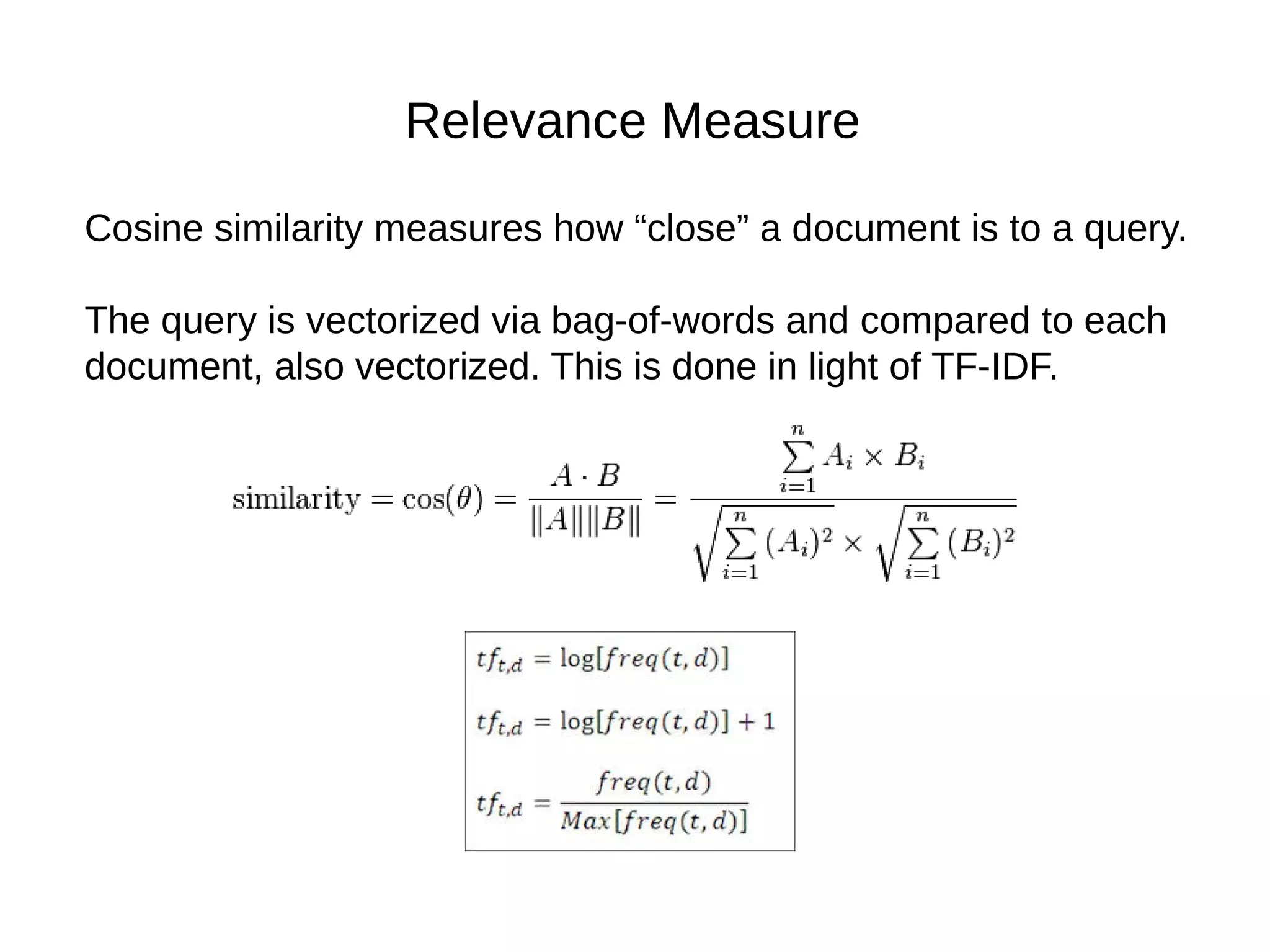
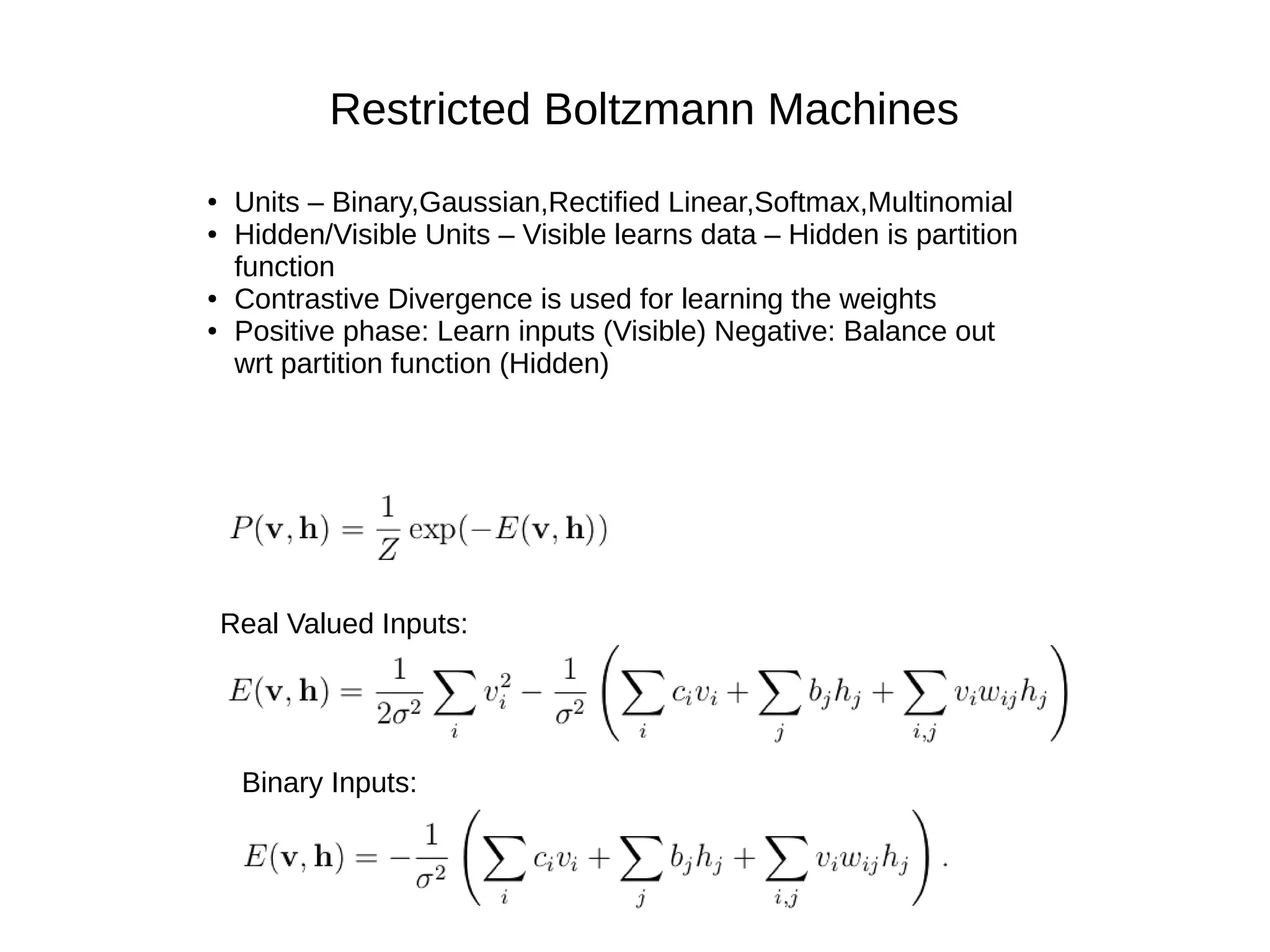
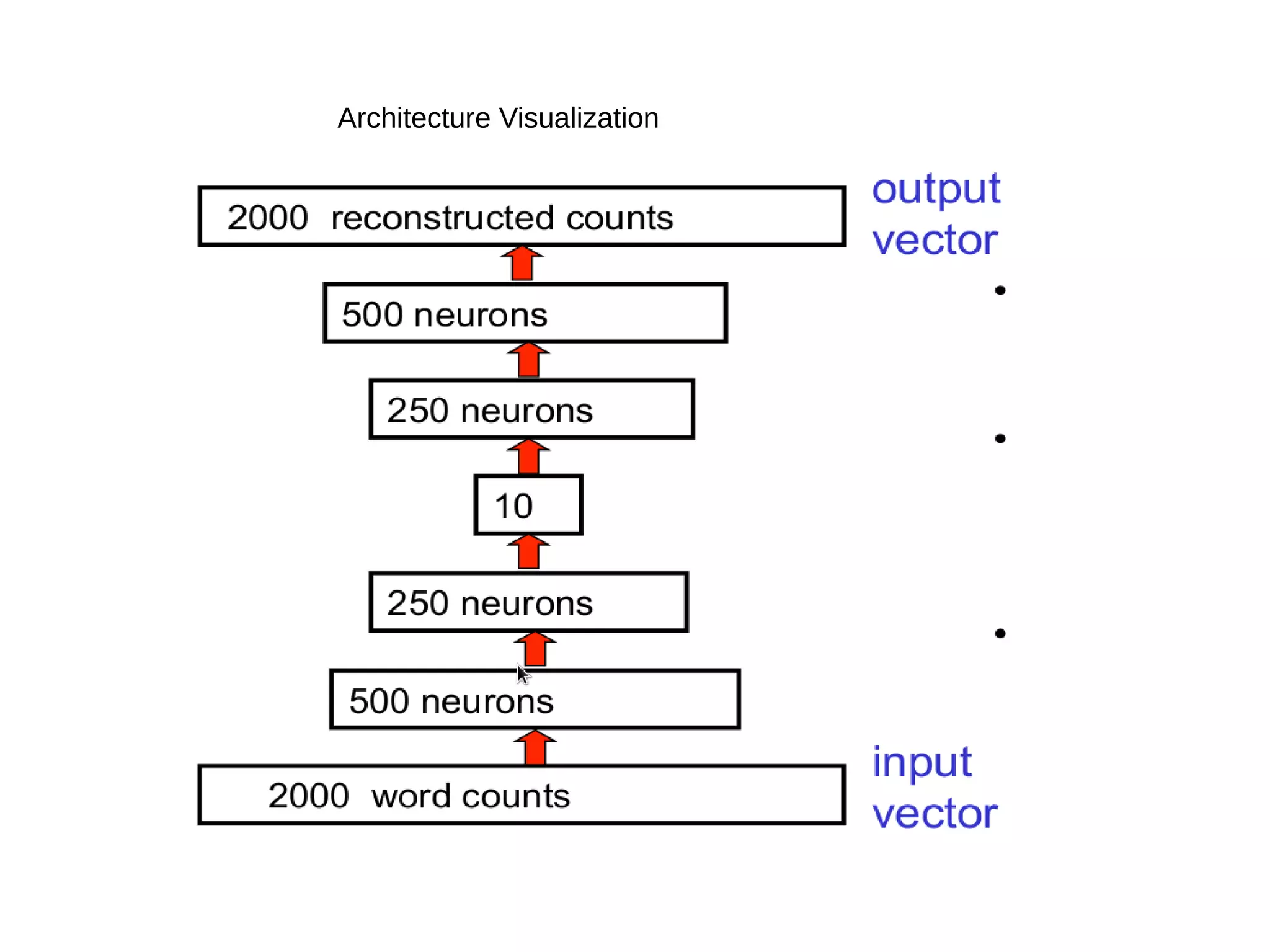
This document provides an overview of using deep autoencoders to improve question answering systems. It discusses how deep autoencoders can encode text or images into codes that are indexed and stored. This allows for fast lookup of potential answer candidates. The document describes the components of question answering systems and information retrieval systems. It also provides details on how deep autoencoders work, including using a stacked restricted Boltzmann machine architecture for encoding and decoding layers.