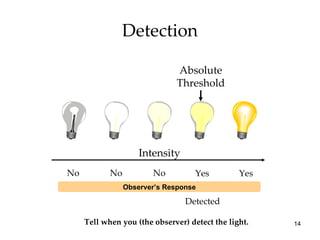
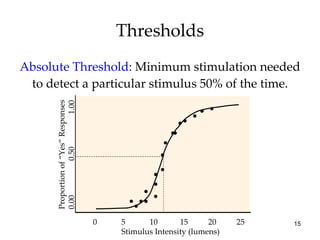
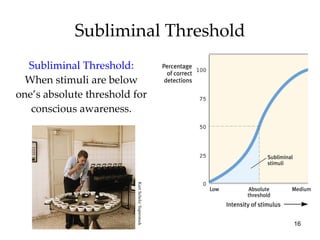
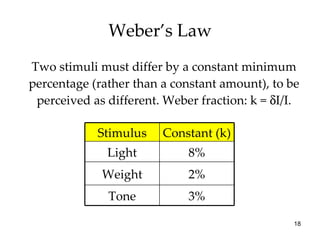
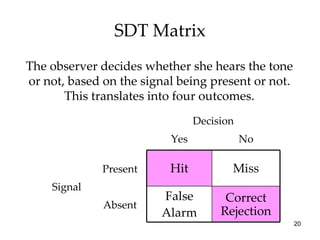
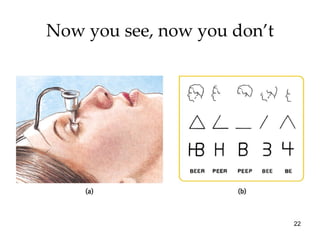
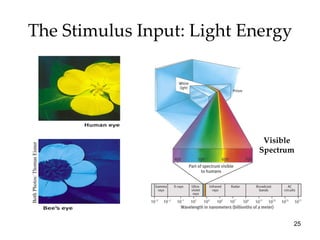
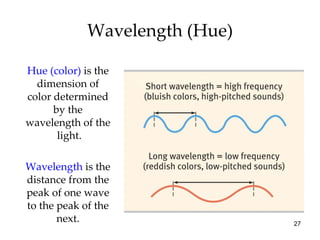
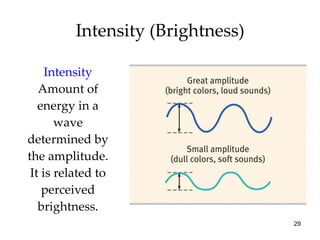
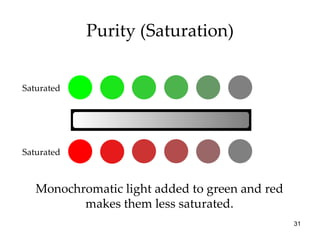
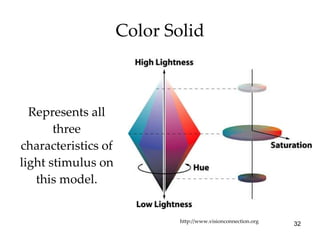
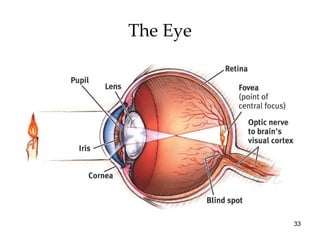
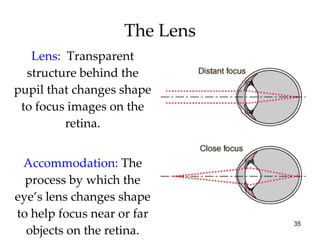
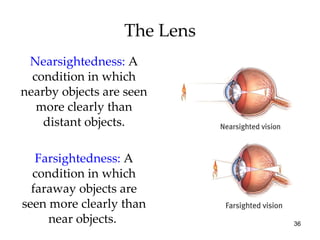
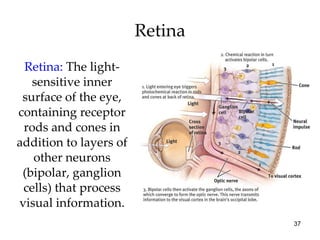
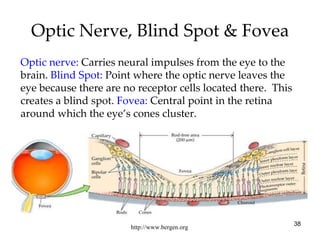
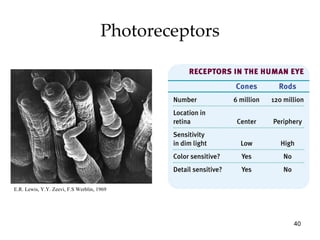
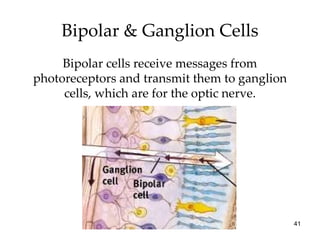
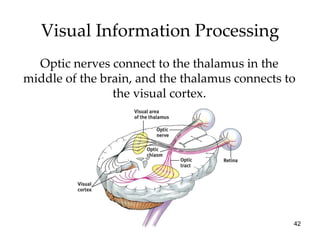
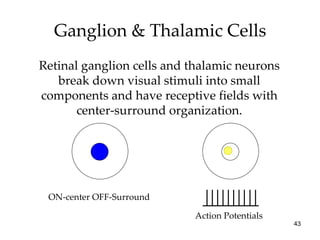
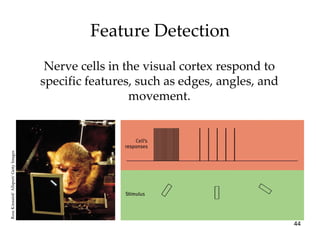
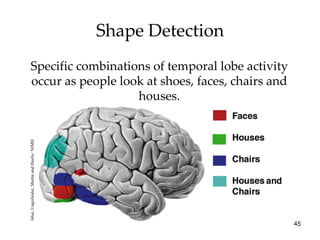
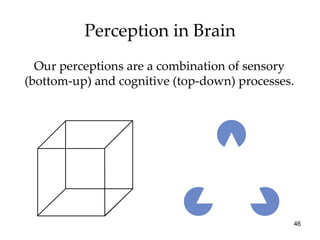
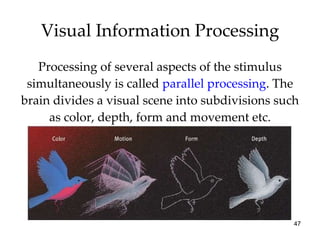
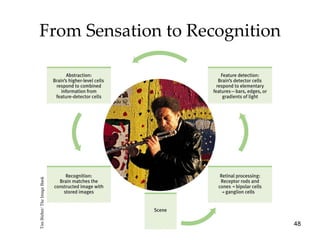
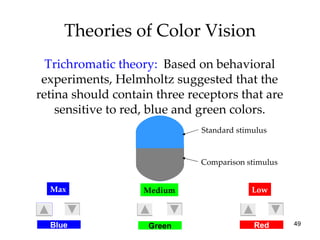
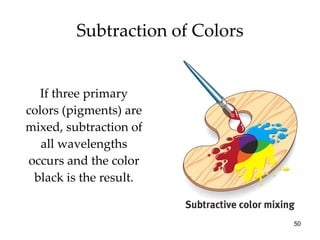
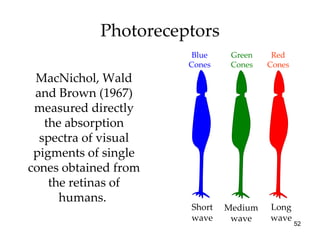
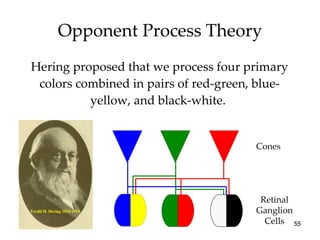
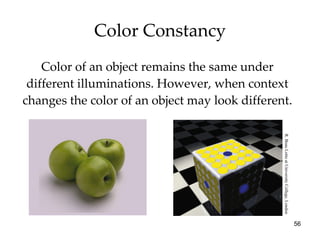
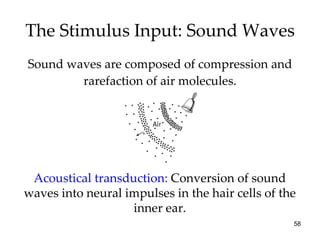
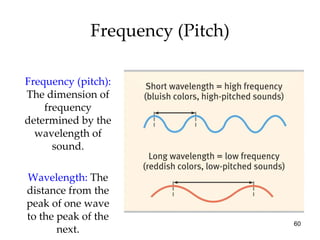
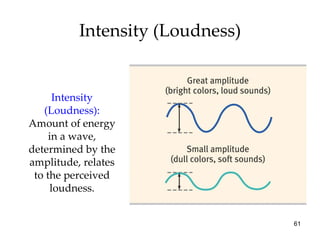
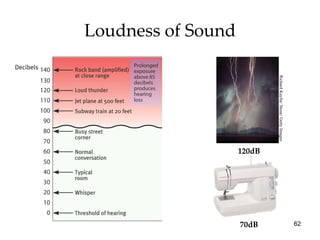
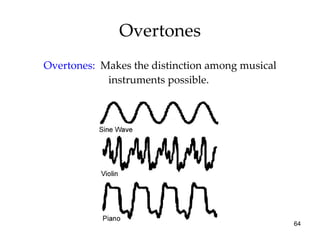
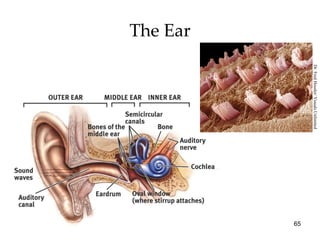
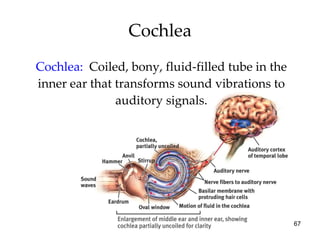
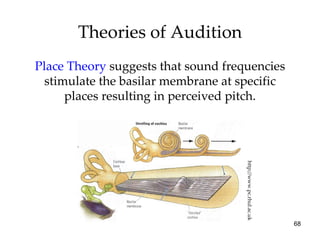
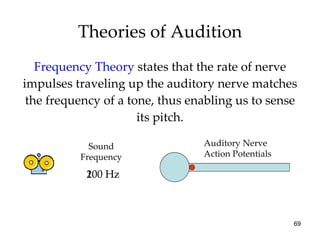
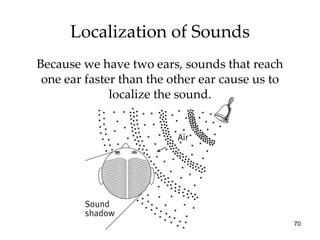
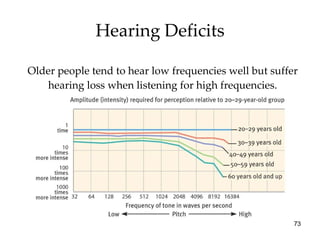
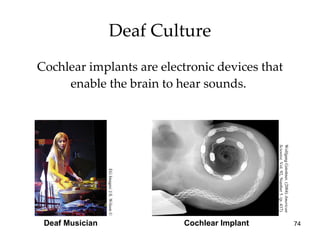
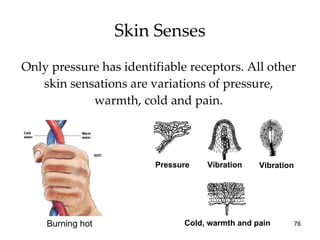
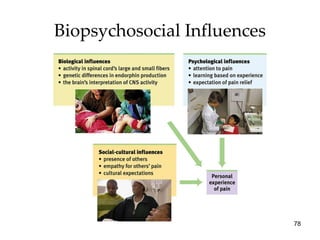
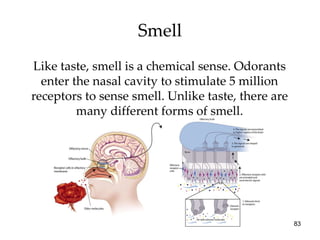
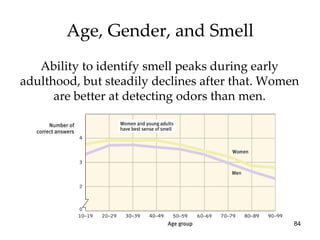
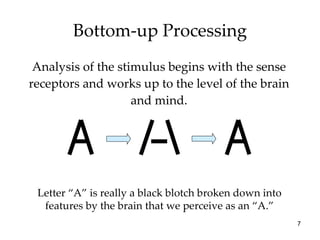
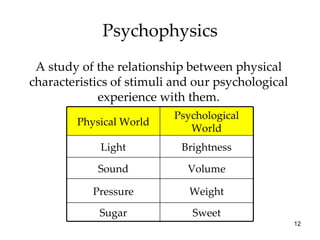
The document provides an overview of key concepts in sensation and perception. It discusses the basic principles of sensation including thresholds, adaptation and psychophysics. It then examines the senses of vision, hearing, touch, taste, smell and movement. For vision it explores light characteristics, the eye anatomy, visual processing and color vision. For hearing it covers sound characteristics, ear anatomy, theories of audition and localization of sounds. It emphasizes that sensation and perception involve both bottom-up and top-down processing to construct representations of the external world.










![22 nd October 1850 A relative increase in mental intensity, [Fechner] realized, might be measured in terms of the relative increase in physical energy required to bring it about (Wozniak, 1999). Gustav Fechner (1801-1887)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-091108041449-phpapp01/85/Chapter-5-13-320.jpg)