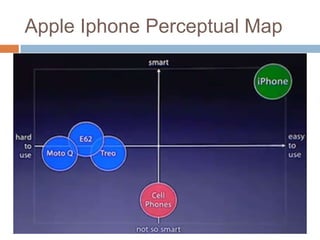
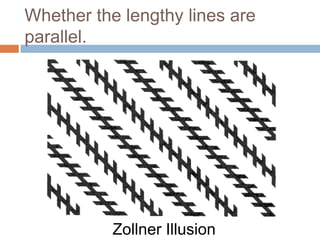
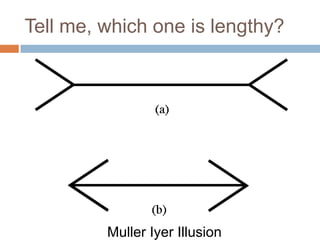
The document explores the concept of perception in marketing, emphasizing how consumers interpret stimuli through selection, organization, and interpretation. It outlines various types of perceptual phenomena such as subliminal perception, selective perception, and the halo effect, as well as the factors that influence consumer imagery and product positioning. Additionally, it discusses the implications of perceived risk and how consumers evaluate product quality and price in their purchasing decisions.


![Dynamics of Perception
Sensation – immediate and direct response of
the sensory organs to stimuli.
Stimulus – any unit of input to any of the
senses.
Sensory receptors – Eyes, Ears, Nose, Mouth
and Skin
THE ABSOLUTE THRESHOLD:-
Thelowest level at which an individual can
experience a sensation. [ Detecting difference
between “something and nothing”]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perception-120918024010-phpapp01/85/Consumer-Perception-8-320.jpg)






![SELECTIVE PERCEPTION
Example: Airtel Super Singer.
Selective exposure:-
Peoplelook for pleasant and sympathetic
messages and avoid painful or threatening ones.
Selective attention:-
People look into ads which will satisfy their need.
Perceptual Defense:-
People avoid psychologically threatening ones.
Hence constantly change the ad nature. [
Smoking – warning with words, and now with
images ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perception-120918024010-phpapp01/85/Consumer-Perception-17-320.jpg)