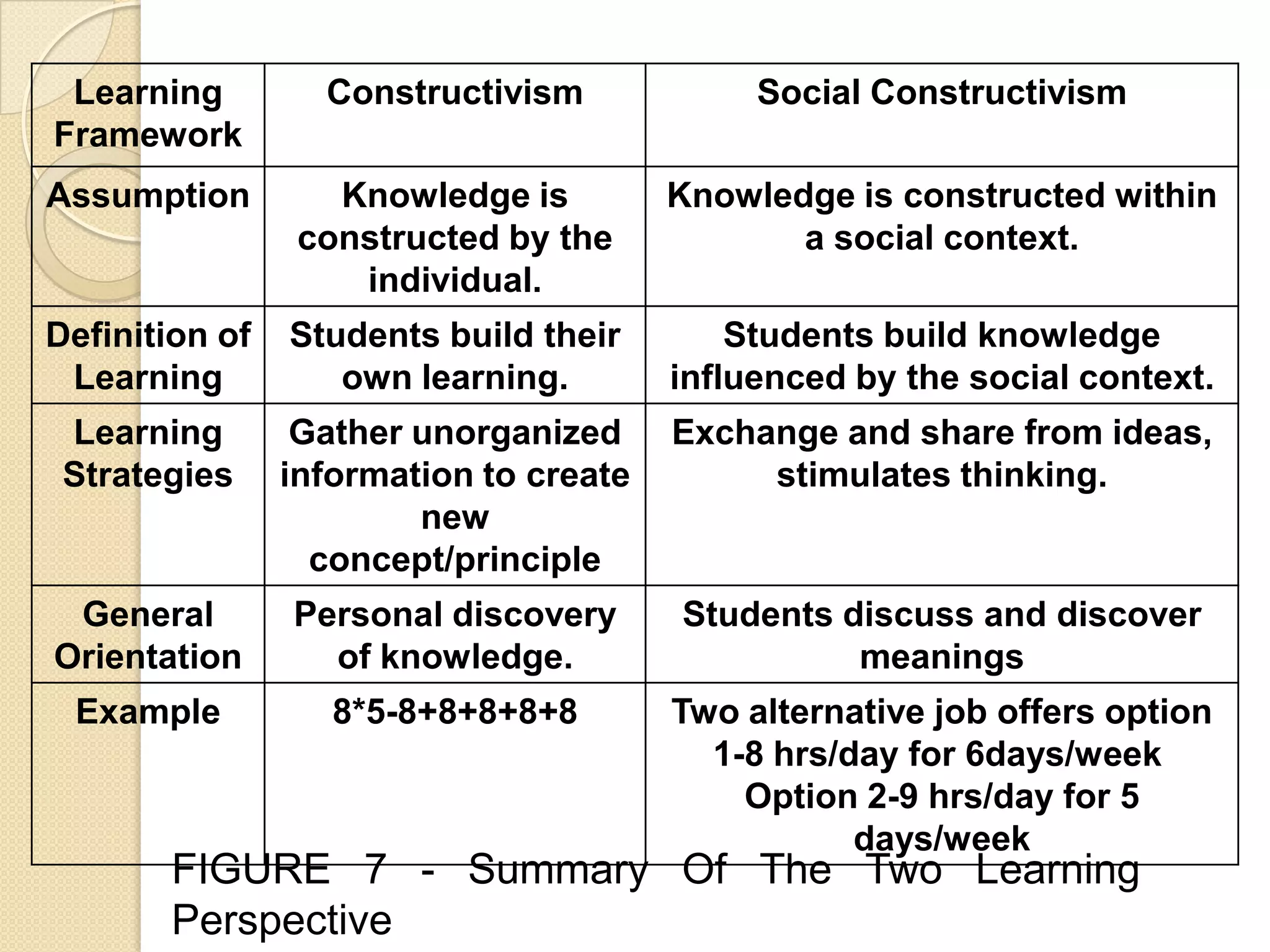
This document discusses how computers can support constructivist and social constructivist learning paradigms. It describes constructivism as knowledge constructed by individuals and social constructivism as knowledge constructed within social contexts. The computer is presented as a tool that can provide information, foster social knowledge building, and enhance communication. Specifically, it can serve as an informative tool, communication tool, constructive tool, co-constructive tool, and situating tool to support different aspects of individual and social learning.