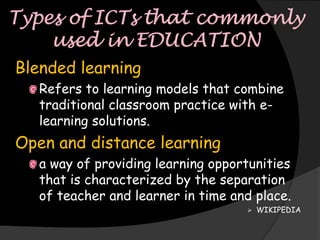
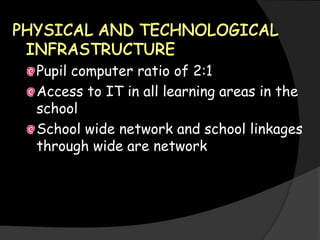
The document discusses strategies and plans for integrating information and communication technologies (ICT) into education systems in several countries and regions, including:
- Singapore's "In2015" plan aims to create an enriching learner-centric environment and position Singapore as an innovation hub for education technologies.
- Hong Kong launched a 5-year ICT strategy in 1998 to provide IT infrastructure in schools and training for teachers in using technologies.
- Other places discussed include the goals of ICT plans in Australia, vision and infrastructure aspects of ICT strategies in the Philippines and India. Infrastructure requirements, teacher training, and curriculum integration are common themes.