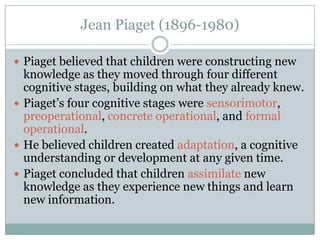
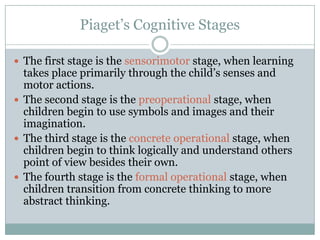
Constructivism is a learning theory where learners actively construct their own understanding and knowledge through experiences and reflecting on those experiences. Key aspects include students using critical thinking to analyze problems and collaborating to construct their own ideas. Major theorists who contributed to constructivism include Piaget, Bruner, Vygotsky, and Dewey. Piaget believed knowledge is built through stages while Vygotsky emphasized social learning and scaffolding. The theory suggests teachers guide students to draw their own conclusions and use technology to teach in a student-centered approach.