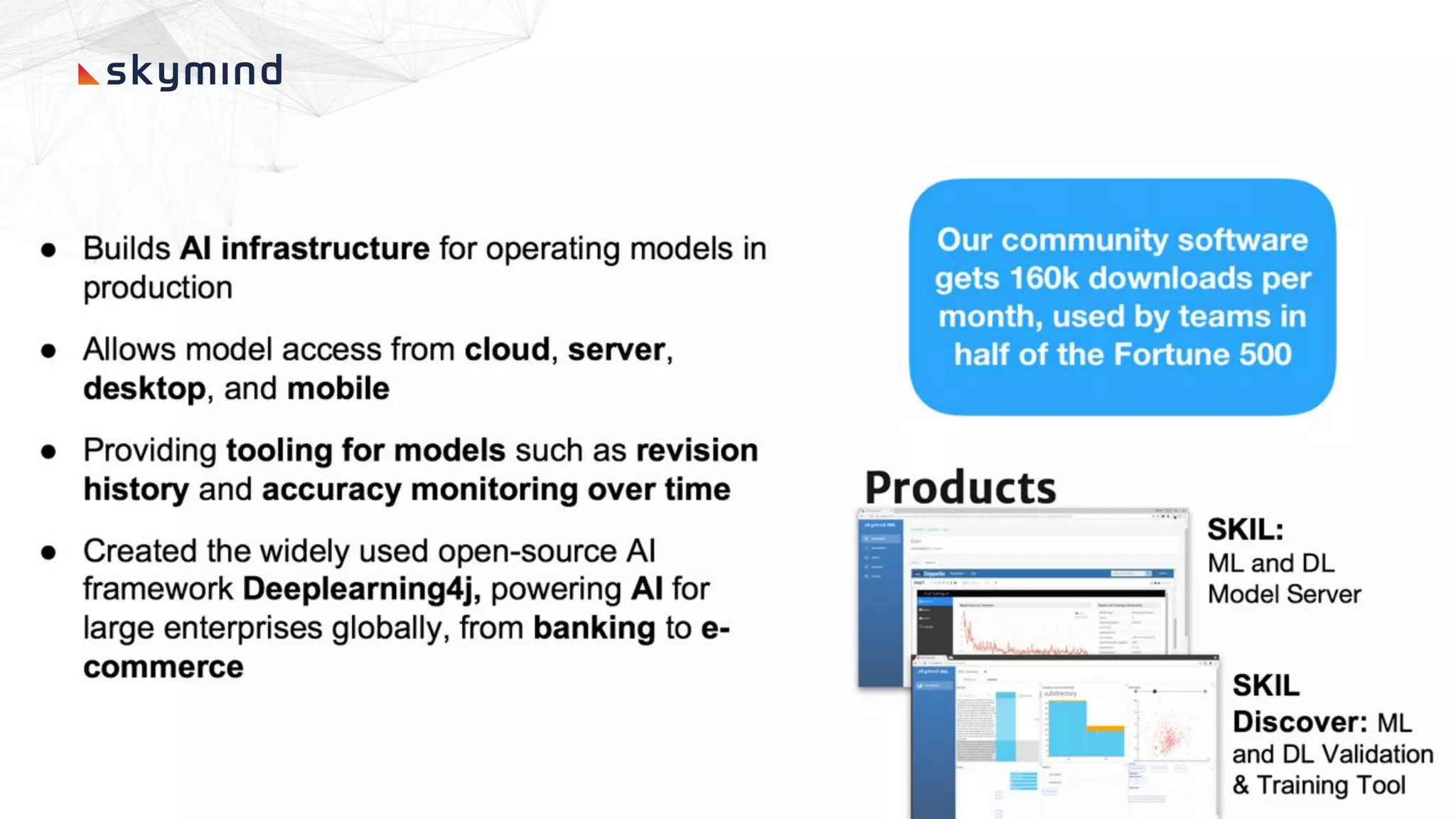
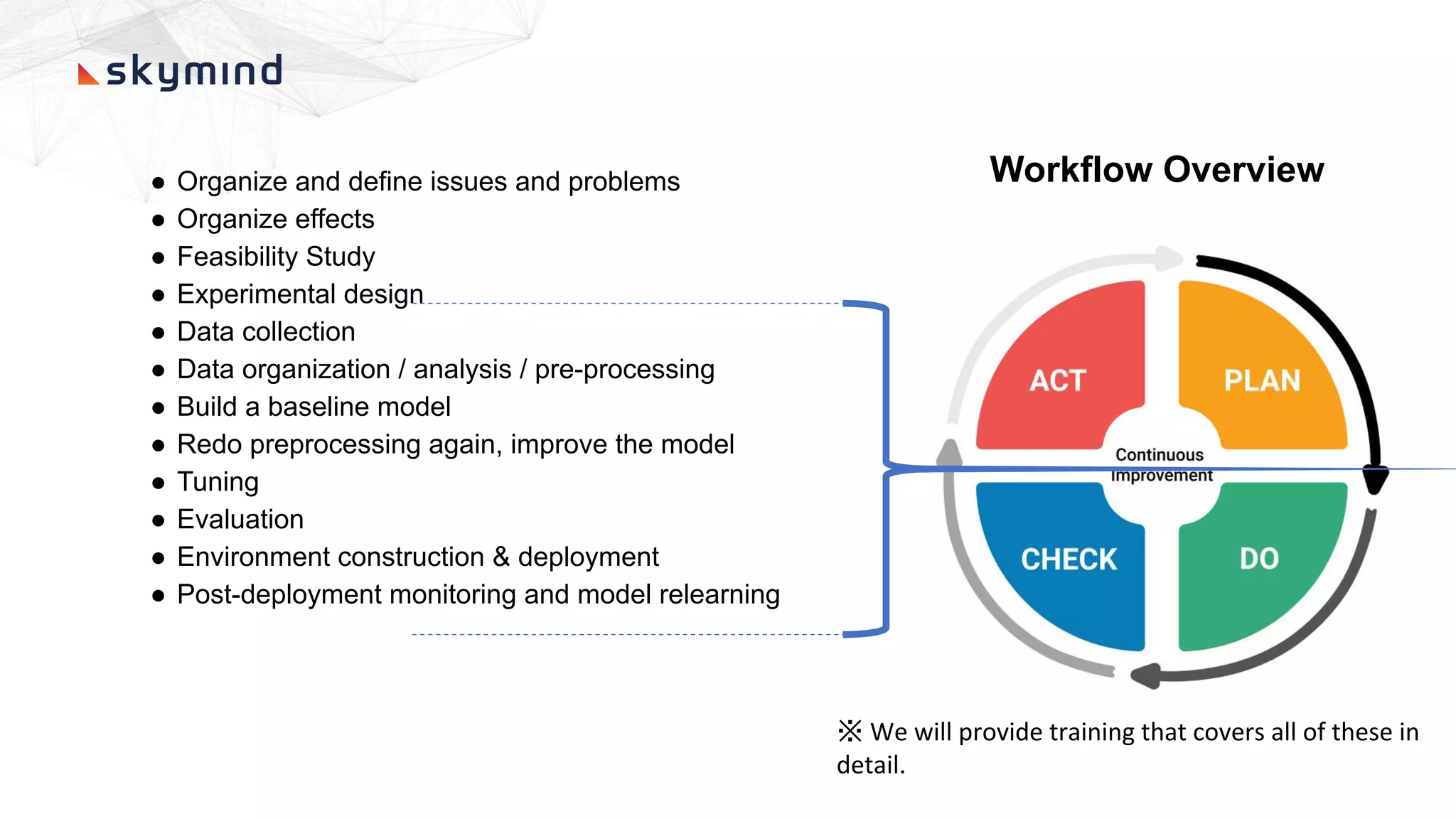
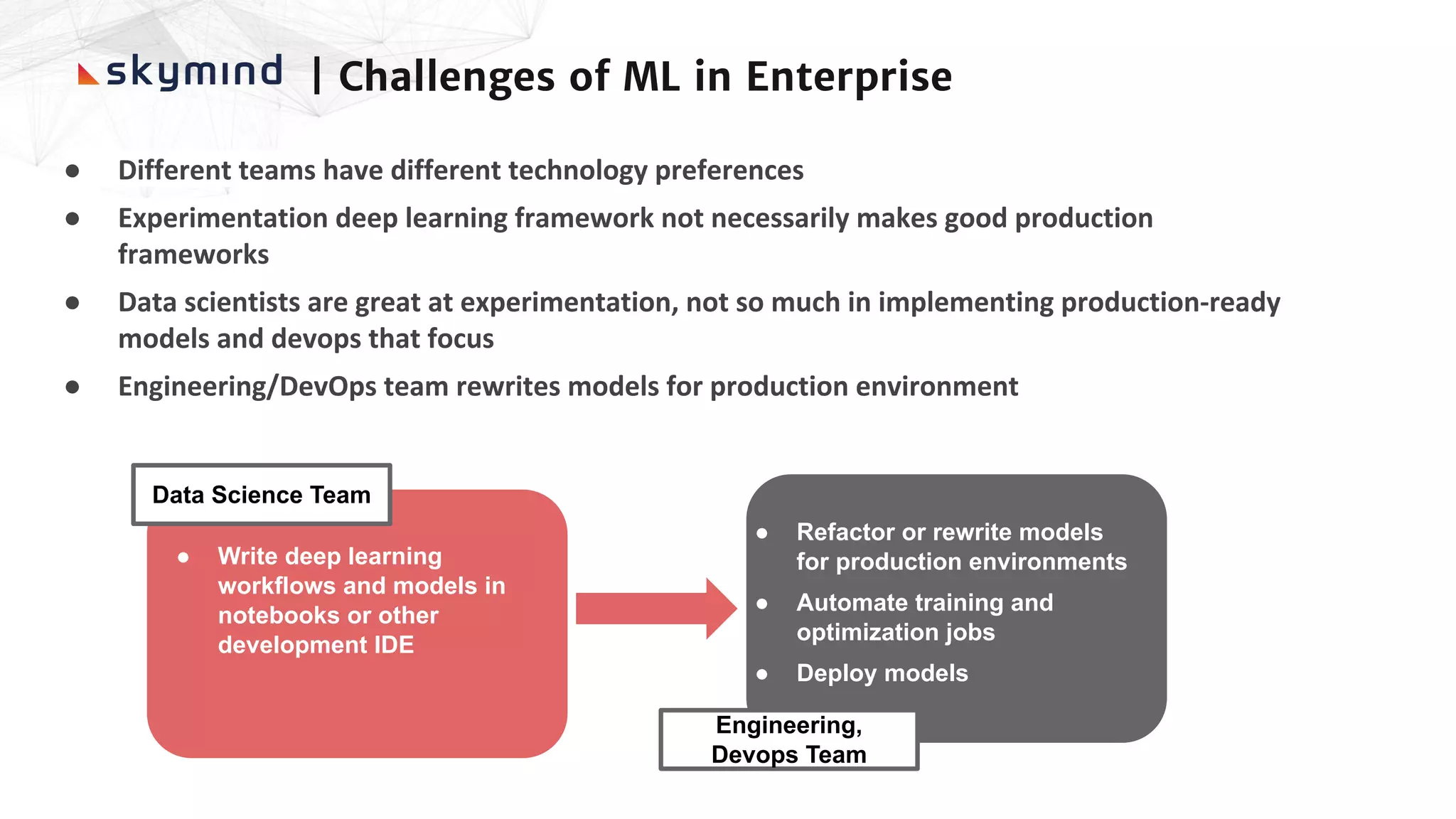
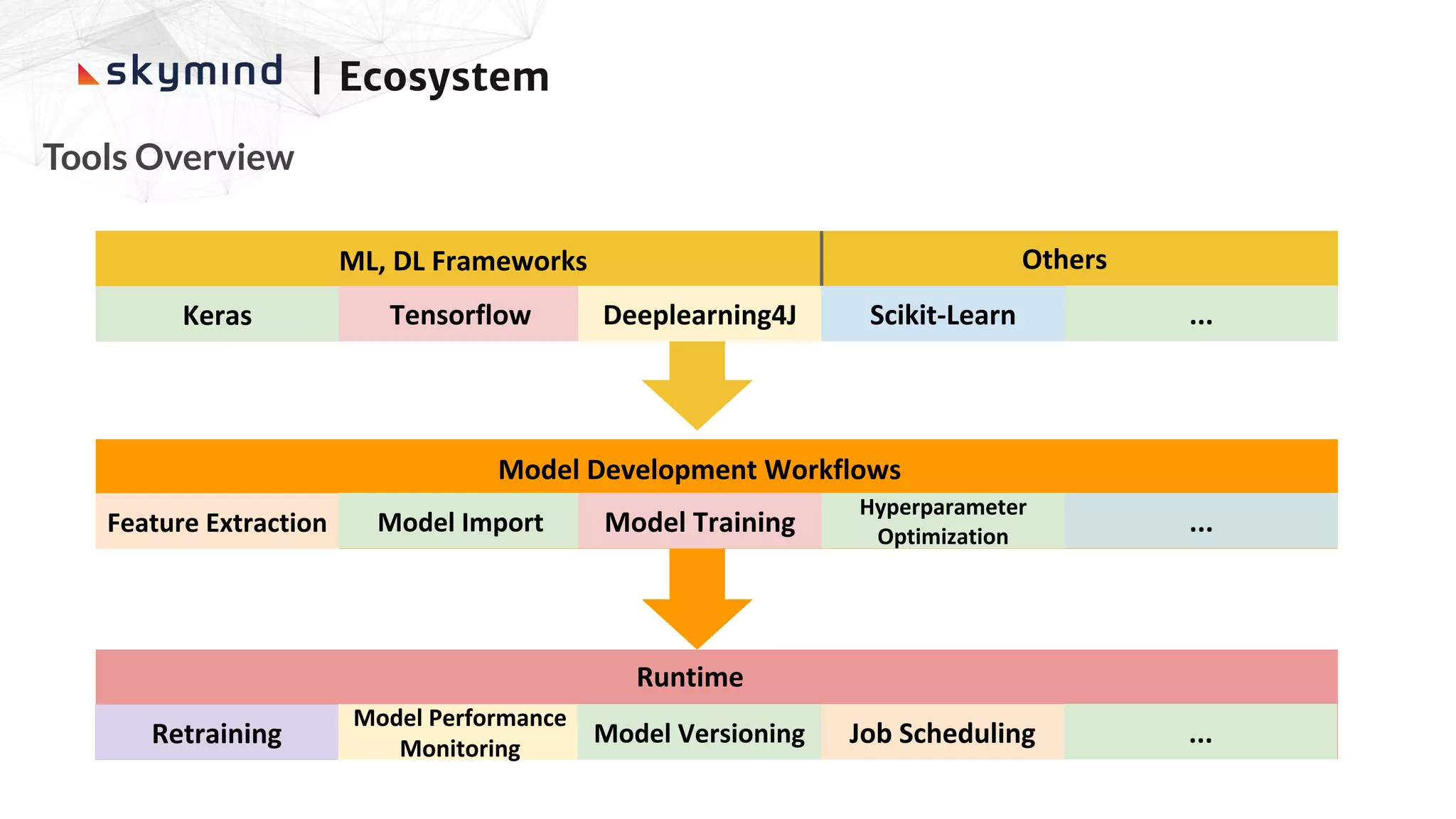
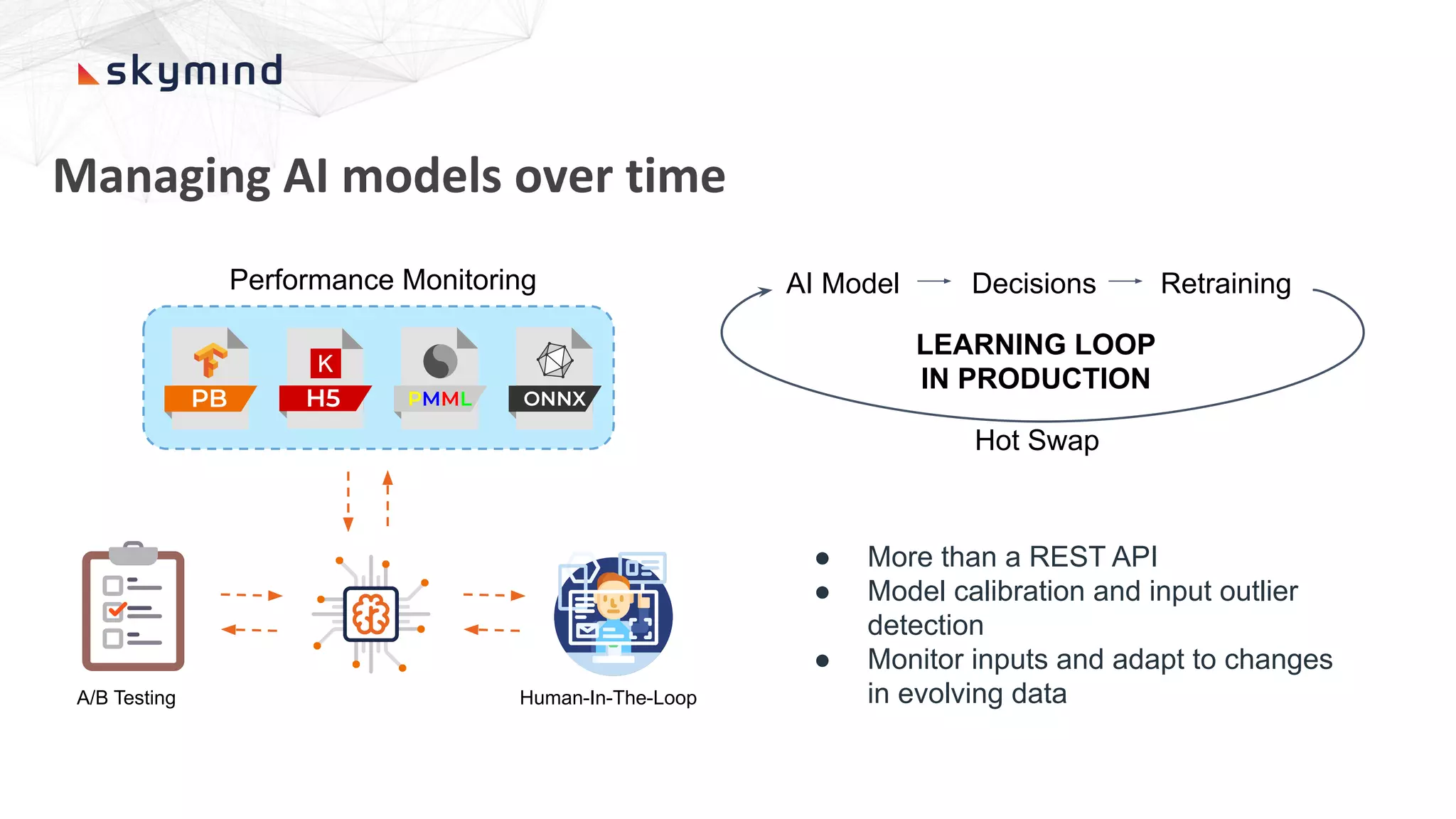
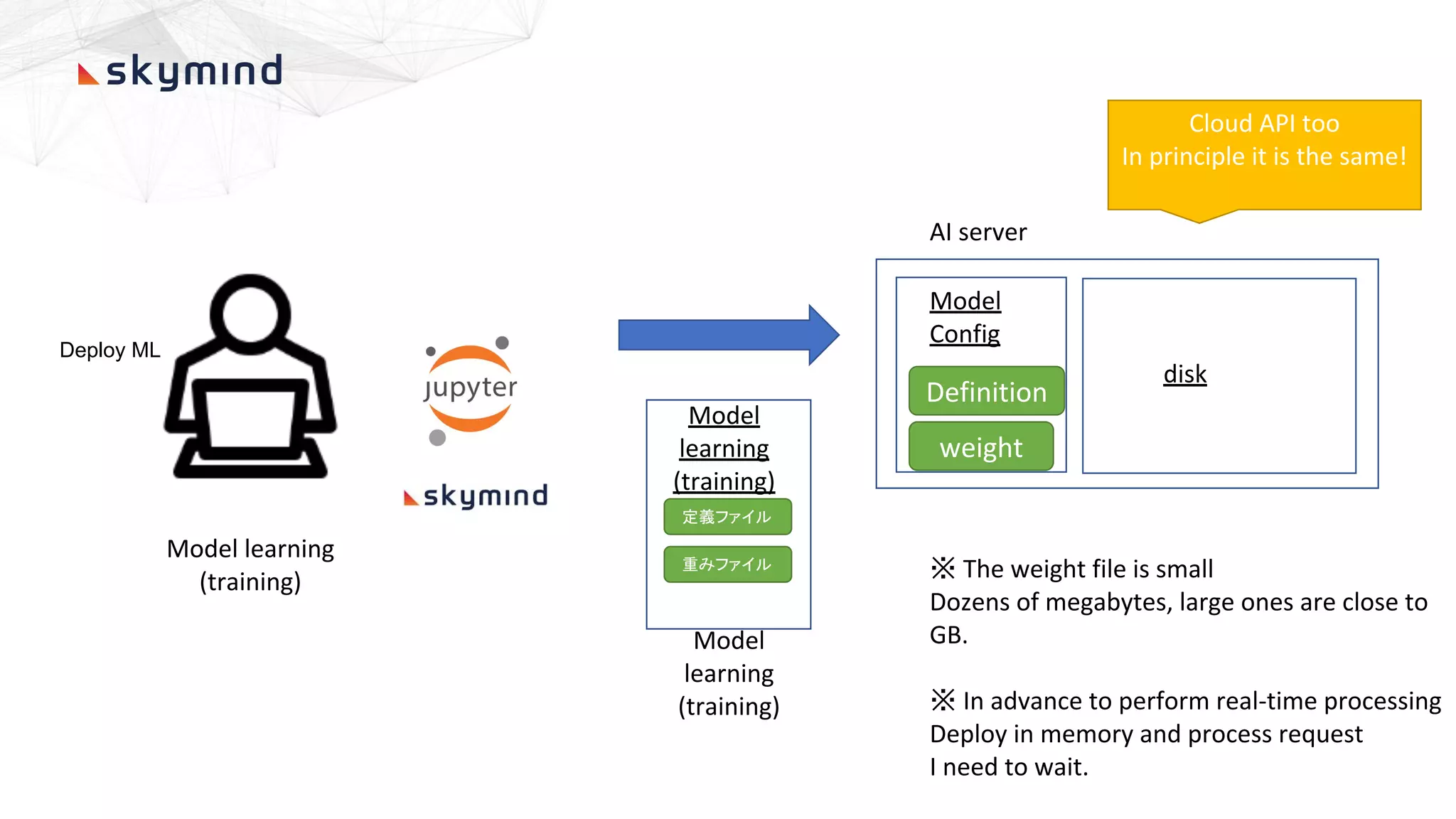
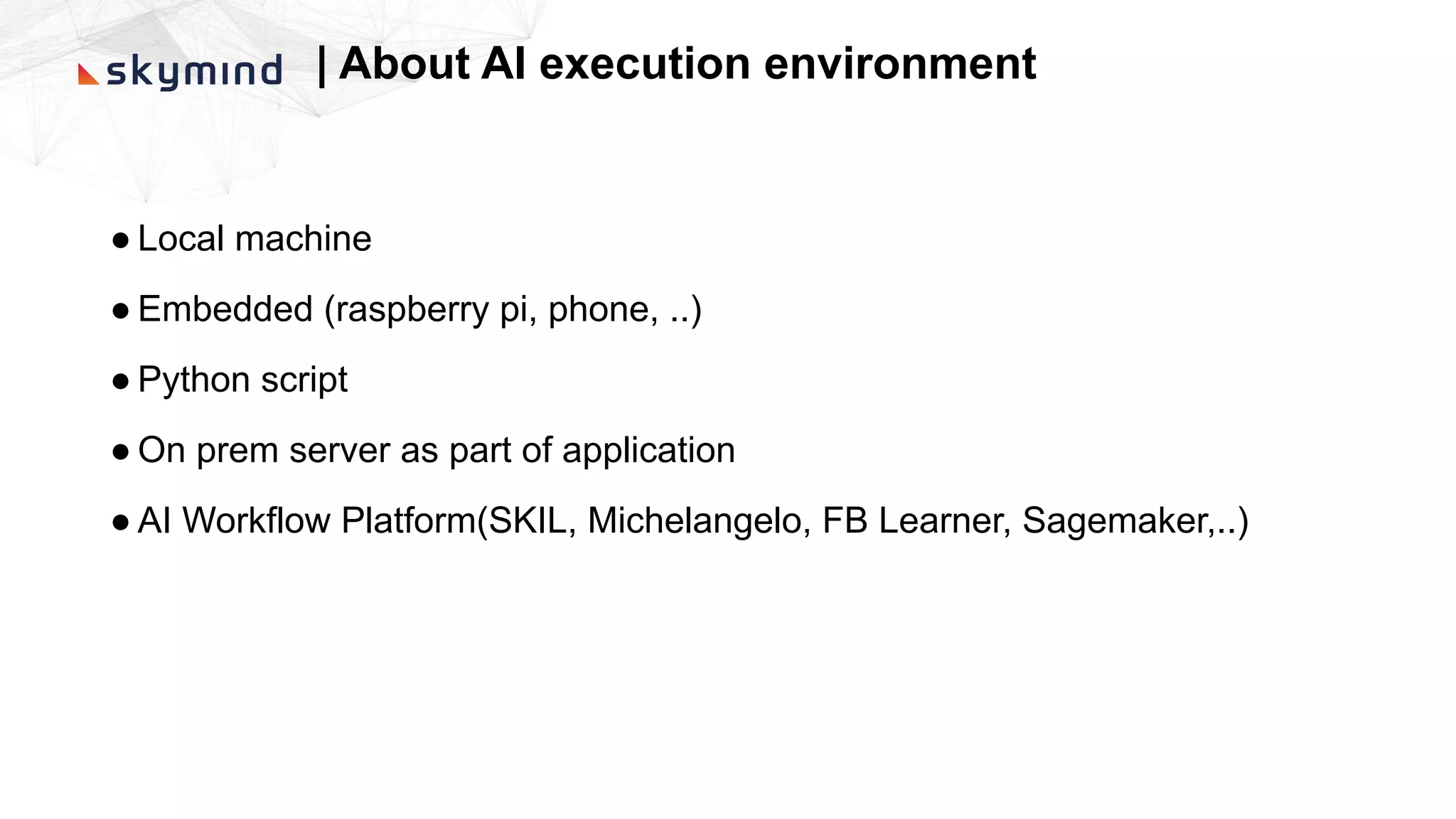
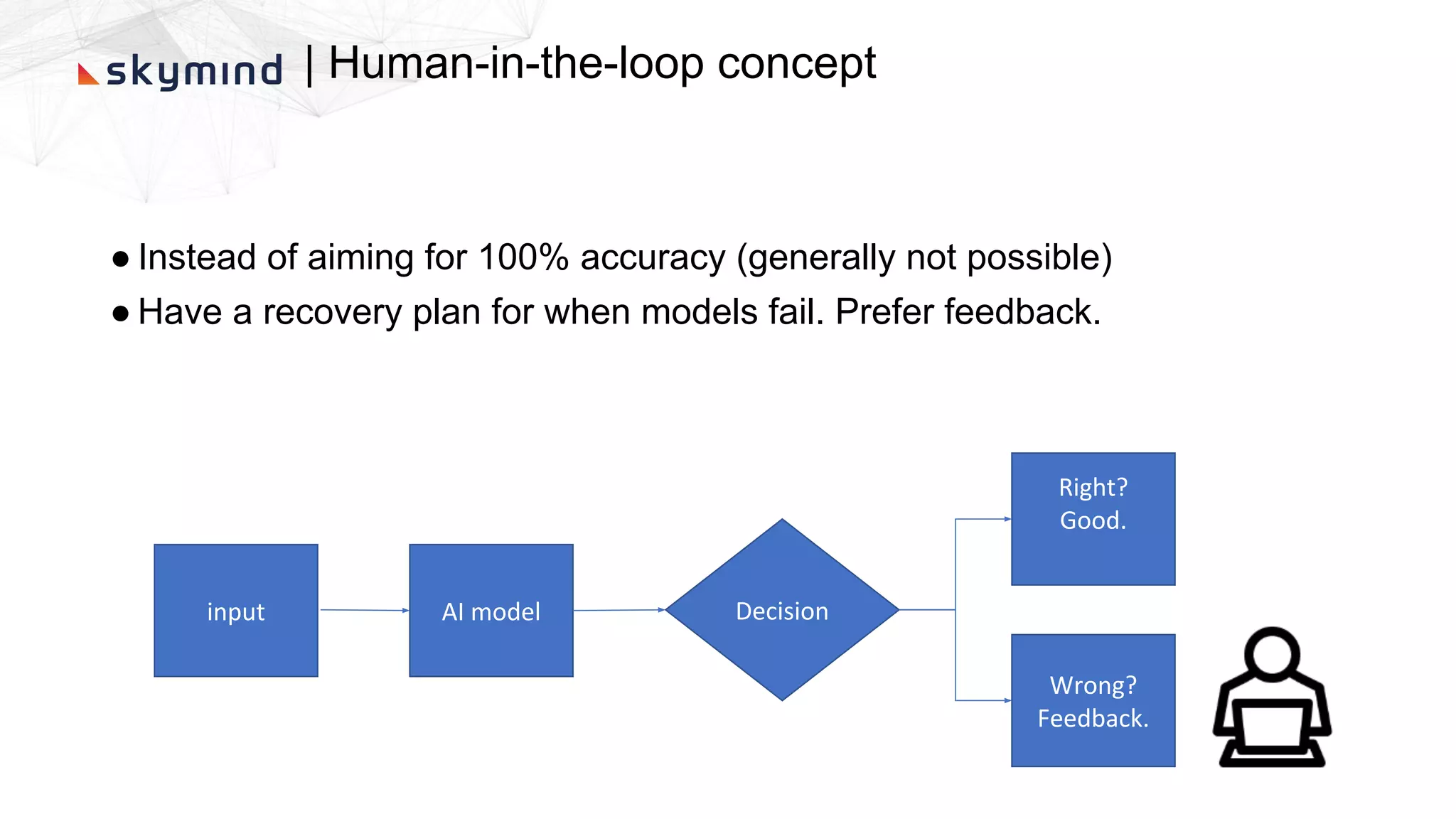
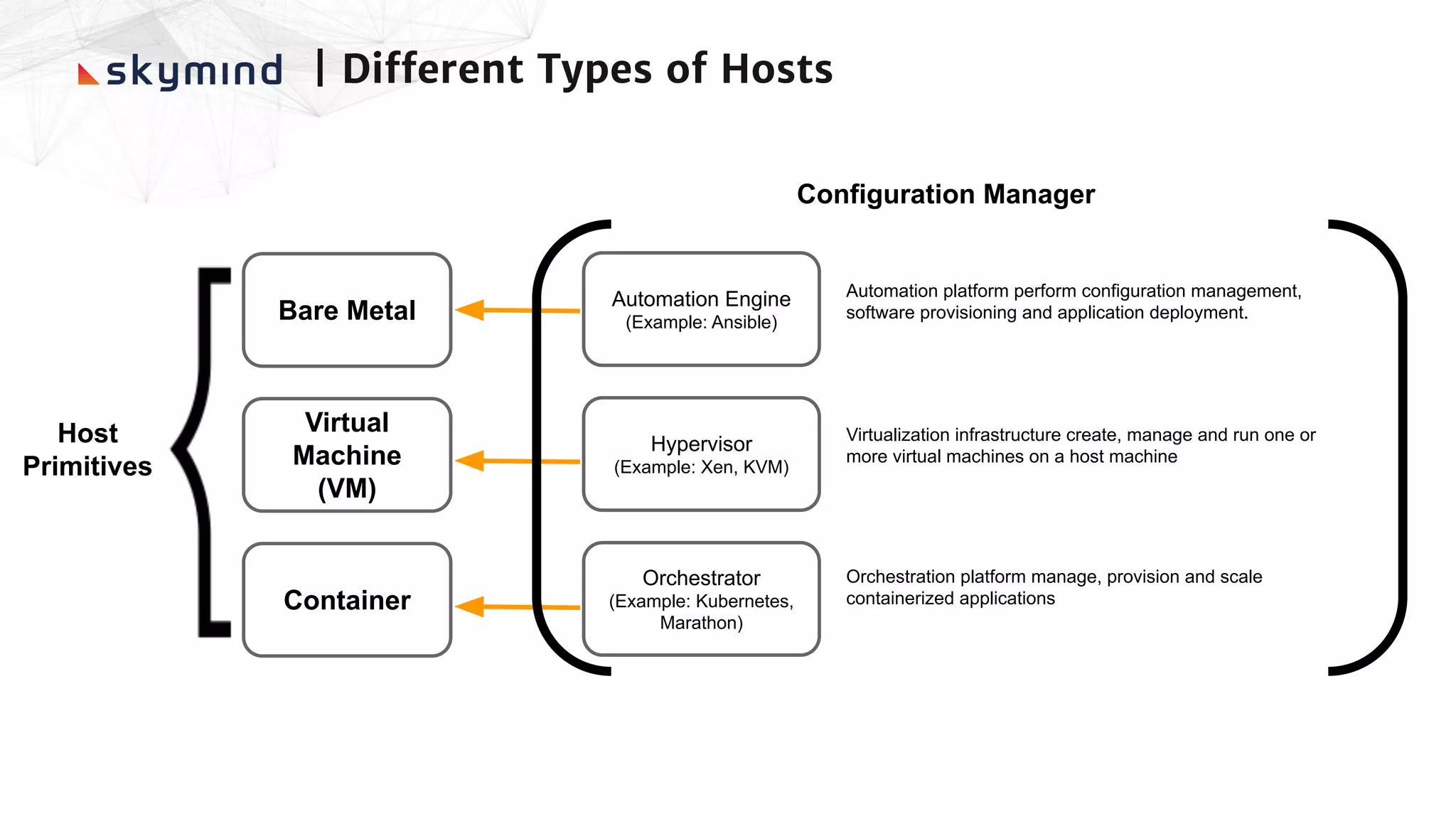
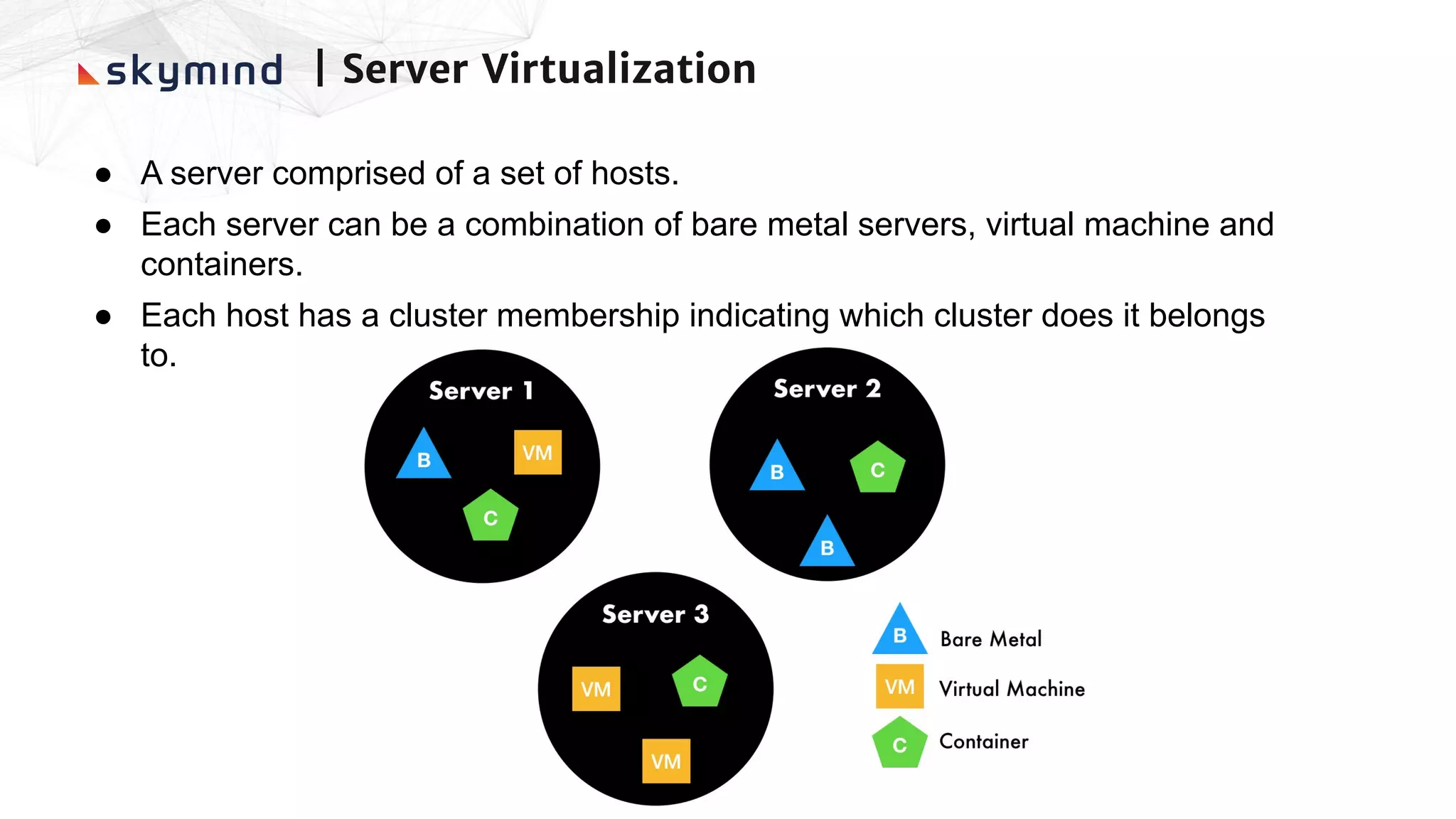
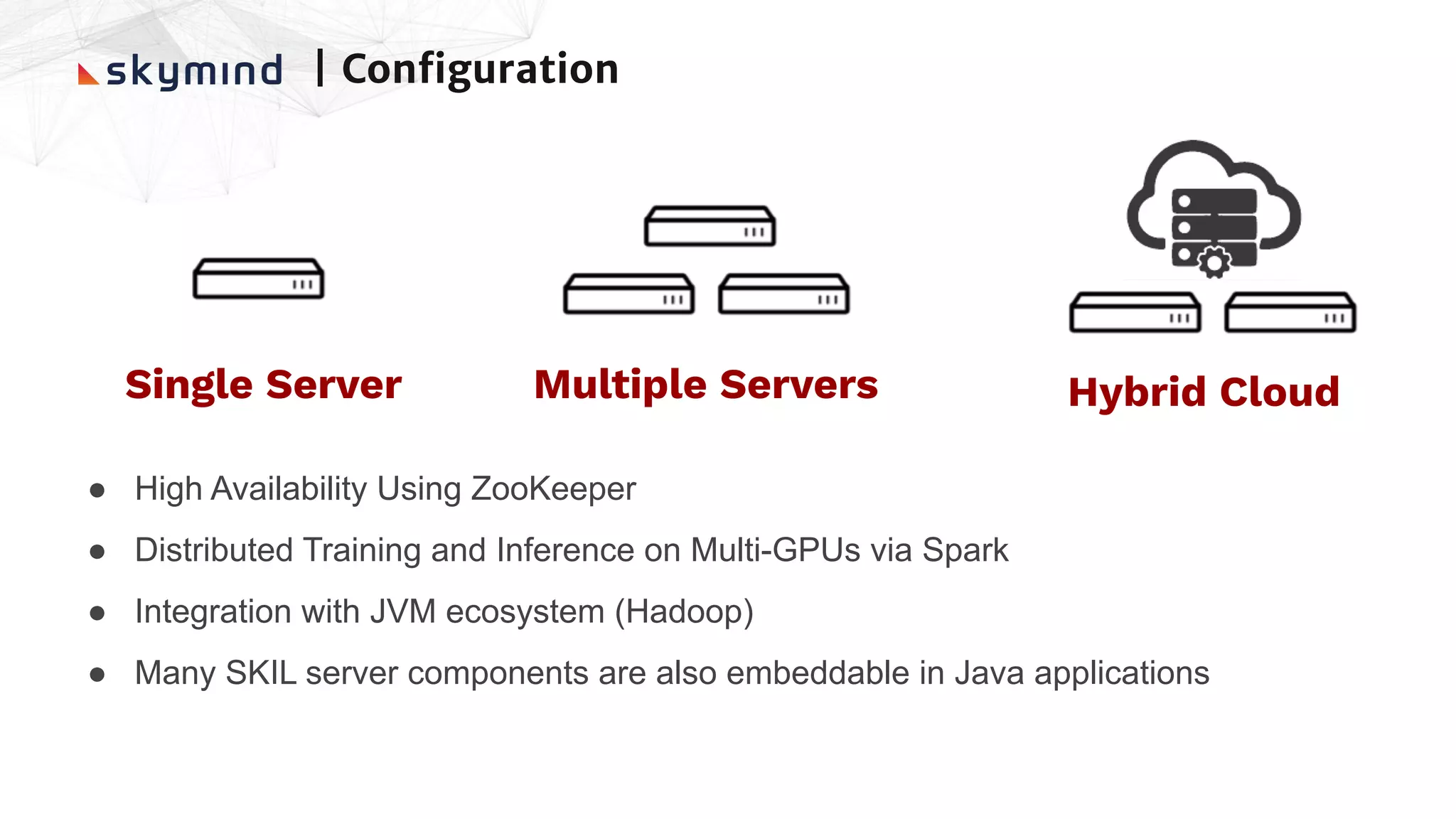
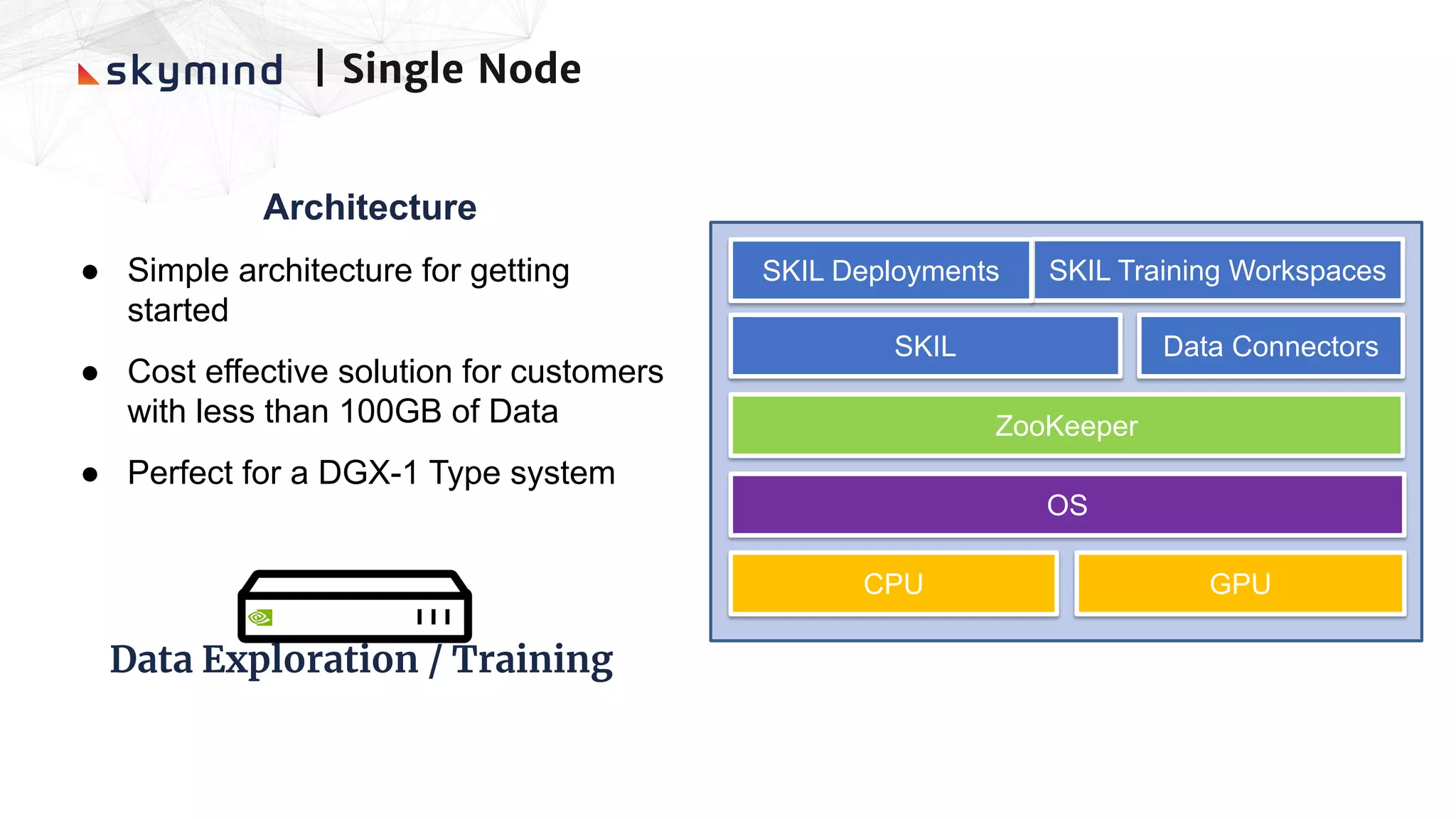
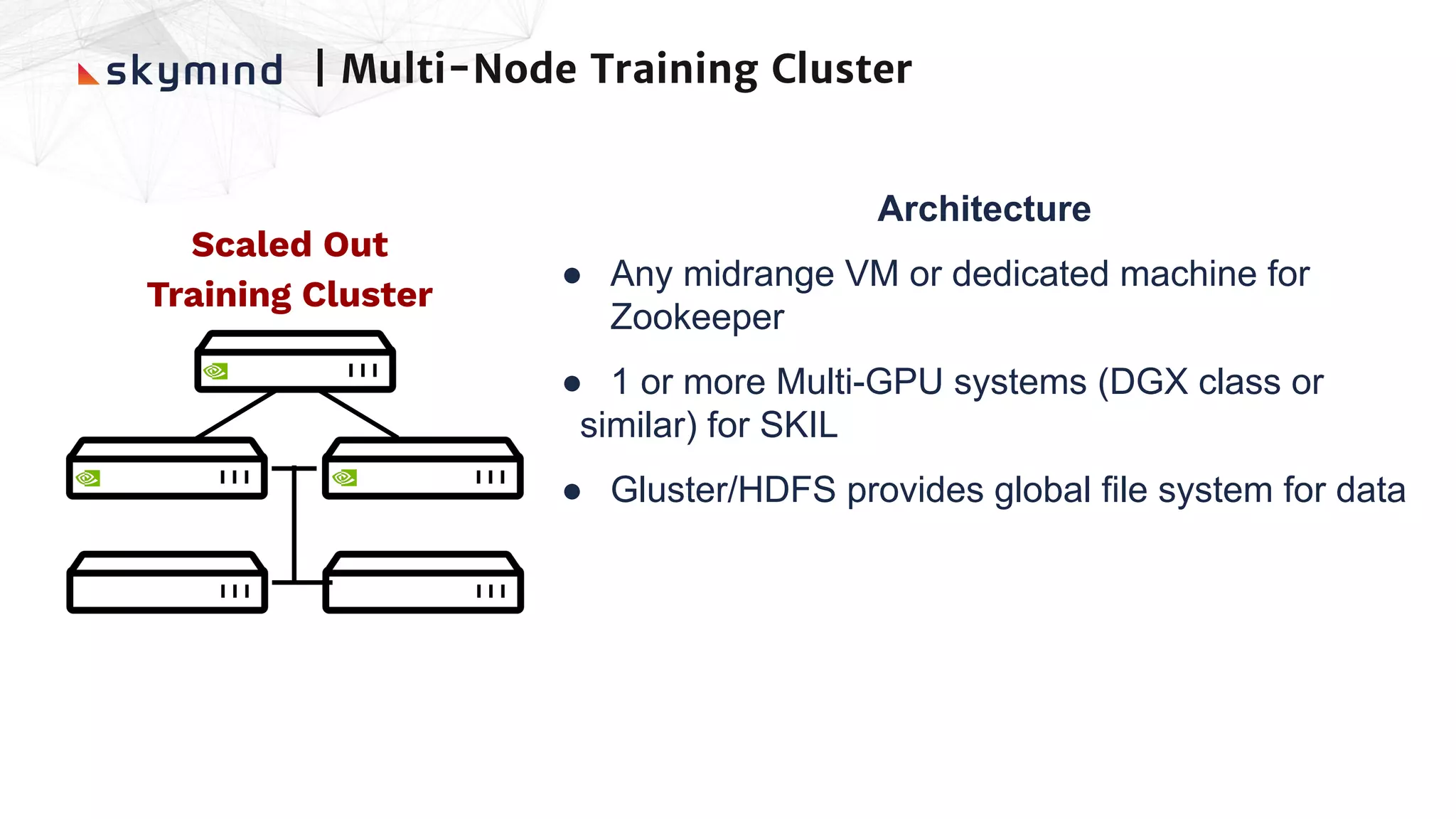
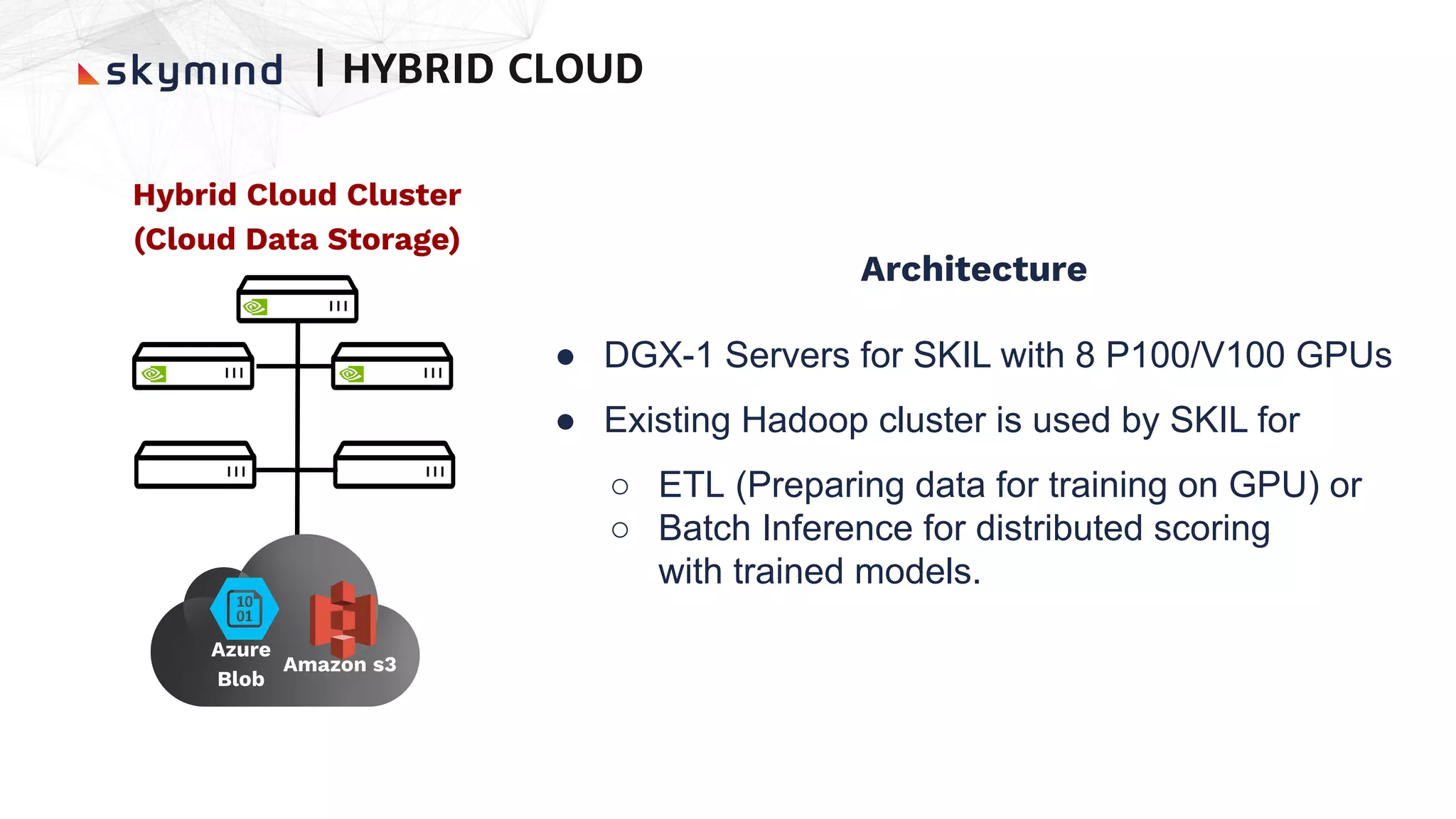
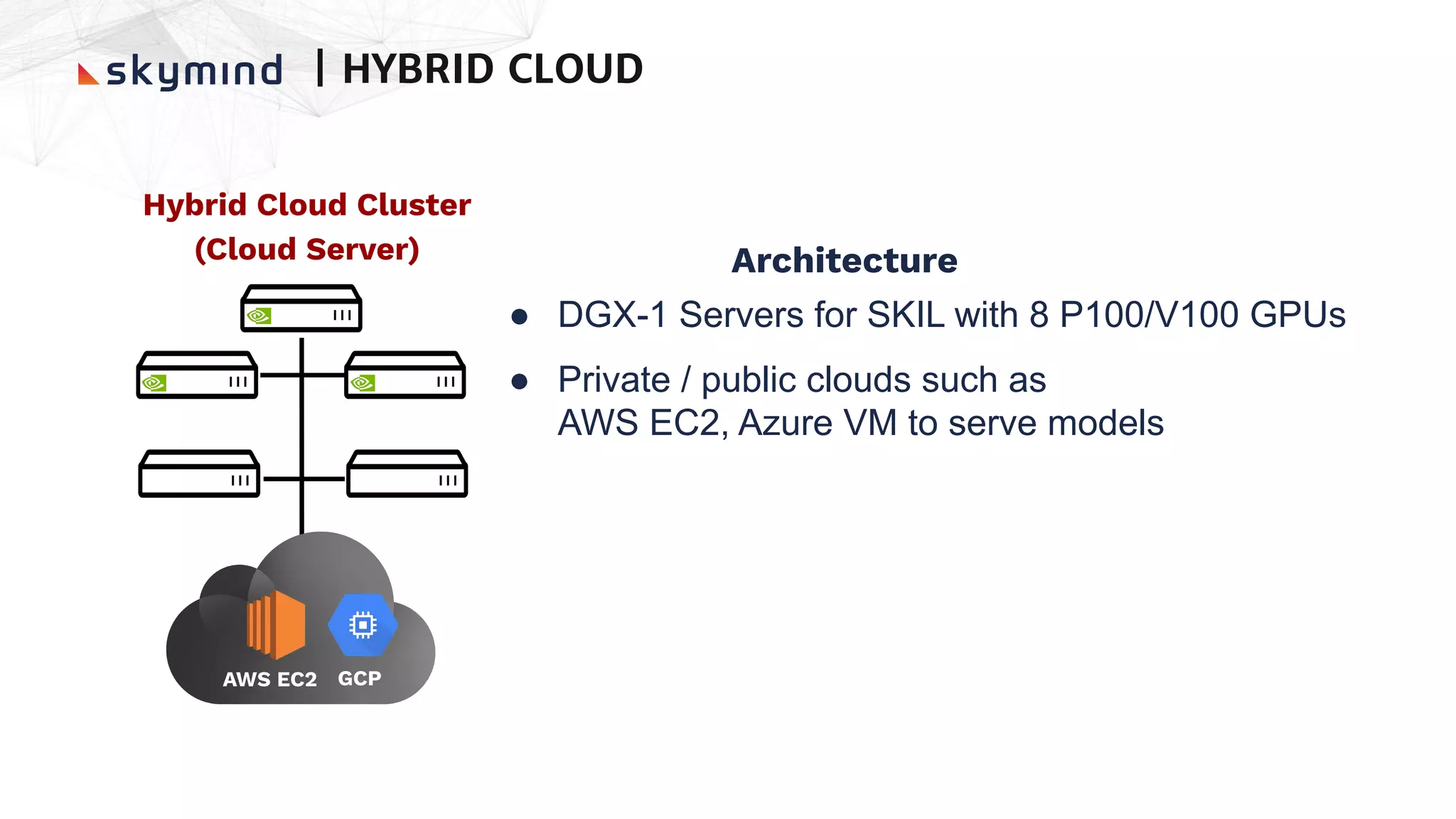
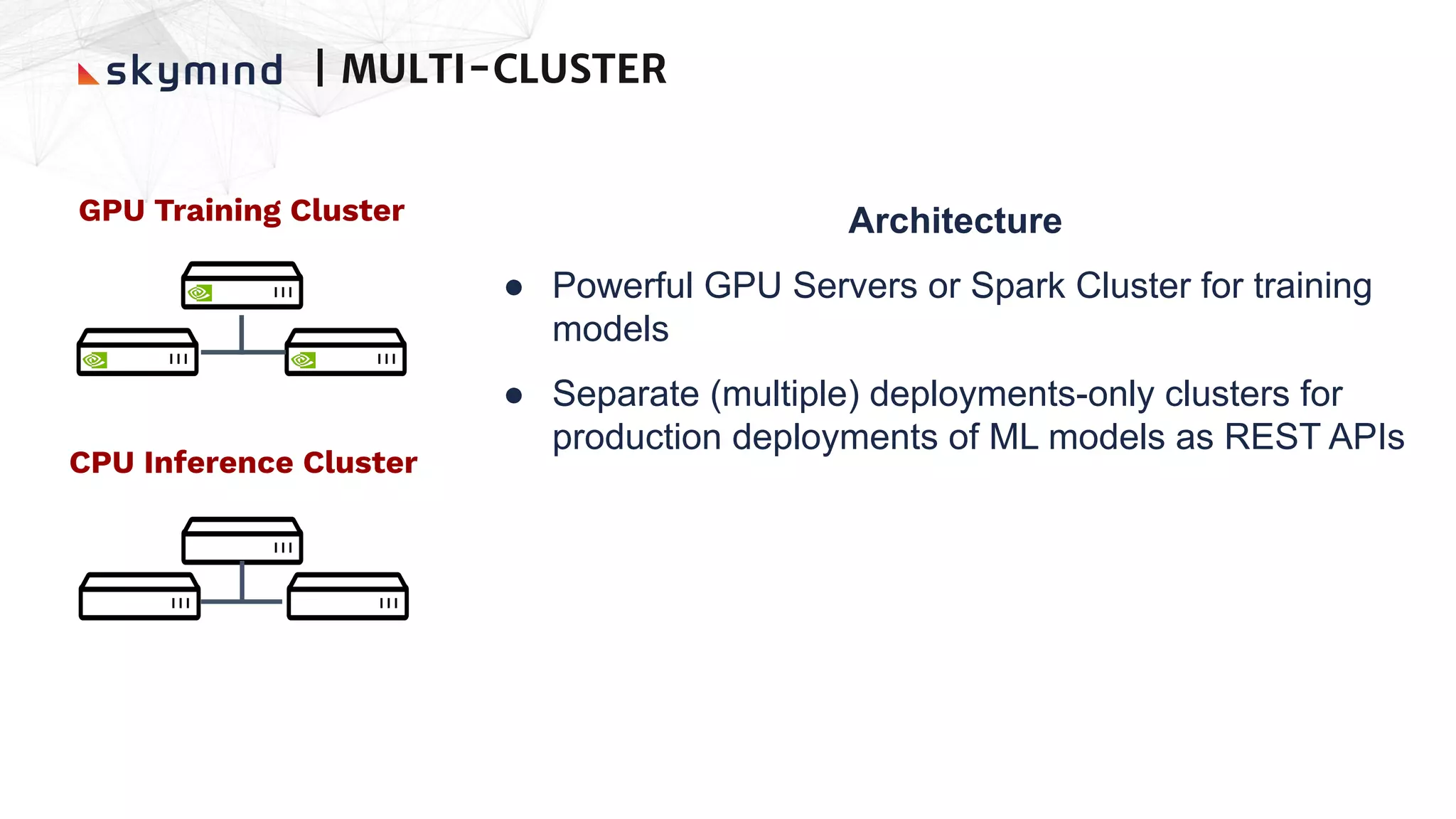
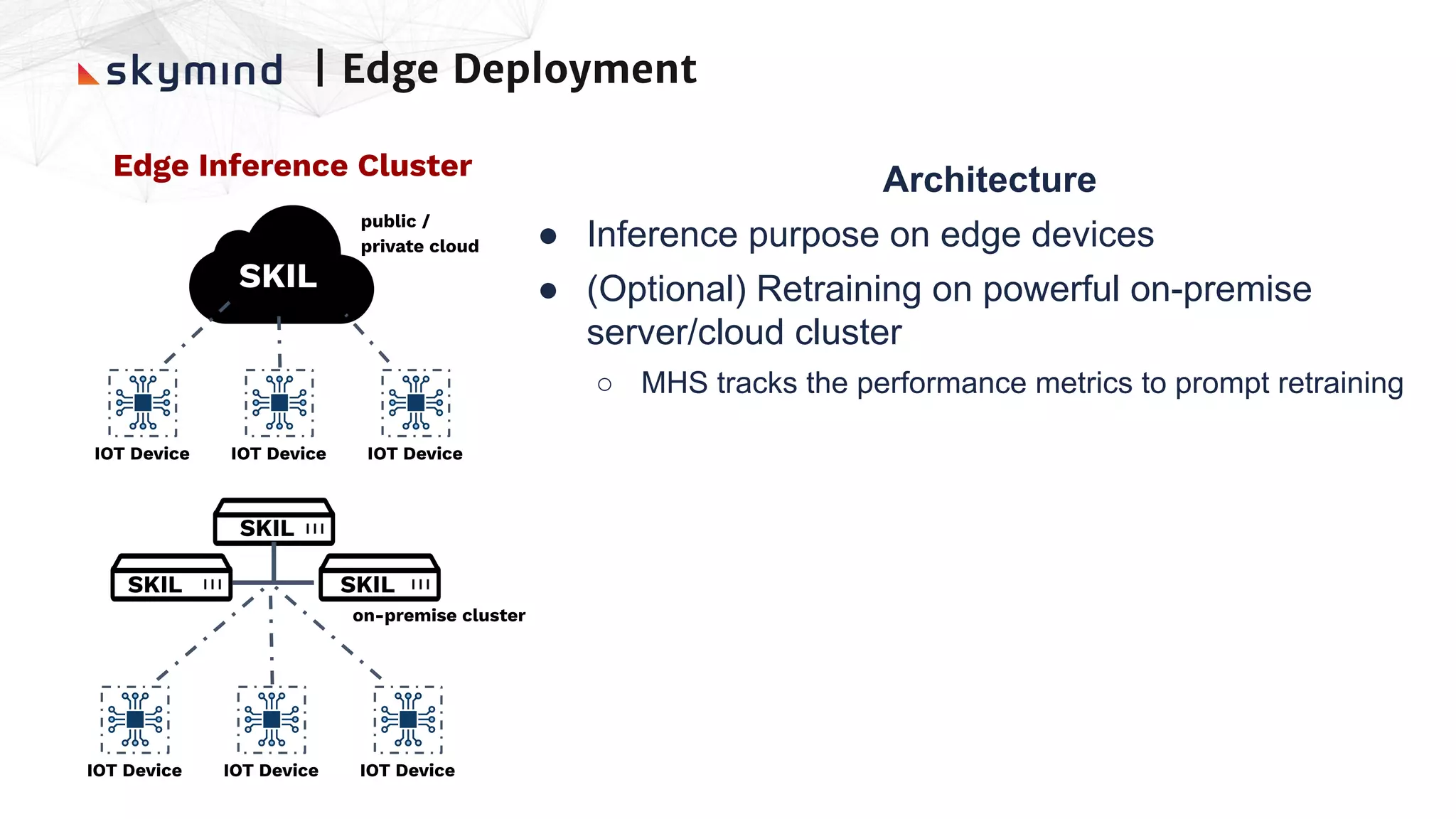
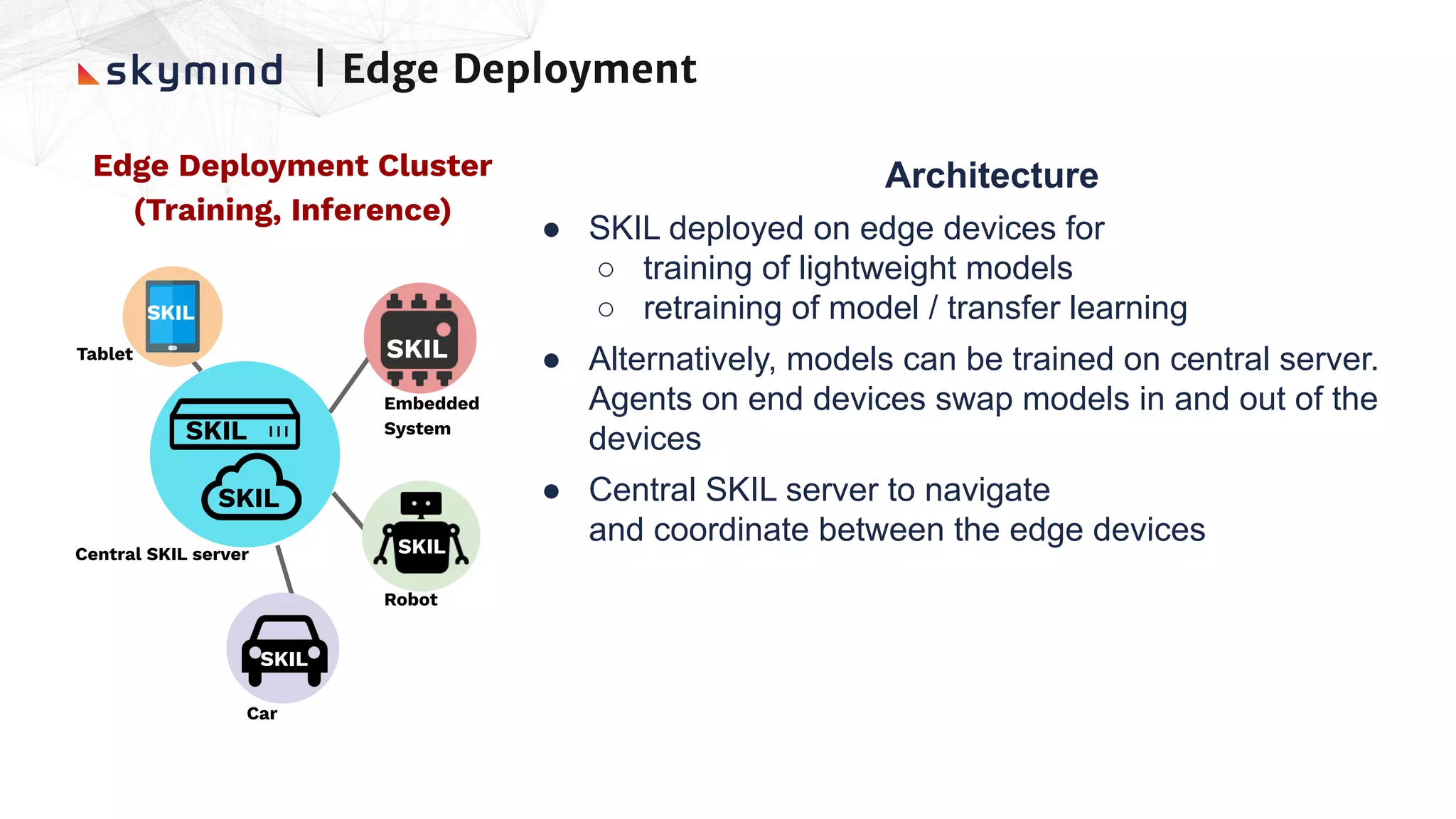
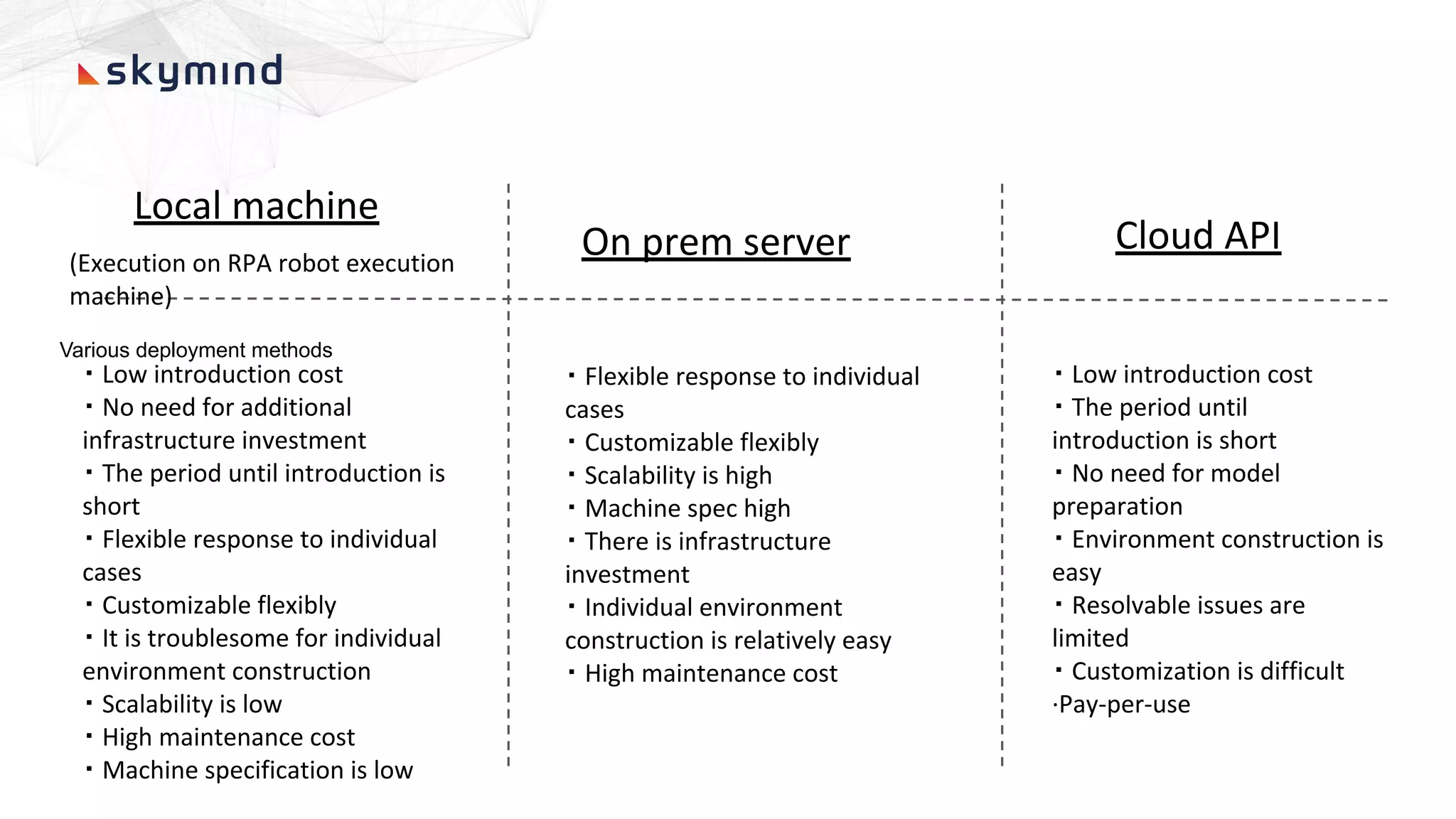
The document provides an overview of end-to-end AI workflows using Skymind. It includes an agenda for a workshop covering topics like workflow scoping, data collection/preprocessing, model building, deployment considerations, and monitoring models in production. Challenges of applying machine learning in enterprises are discussed, such as different tool preferences between teams. The document also outlines model deployment scenarios including single node, multi-node clusters, hybrid/multi-cloud, and edge deployments.