The document discusses several concepts related to meaningful learning environments:
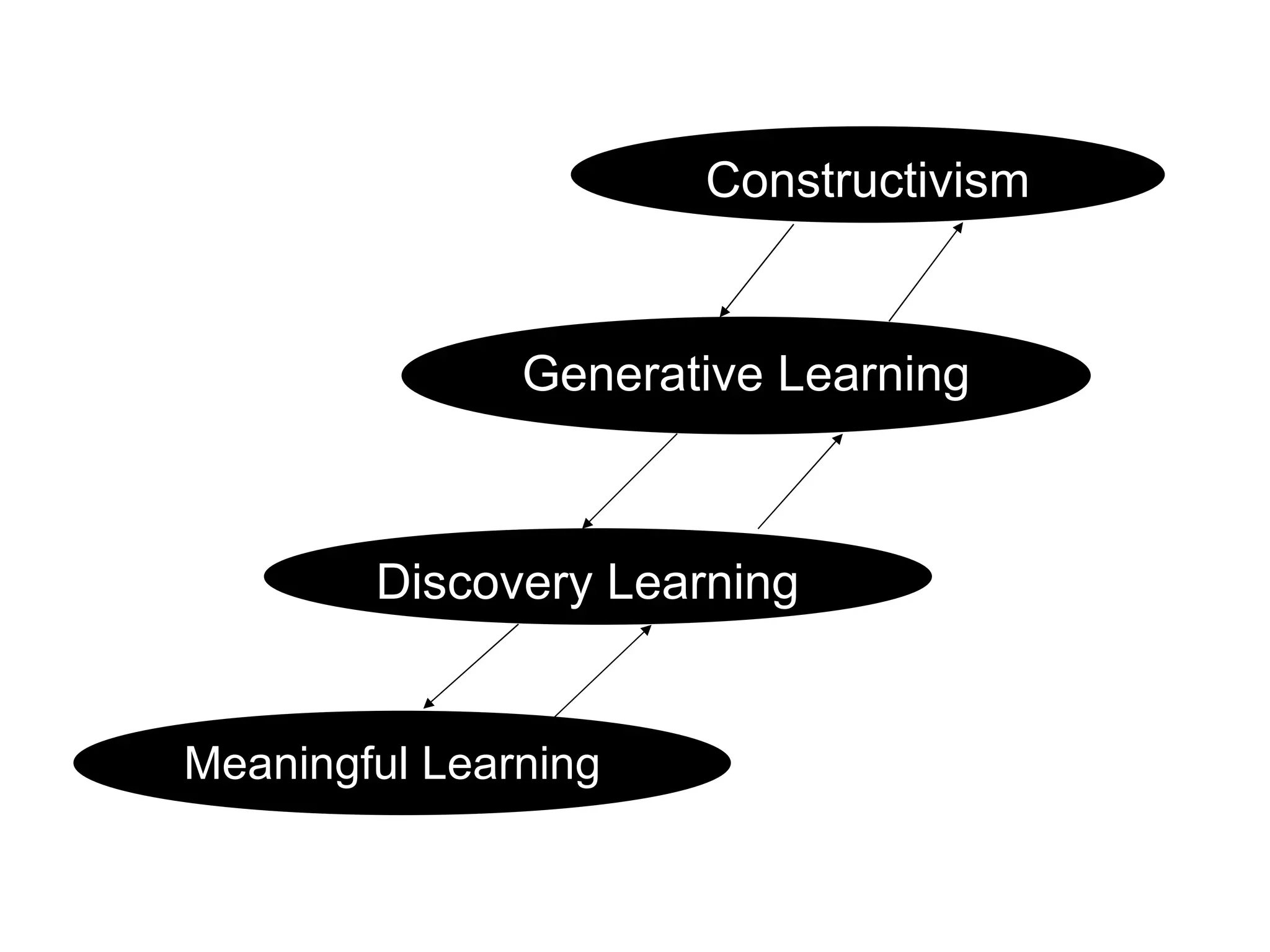
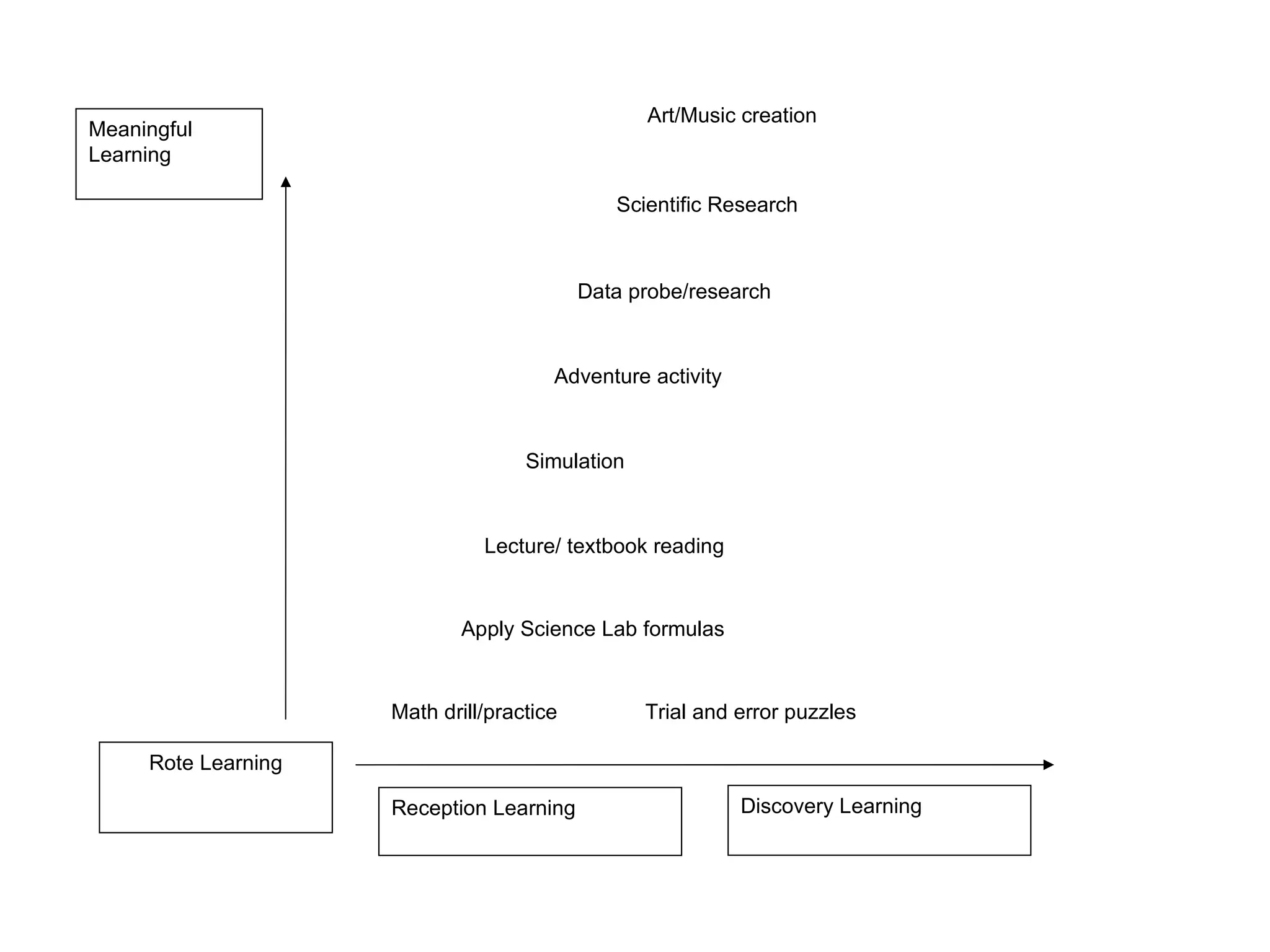
1. Meaningful learning focuses on relating new experiences to prior knowledge and understanding meaning rather than just memorizing facts.
2. Discovery learning involves students uncovering ideas through tasks rather than being directly taught, allowing them to engage personally and think independently.
3. Generative learning emphasizes generating meaning from experiences and drawing inferences to create personal explanations, rather than just storing information.
4. Constructivism holds that learning is actively constructed by learners based on their experiences and understanding of their personal world. The teacher facilitates meaningful learning connections.