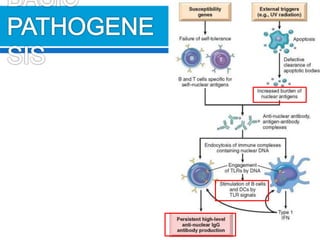
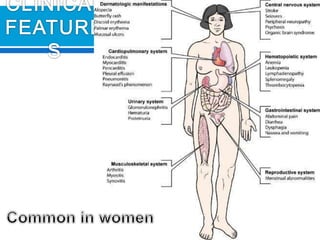
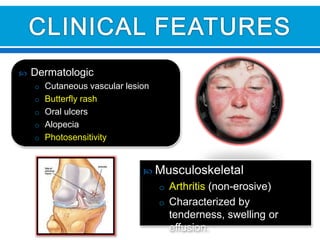
This document discusses systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by the formation of autoantibodies. SLE can affect many parts of the body including the skin, joints, heart, lungs, kidneys, and nervous system. Diagnosis involves detecting antinuclear antibodies (ANAs) and other autoantibodies in the blood through tests like the fluorescent antinuclear antibody (FANA) test. FANA testing can identify different antibody patterns that may indicate SLE or other autoimmune conditions. Laboratory tests are also used to monitor disease activity and screen for organ involvement.