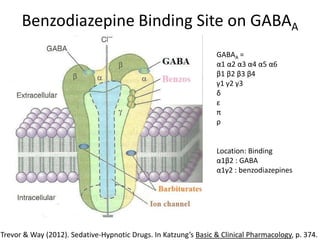
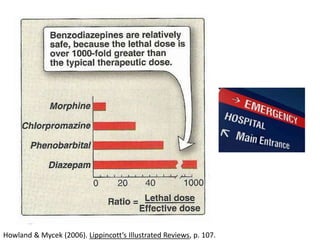
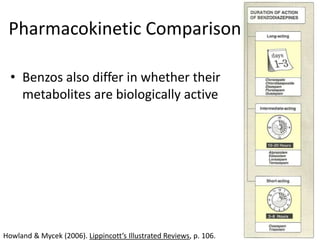
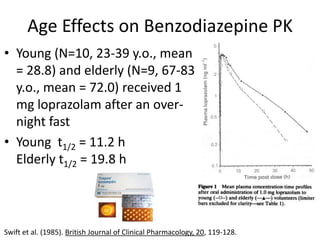
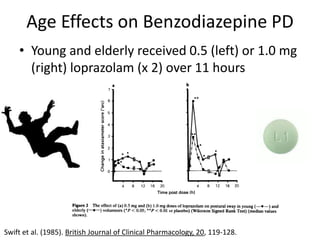
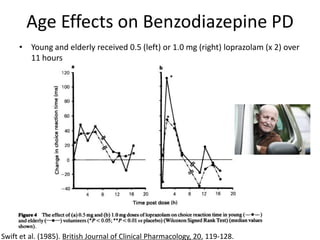
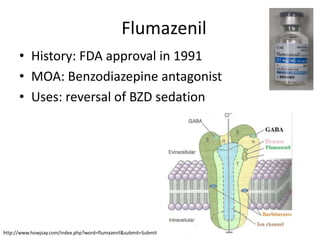
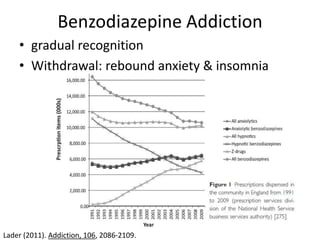
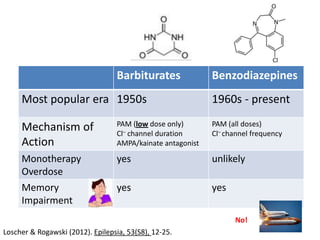
This document discusses sedative and hypnotic drugs, focusing on barbiturates and benzodiazepines, their pharmacodynamics, and implications for overdose and addiction. It highlights key differences in the mechanisms of action, metabolism, and effects of these drug classes, as well as their use in various medical contexts. Additionally, the document provides insight into age effects on drug pharmacokinetics and dynamics, along with considerations for use during pregnancy.