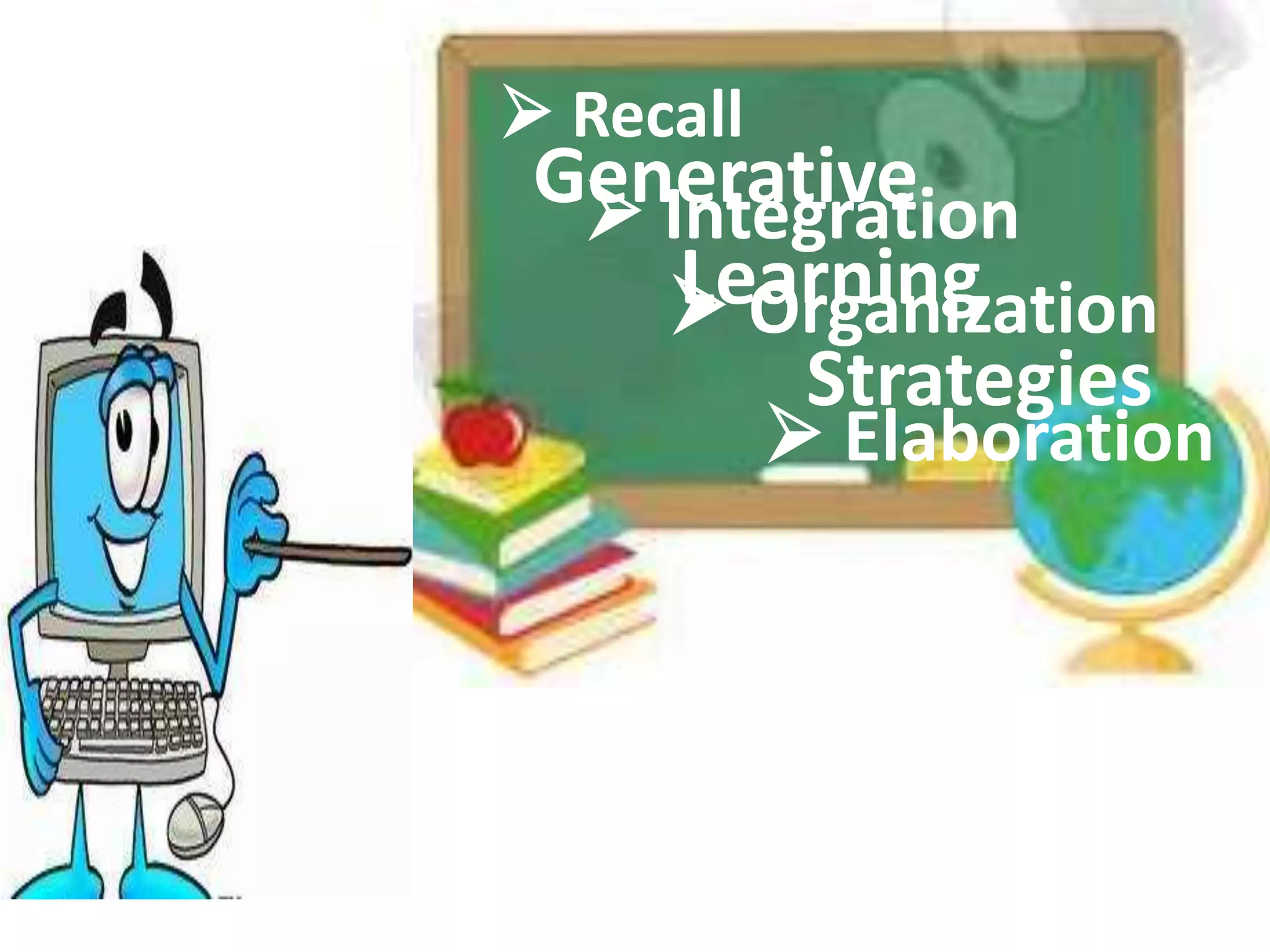
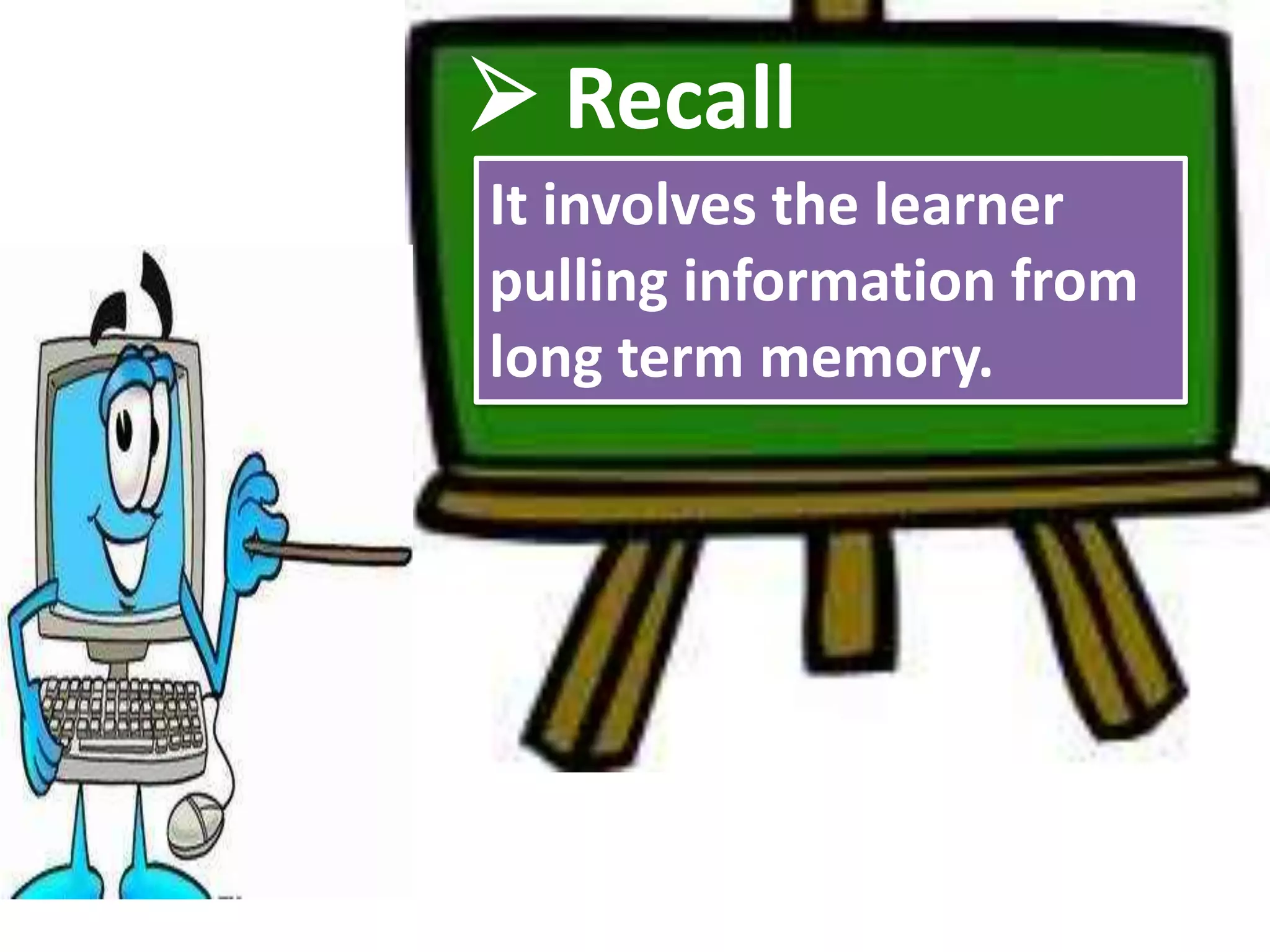
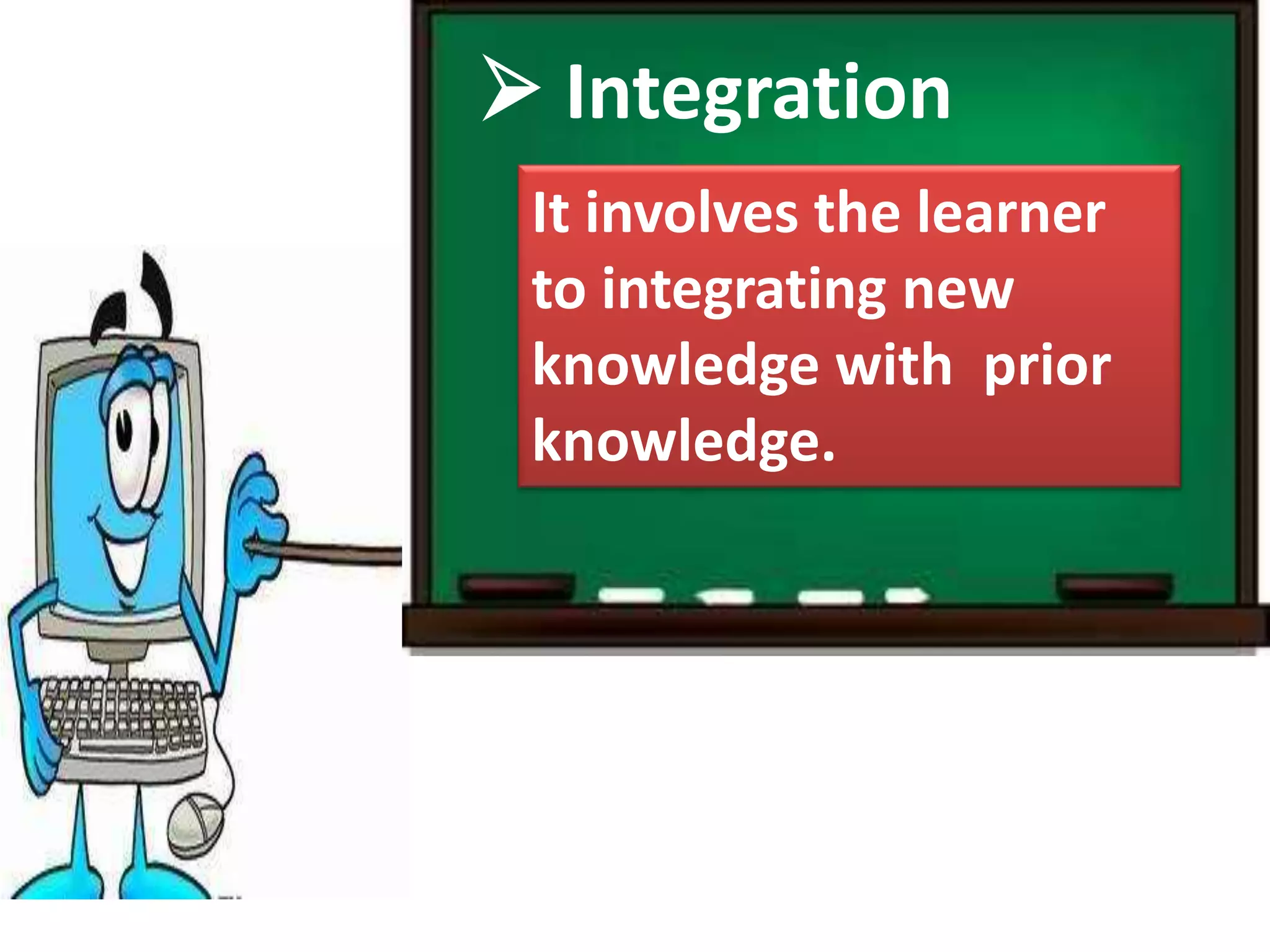
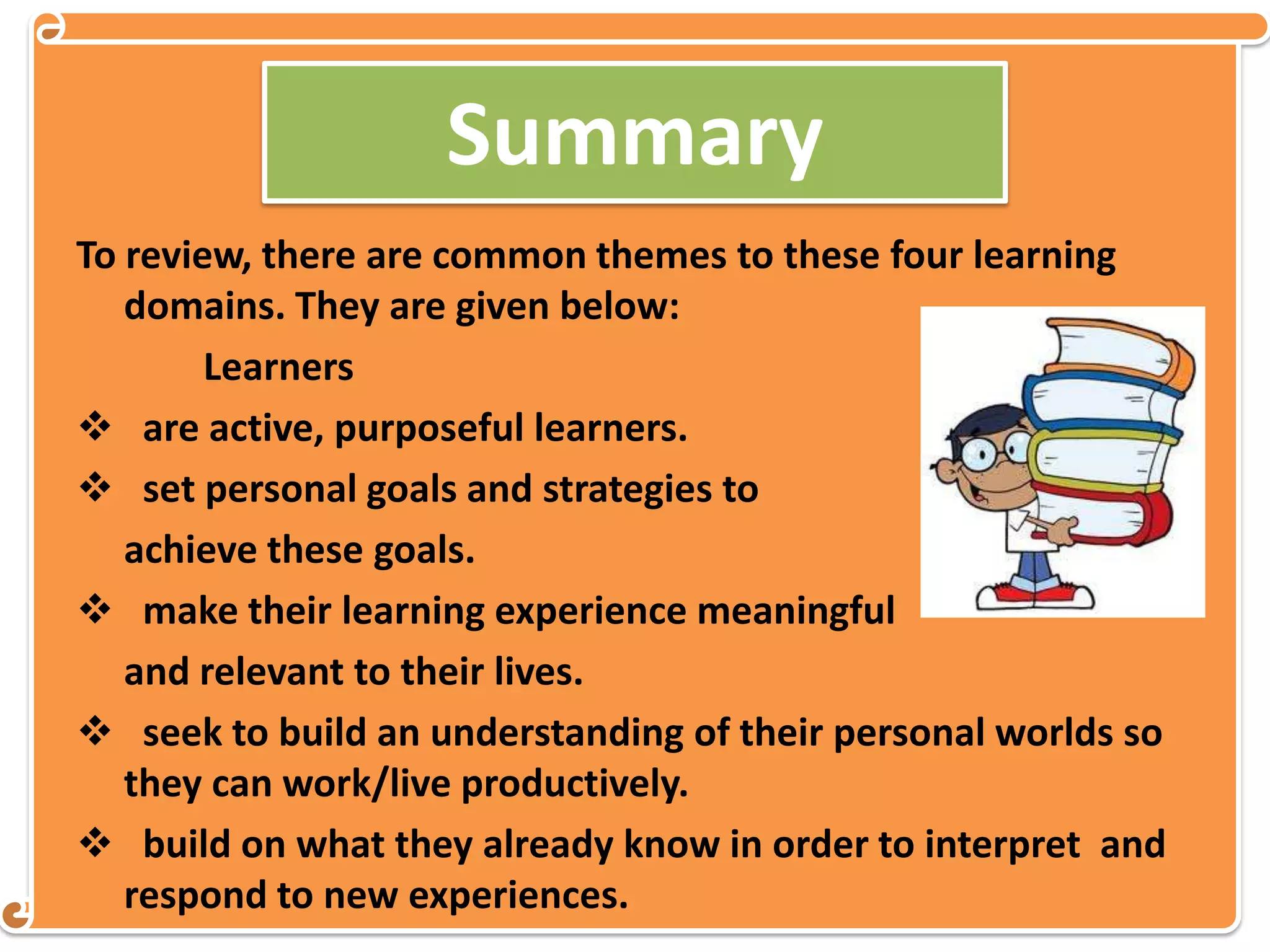
The document discusses four learning domains: meaningful learning, discovery learning, generative learning, and constructivism. For meaningful learning, students relate new knowledge to prior knowledge through hands-on activities and positive learning environments. Discovery learning involves students uncovering knowledge through inquiry and tasks. Generative learning focuses on students actively generating meaning from experiences by recalling, integrating, organizing, and elaborating on information. Constructivism posits that learning involves learners constructing understanding from new information and experiences based on existing knowledge.