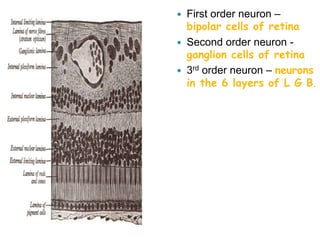
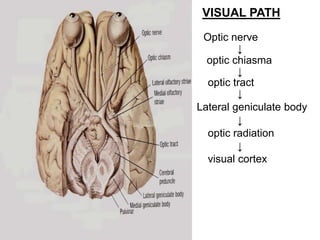
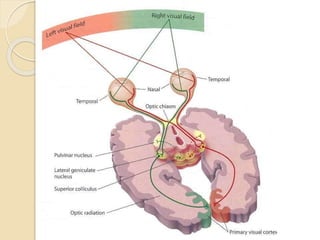
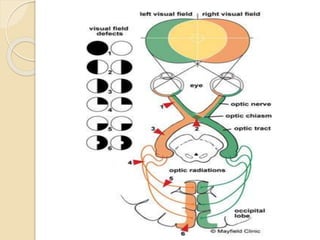
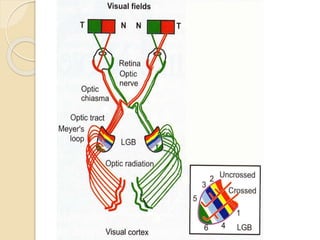
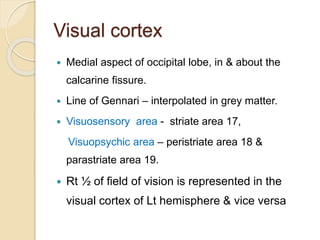
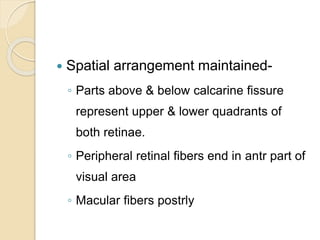
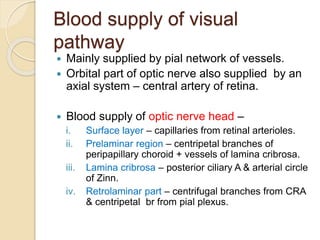
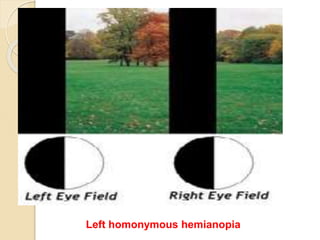
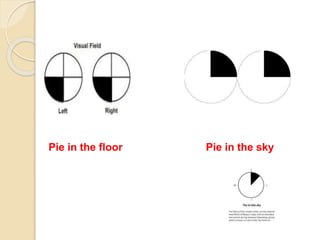
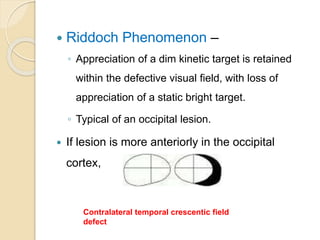
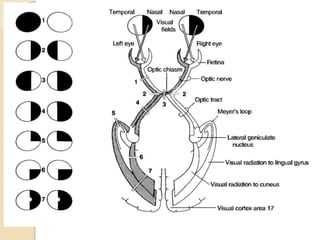
The visual pathway conveys visual signals from the retina to the visual cortex. Light is detected by photoreceptors (rods and cones) and converted to electrical signals. These signals pass through bipolar and ganglion cells in the retina and then through the optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic tracts and lateral geniculate body to the visual cortex via the optic radiations. Lesions along this pathway can cause different visual field defects including hemianopia and quadrantic defects depending on the location of the lesion. Common causes of lesions include tumors, vascular abnormalities and infections.