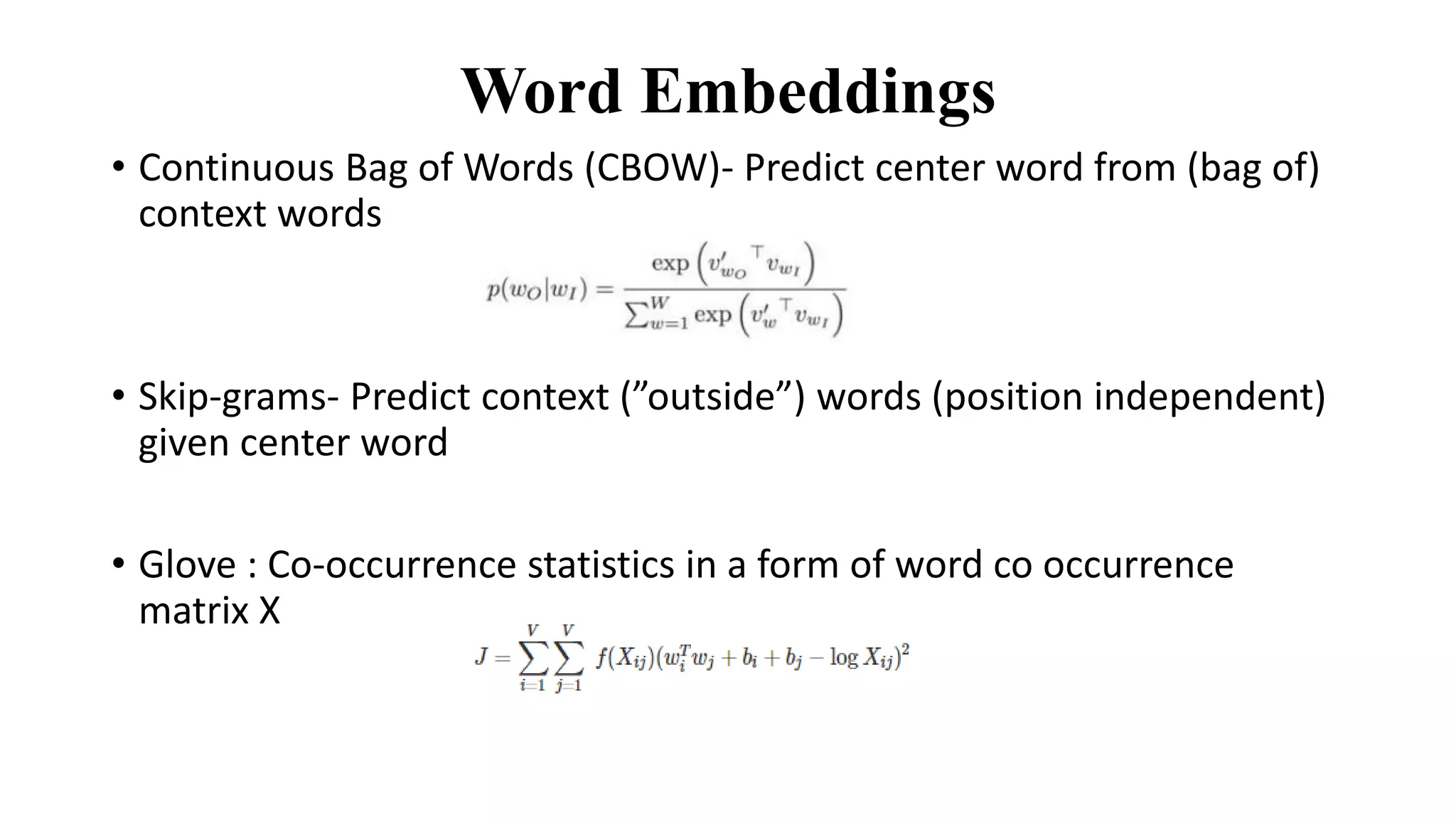
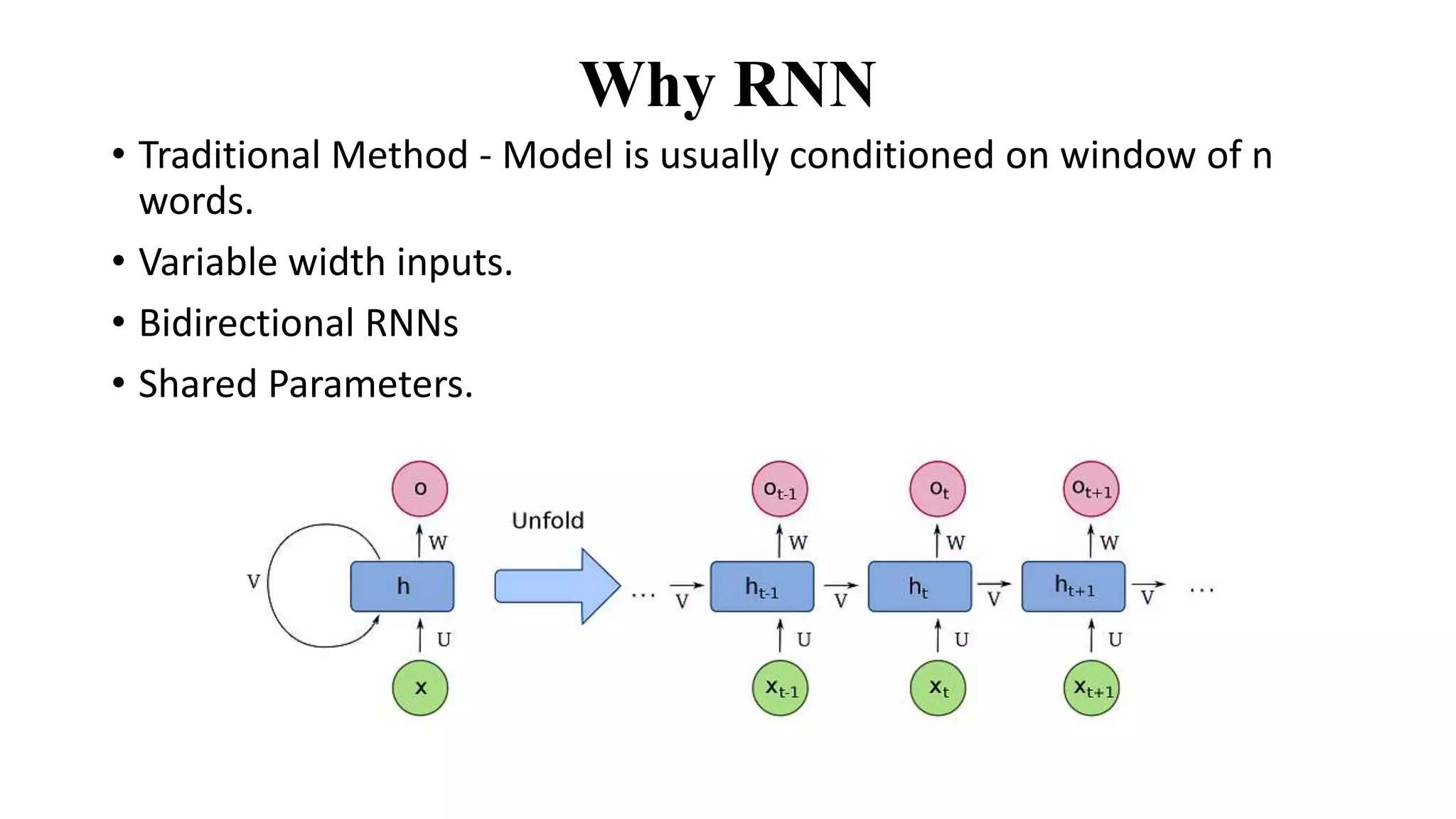
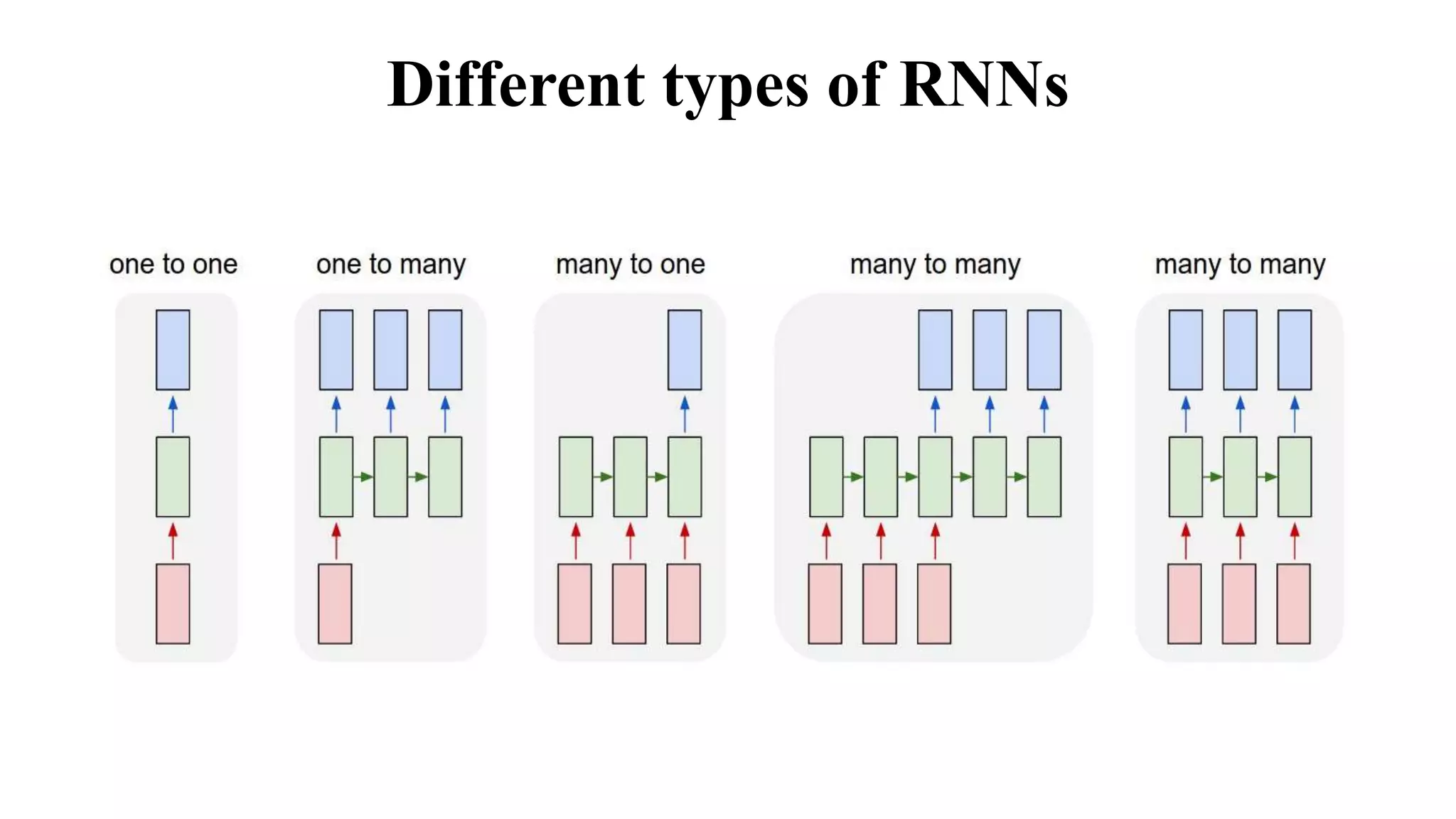
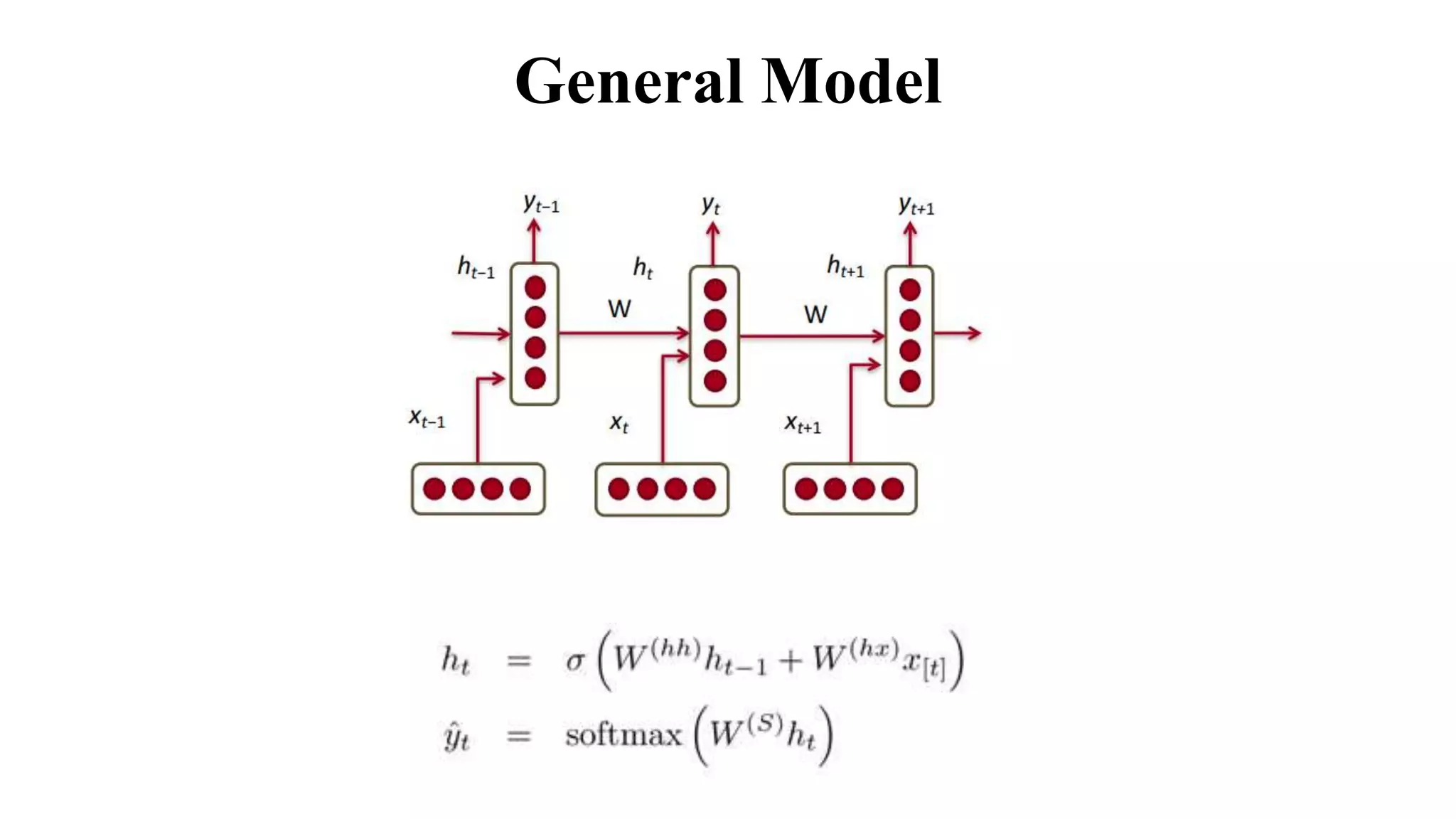
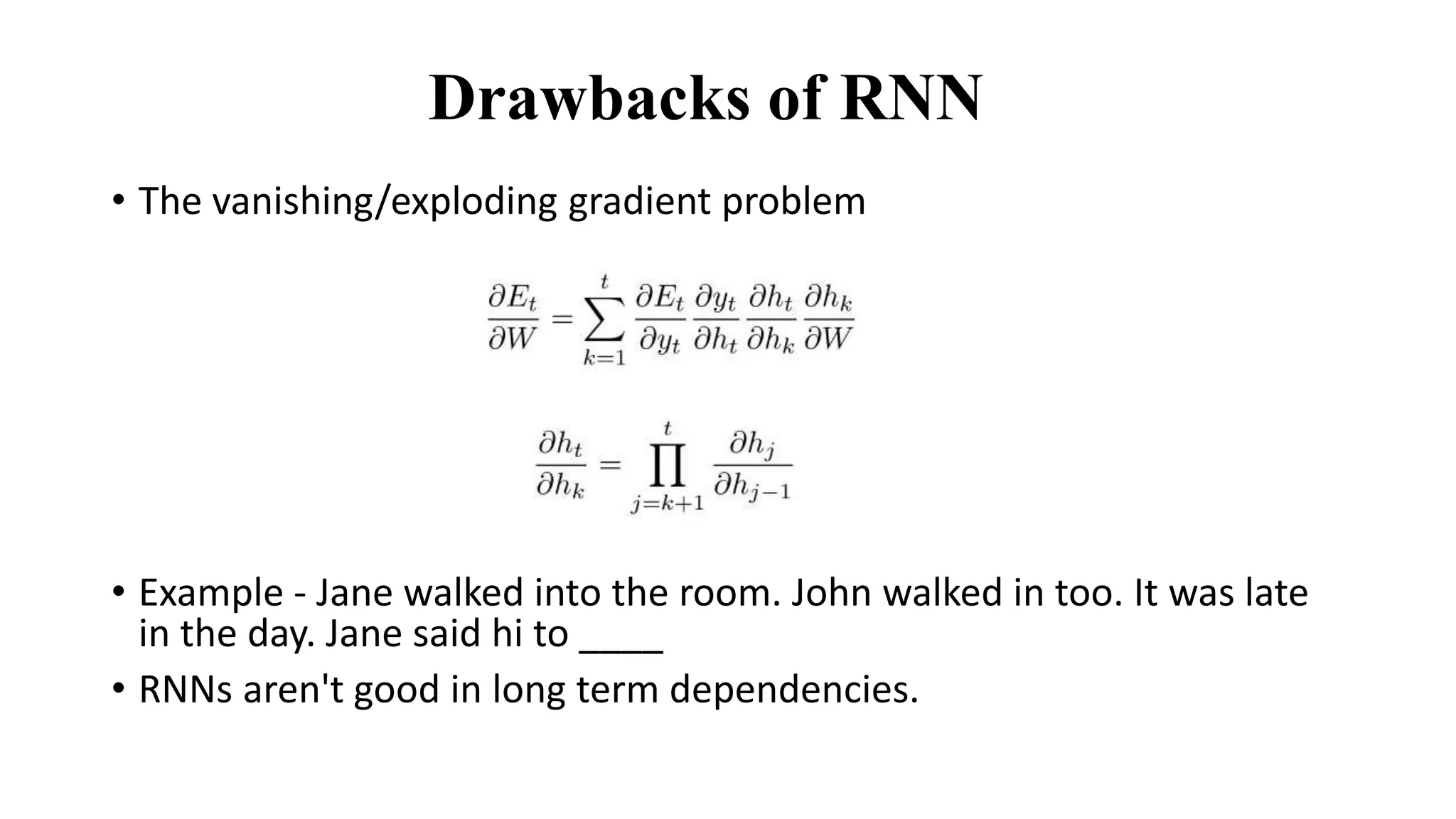
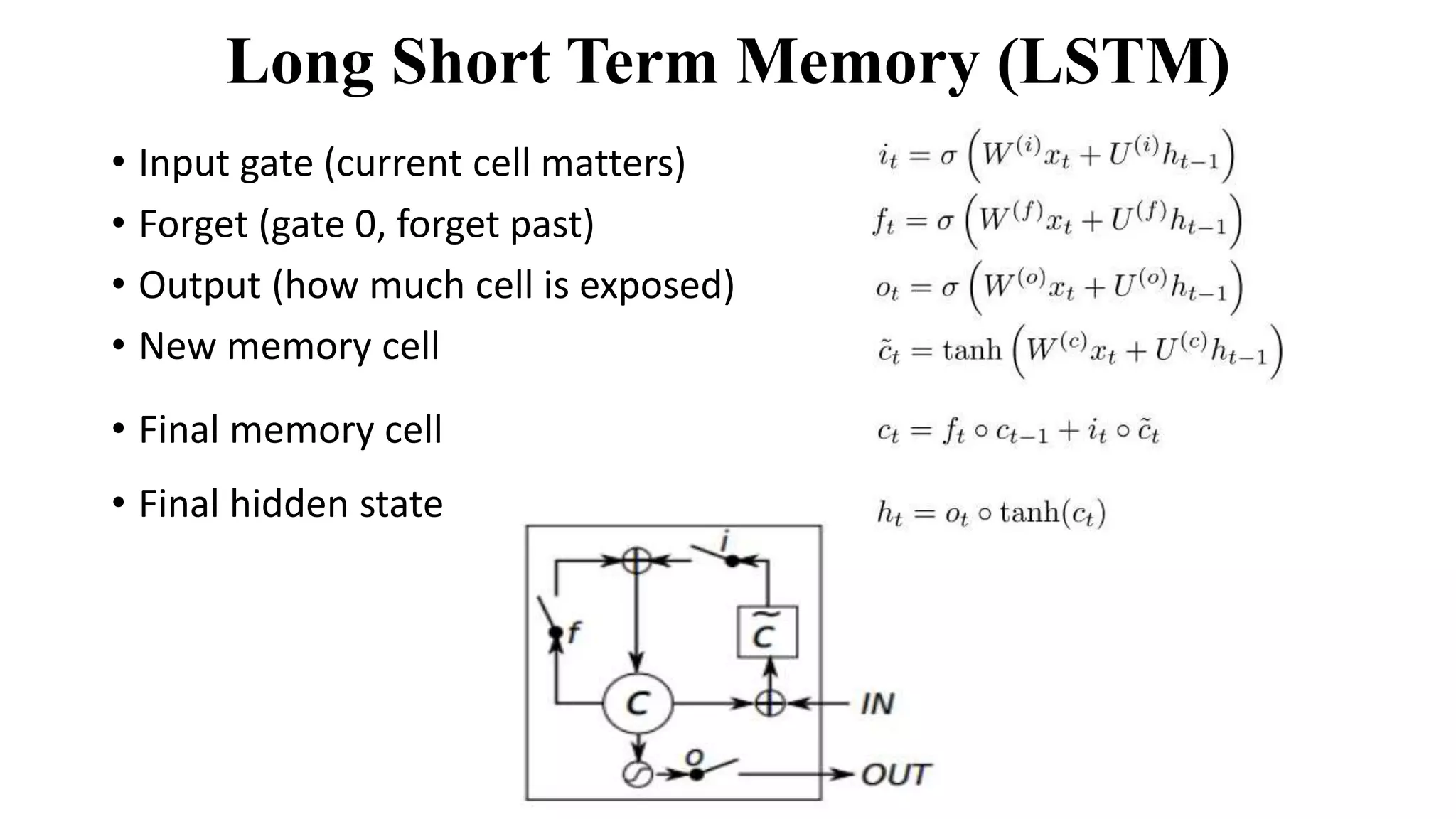
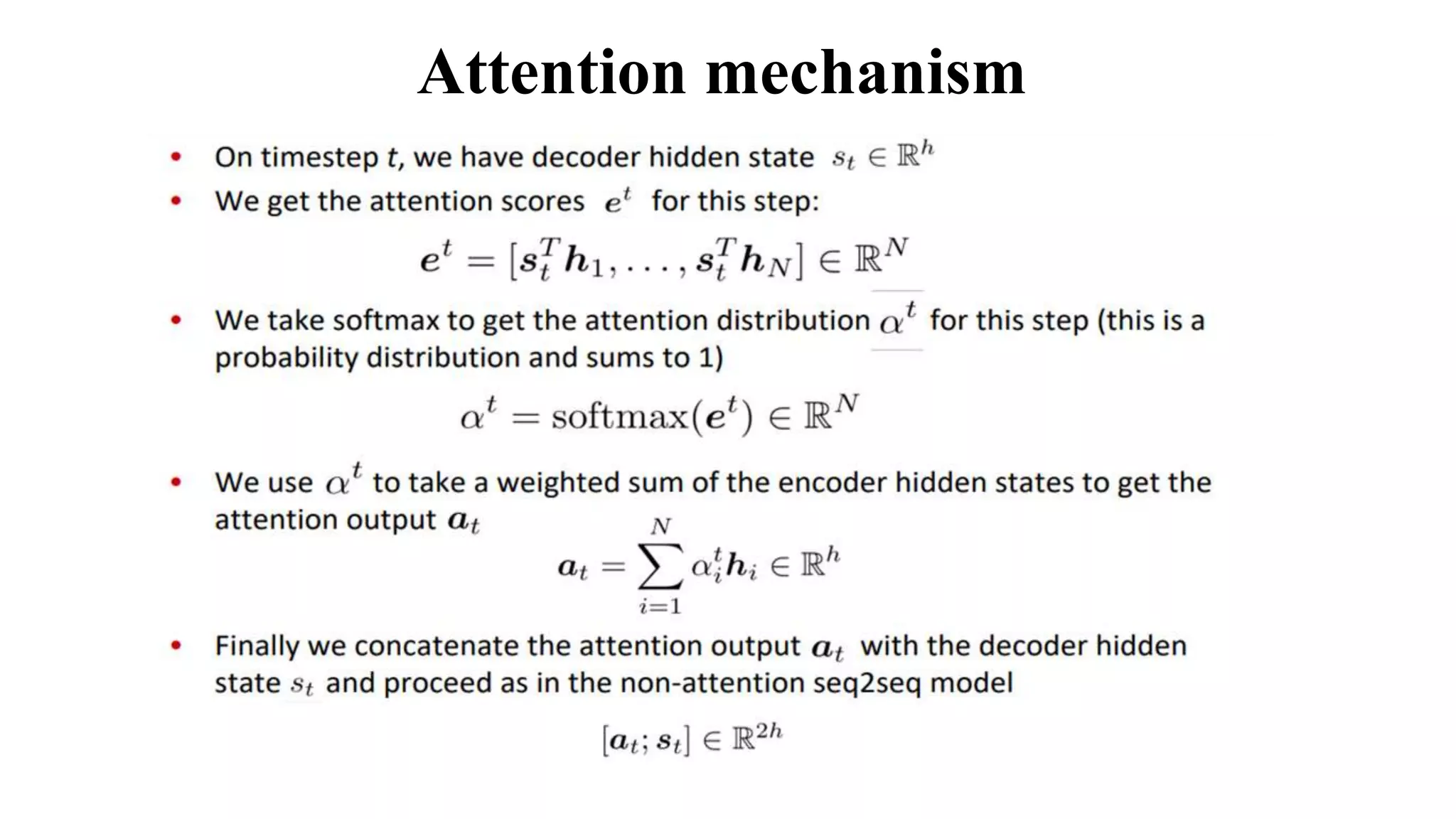
The document discusses word embeddings and various RNN techniques used in sequence modeling, including GRU and LSTM architectures. It details applications such as text classification, machine translation, and speech recognition, while also addressing the limitations of RNNs like the vanishing gradient problem. The document emphasizes the importance of attention mechanisms for improving long-term dependencies in sequence data.