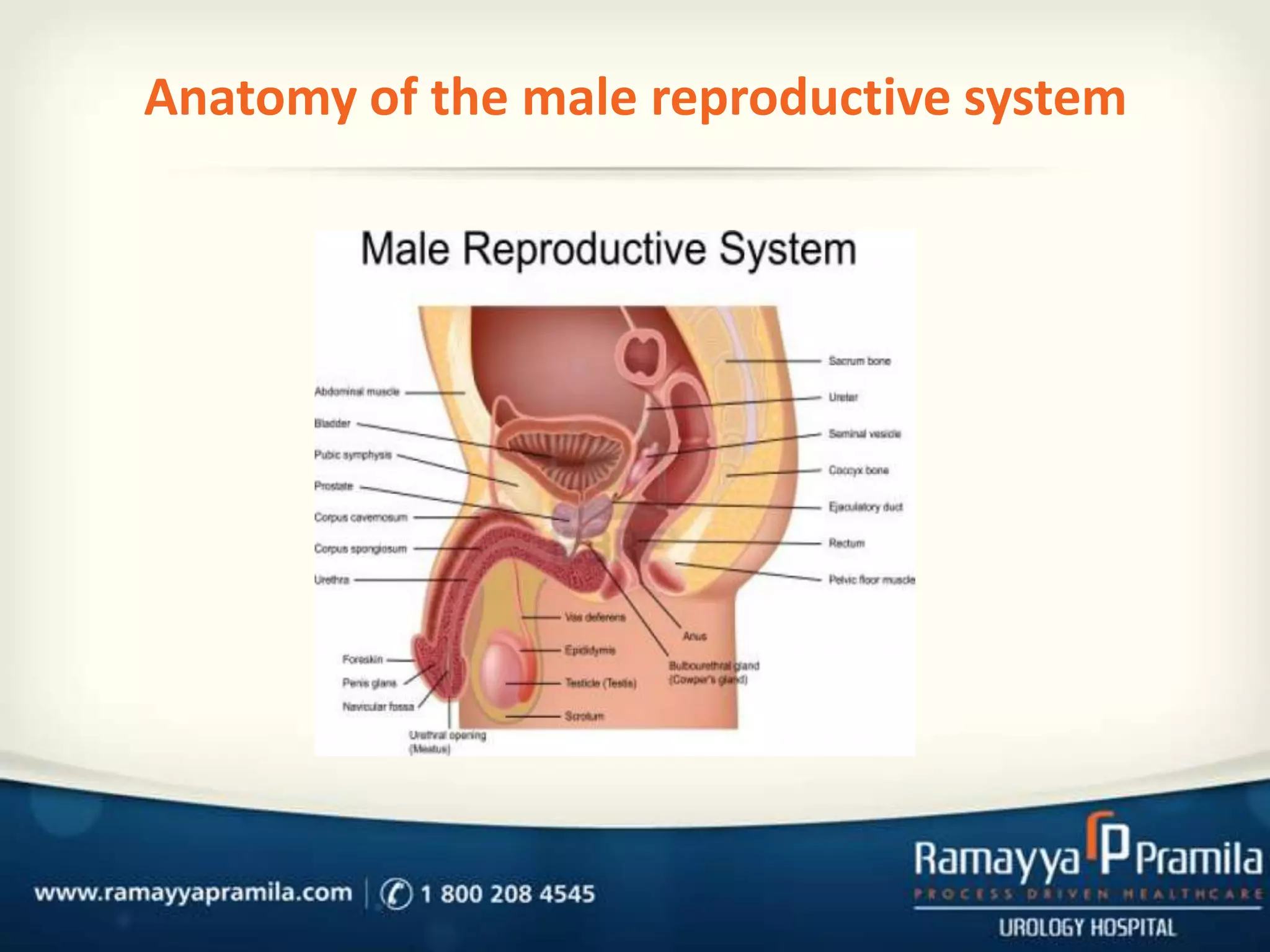
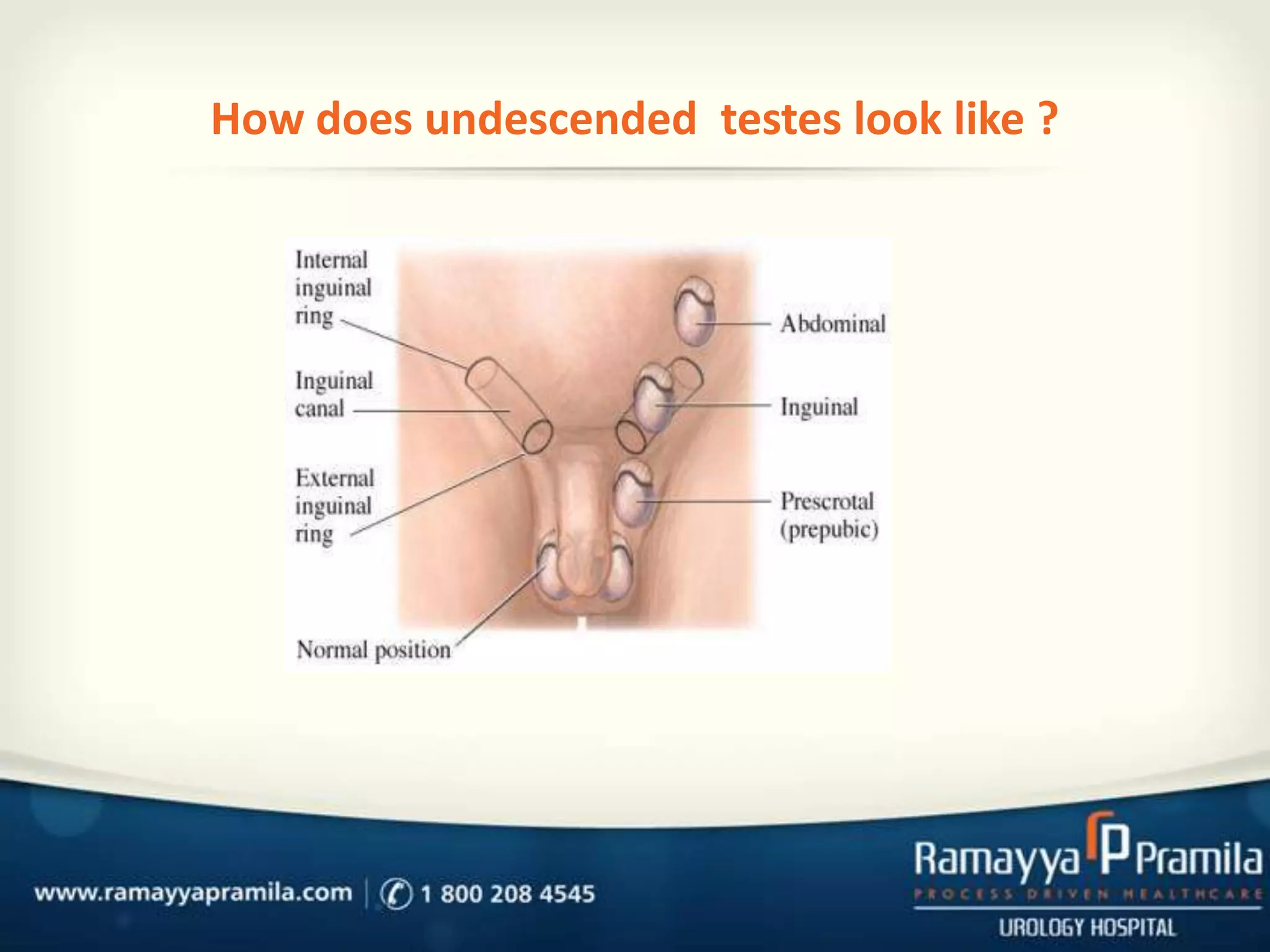
This document discusses undescended testes (cryptorchidism), which is when one or both testes fail to descend into the scrotum. It describes the normal development of the testes and how they are meant to descend into the scrotum in the womb. Undescended testes can be caused by hormonal issues or physical abnormalities that prevent descent. Ultrasound or MRI is used to diagnose undescended testes. Surgery called an orchiopexy is usually performed between 6-18 months to bring the testes into the scrotum, and patients should have regular checkups after to monitor development.