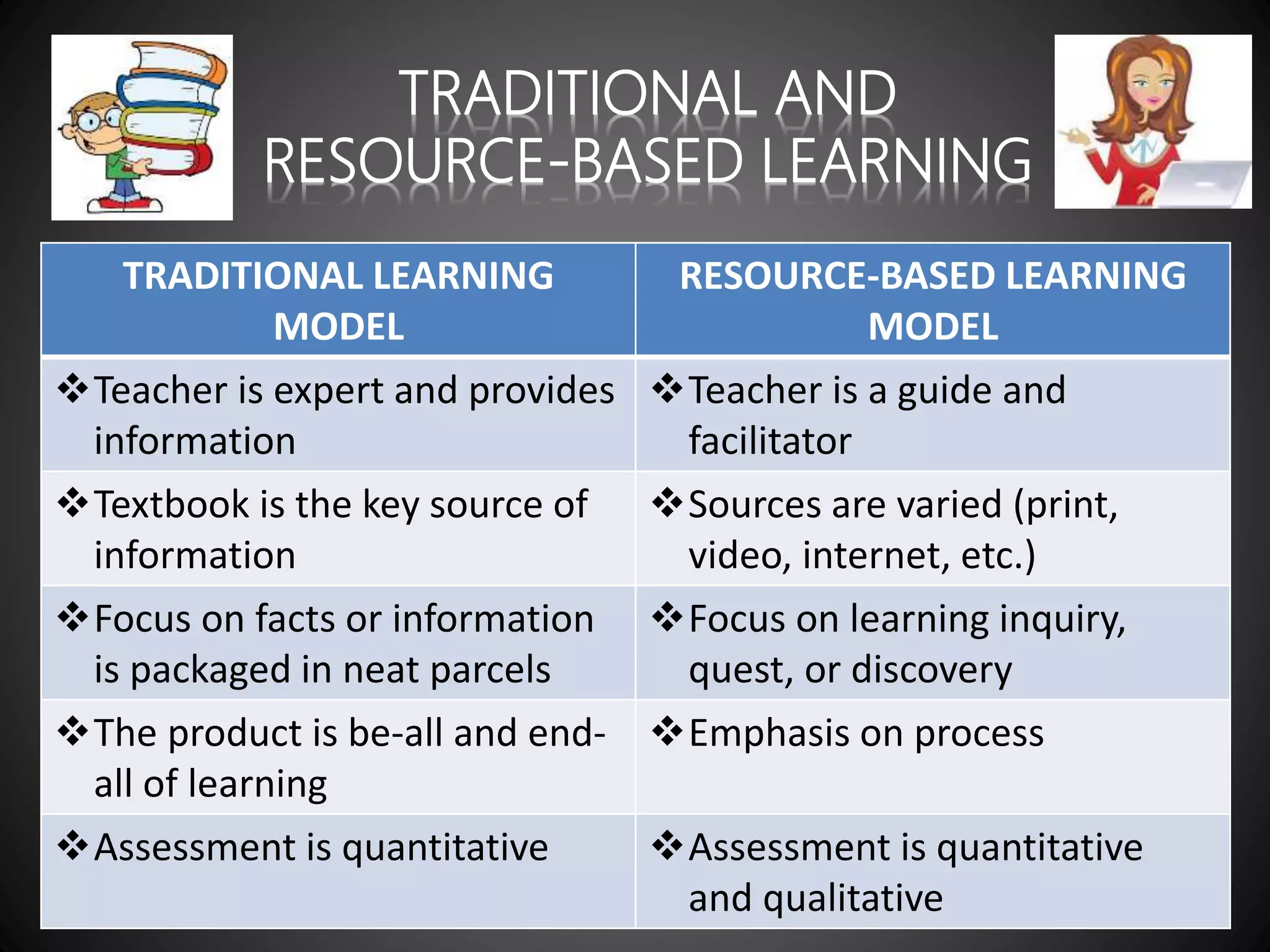
This document outlines four IT-based project types for developing higher-order thinking skills: 1) Resource-based projects where students research topics independently, 2) Simple creations where students design software or multimedia materials, 3) Guided hypermedia projects where students create presentations or multimedia reports, and 4) Web-based projects where students design webpages. The document also discusses constructivist teaching approaches and compares traditional versus resource-based learning models.