This document provides an introduction to deep learning for natural language processing (NLP) over 50 minutes. It begins with a brief introduction to NLP and deep learning, then discusses traditional NLP techniques like one-hot encoding and clustering-based representations. Next, it covers how deep learning addresses limitations of traditional methods through representation learning, learning from unlabeled data, and modeling language recursively. Several examples of neural networks for NLP tasks are presented like image captioning, sentiment analysis, and character-based language models. The document concludes with discussing word embeddings, document representations, and the future of deep learning for NLP.













![A NOT-SO-SHORT INTRODUCTION TO DEEP LEARNING NLP - FRANCESCO GADALETA
No. 2
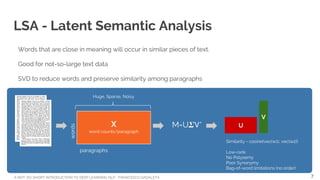
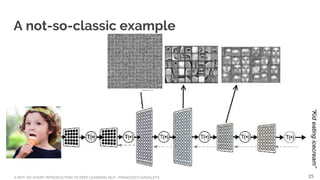
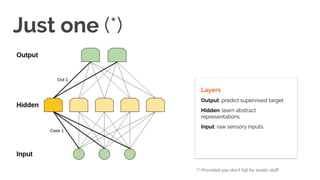
Learning from unlabeled data
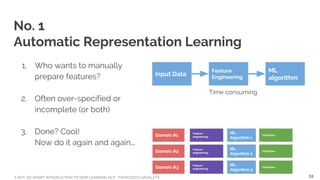
Traditional NLP requires labeled training data
Guess what?
Almost all data is unlabeled
Learning how data is generated is essential to ‘understand’ data
[Demo]
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deeplearningnlp-160617072047/85/Deeplearning-NLP-19-320.jpg)



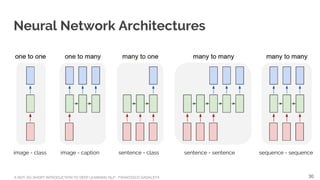



![A NOT-SO-SHORT INTRODUCTION TO DEEP LEARNING NLP - FRANCESCO GADALETA
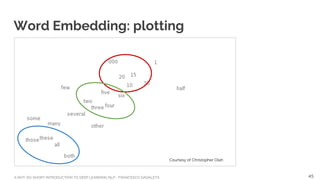
Courtesy of Christopher Olah
Word Embedding: algebraic operations
MAN + ‘something good’ == WOMAN
WOMAN - ‘something bad’ == MAN
MAN + ‘something’ == WOMAN
KING + ‘something’ == QUEEN
Identification of text regularities in [3] with 80-1600
dimensions, 320M words Broadcast news, 82k unique
words.
46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deeplearningnlp-160617072047/85/Deeplearning-NLP-46-320.jpg)
![A NOT-SO-SHORT INTRODUCTION TO DEEP LEARNING NLP - FRANCESCO GADALETA
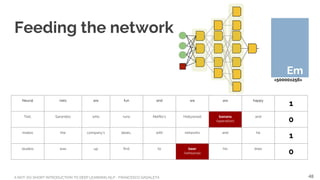
Demo: word embeddings
Training set 9 GB free text
Vocabulary size 50000
Embedding
dimensions
256
Context window 10
Skip top common
words
100
Layers [10,100,512,1]
Embeddings <50000, 256>
47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deeplearningnlp-160617072047/85/Deeplearning-NLP-47-320.jpg)




![A NOT-SO-SHORT INTRODUCTION TO DEEP LEARNING NLP - FRANCESCO GADALETA
References
[1] Recursive Deep Models for Semantic Compositionality Over a Sentiment Treebank
Richard Socher, Alex Perelygin, Jean Y. Wu, Jason Chuang, Christopher D. Manning, Andrew Y. Ng and Christopher Potts
Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA
[2] Document Embedding with Paragraph Vectors
Andrew M. Dai, Christopher Olah, Quoc V. Le Google
[3] Linguistic Regularities in Continuous Space Word Representations
Tomas Mikolov, Wen-tau Yih, Geoffrey Zweig, Microsoft Research
[4] Distributed Representations of Sentences and Documents
Quoc Le, Tomas Mikolov, Google Inc
[5] Skip-Thought Vectors
Ryan Kiros, Yukun Zhu, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Richard S. Zemel, Antonio Torralba, Raquel Urtasun, Sanja Fidler
[6] Text Understanding from Scratch
Xiang Zhang, Yann LeCun Computer Science Department, Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York
University
[7] World of Piggy - Data Science at Home Podcast - History and applications of Deep Learning http://worldofpiggy.
com/history-and-applications-of-deep-learning-a-new-podcast-episode/
54](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deeplearningnlp-160617072047/85/Deeplearning-NLP-54-320.jpg)
