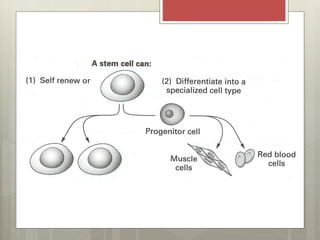
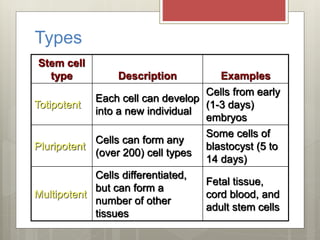
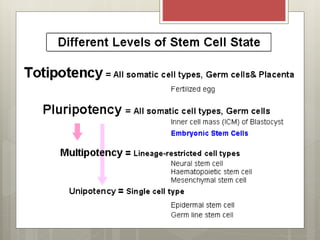
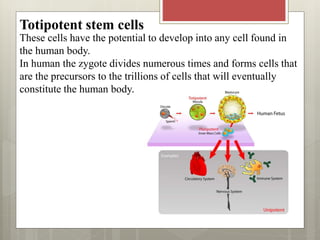
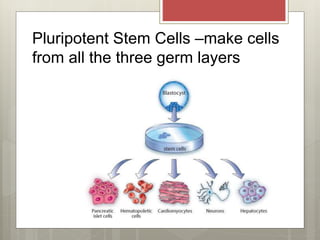
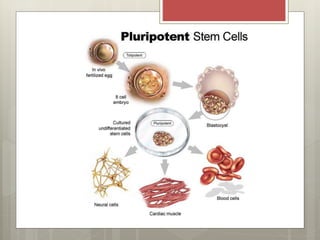
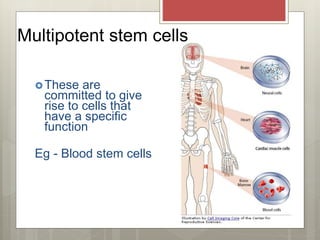
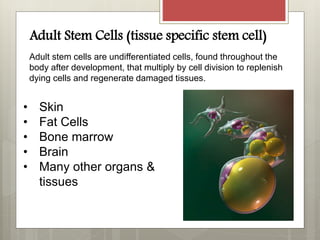
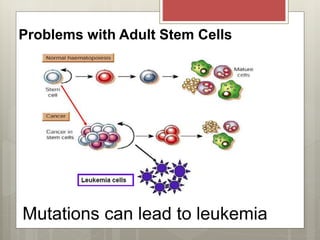
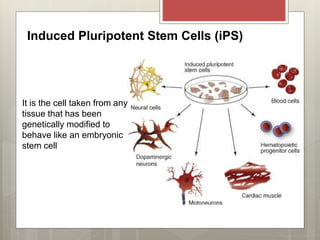
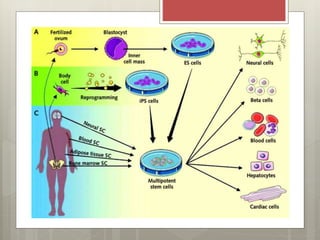
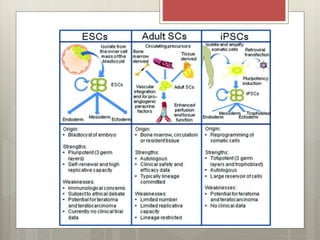
Stem cells are cells that can differentiate into other cell types and can self-renew to produce more stem cells. There are several types of stem cells including totipotent stem cells found in early embryos, pluripotent stem cells found in blastocysts that can form any cell type, and multipotent adult stem cells that can form a limited number of cell types. Induced pluripotent stem cells are adult cells that have been genetically modified to behave like embryonic stem cells. While stem cells show promise for research and medical applications, growing entire organs from stem cells remains a challenge.