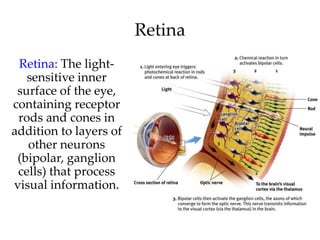
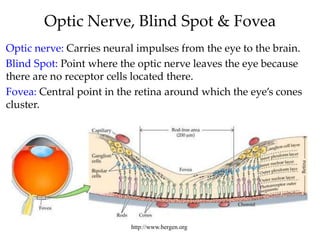
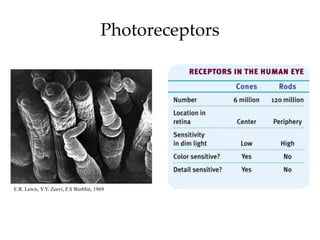
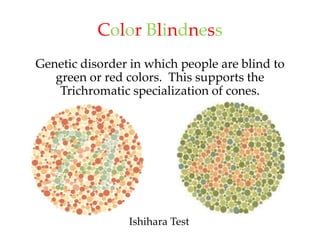
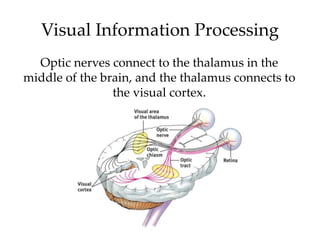
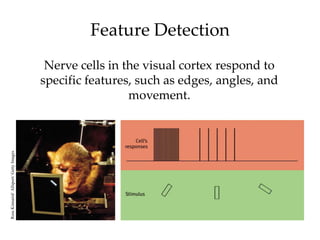
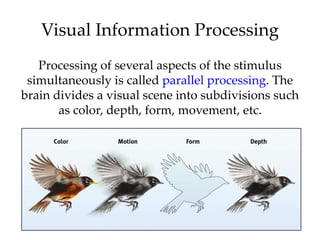
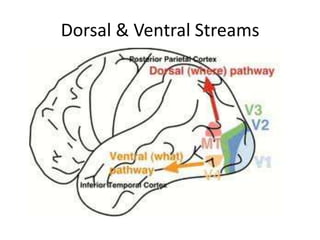
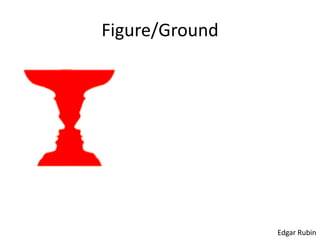
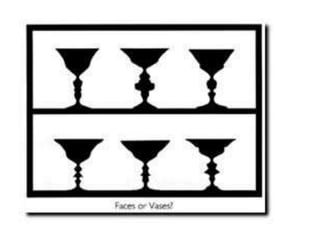
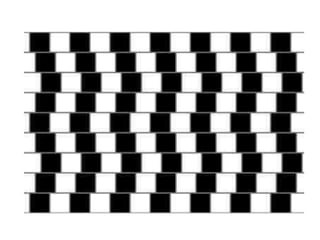
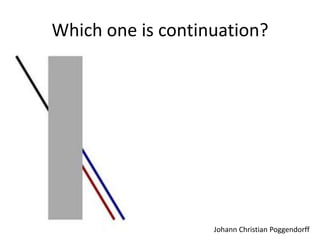
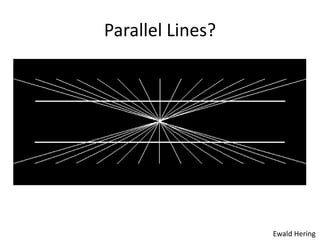
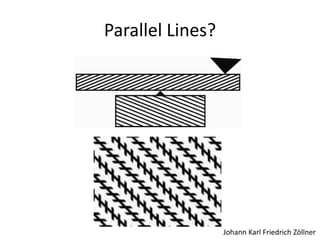
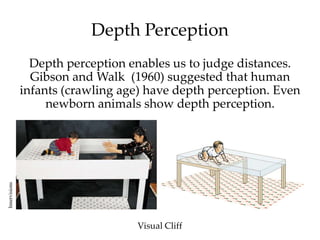
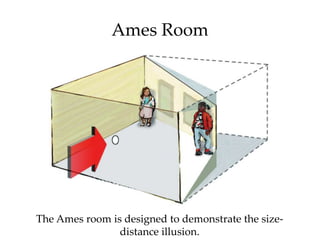
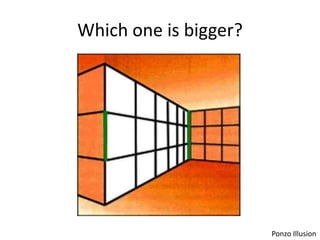
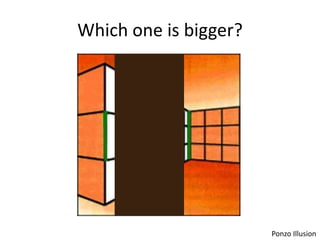
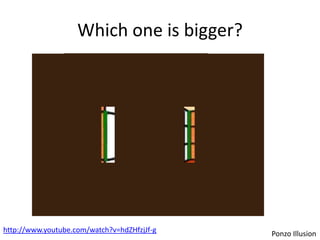
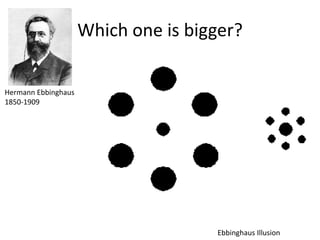
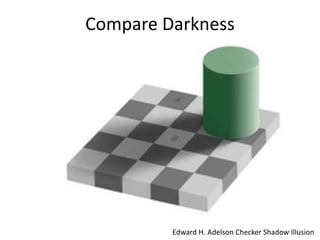
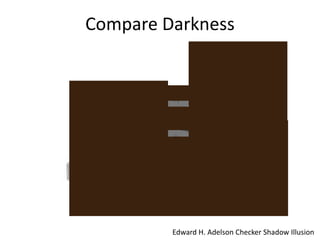
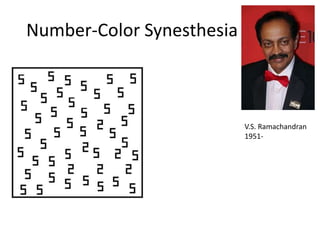
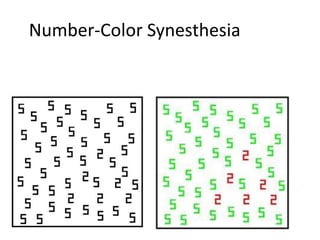
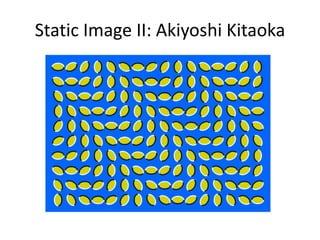
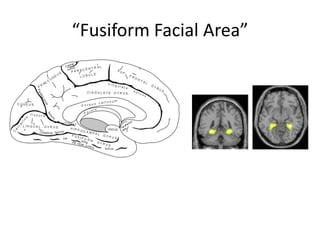
The document discusses the concepts of sensation and perception, detailing the processes involved and their distinctions. It explores psychophysics, various theories of vision, and highlights the anatomy of the eye, including the retina and optic nerve. Additionally, it touches upon perceptual phenomena such as illusions and depth perception, emphasizing the complexities of how we interpret visual information.